|
Protopyknosia
Protopyknosia is an extinct clade of archosauriform reptiles from the Late Triassic of India and the United States. First identified by Sterling Nesbitt ''et al.'' in 2021, the clade contains two genera: ''Kranosaura'' and ''Triopticus''. Members of Protopyknosia characteristically have an unusually domed head reminiscent of the later pachycephalosaurian dinosaurs in an example of convergent evolution Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last com .... References Prehistoric archosauriforms Late Triassic extinctions Taxa named by Sankar Chatterjee Taxa named by Jack Horner Taxa named by Sterling Nesbitt Taxa named by Michelle R. Stocker {{Triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kranosaura
''Kranosaura'' is an extinct genus of archosauriformes, archosauriform reptile from the Late Triassic Upper Maleri Formation of India. It contains a single species, ''K. kuttyi'', described in 2021 by Sterling Nesbitt ''et al''. It had an unusually domed head reminiscent of the later pachycephalosaurian dinosaurs in an example of convergent evolution, similar to that of ''Triopticus''. ''Kranosaura'' was the sister taxon to ''Triopticus'', with which it forms the clade Protopyknosia. The genus is based on two domes of long, discovered by T. S. Kutty in the 1990s. References Prehistoric archosauriforms Prehistoric reptile genera Norian genera Late Triassic reptiles of Asia Triassic India Fossils of India Fossil taxa described in 2021 Taxa named by Sankar Chatterjee Taxa named by Jack Horner Taxa named by Sterling Nesbitt Taxa named by Michelle R. Stocker {{Triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 In Reptile Paleontology
This list of fossil reptiles described in 2021 is a list of new taxa of fossil reptiles that were described during the year 2021, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to reptile paleontology that occurred in 2021. Squamates New taxa Research * A study on the evolution of tooth complexity in squamates, based on data from extant and fossil taxa, is published by Lafuma ''et al.'' (2021). * A study on the diversity of jaw sizes, lower jaw shape and morphology of teeth in Cretaceous squamates is published by Herrera-Flores, Stubbs & Benton (2021), who interpret their findings as indicating that a substantial expansion of ecomorphological diversity of squamates occurred in the mid-Cretaceous, 110–90 Ma, before the first rise in taxonomic diversity of this group in the Campanian. * A study on the dietary preferences of lizards from the Upper Cretaceous Iharkút vertebrate locality (Hungary) is published by Gere ''et al.'' (2021). * A study on the locomotion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
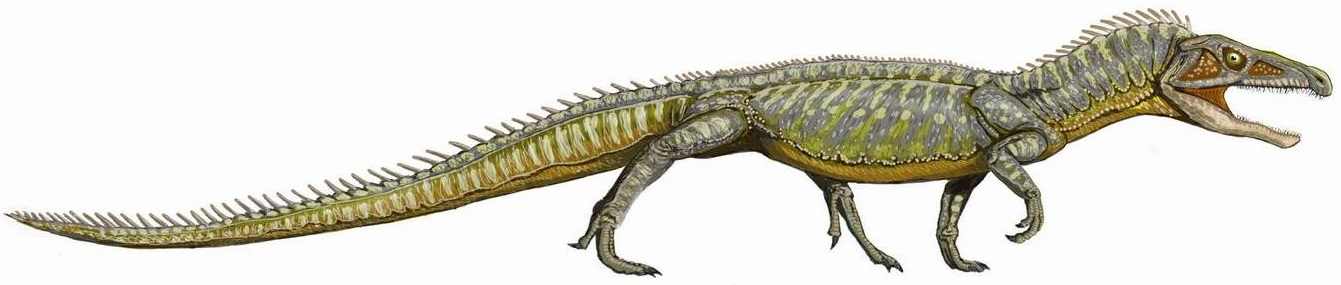
Archosauriform
Archosauriformes (Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles that developed from archosauromorph ancestors some time in the Latest Permian (roughly 252 million years ago). It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria (the group that contains crocodiles, pterosaurs and dinosaurs bird.html"_;"title="ncluding_bird">ncluding_birds;_Phil_Senter.html" ;"title="bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter">bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing ''Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. These reptiles, which include members of the family Proterosuchidae and more advanced forms, were originally superficiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Anatomy
The ''Journal of Anatomy'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Wiley on behalf of the Anatomical Society. It covers all aspects of anatomy and morphology. The journal was first published in 1867 and was originally known as the ''Journal of Anatomy and Physiology'', obtaining its current title in October 1916. The editors-in-chief are Phil Cox (Hull York Medical School), Thomas H. Gillingwater (University of Edinburgh), Stefan Milz (Ludwig-Maximilians University), and Neil Vargesson (University of Aberdeen). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 2.921. In conjunction with their centennial in 2009, the international Special Libraries Association included the ''Journal of Anatomy'' as one of the 100 most influential journals in biology and medicine over the past 100 years. History The journal was established in 1867 as the ''Journal of Anatomy and Physiology''. The journal was conceived at the 1866 meeting of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Jack Horner
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Sankar Chatterjee
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic Extinctions
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Archosauriforms
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last common ancestor of those groups. The cladistic term for the same phenomenon is homoplasy. The recurrent evolution of flight is a classic example, as flying insects, birds, pterosaurs, and bats have independently evolved the useful capacity of flight. Functionally similar features that have arisen through convergent evolution are ''analogous'', whereas '' homologous'' structures or traits have a common origin but can have dissimilar functions. Bird, bat, and pterosaur wings are analogous structures, but their forelimbs are homologous, sharing an ancestral state despite serving different functions. The opposite of convergence is divergent evolution, where related species evolve different traits. Convergent evolution is similar to parallel evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, are among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachycephalosauria
Pachycephalosauria (; from Greek παχυκεφαλόσαυρος for 'thick headed lizards') is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs. Along with Ceratopsia, it makes up the clade Marginocephalia. With the exception of two species, most pachycephalosaurs lived during the Late Cretaceous Period, dating between about 85.8 and 65.5 million years ago. They are exclusive to the Northern Hemisphere, all of them being found in North America and Asia. They were all bipedal, herbivorous/omnivorous animals with thick skulls. Skulls can be domed, flat, or wedge-shaped depending on the species, and are all heavily ossified. The domes were often surrounded by nodes and/or spikes. Partial skeletons have been found of several pachycephalosaur species, but to date no complete skeletons have been discovered. Often isolated skull fragments are the only bones that are found. Candidates for the earliest known pachycephalosaur include ''Ferganocephale adenticulatum'' from Middle Jurassic Period strata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |