|
Prosomapod
Prosomapoda is a clade of euchelicerates including the groups Xiphosura (horseshoe crabs) and Planaterga (a group comprising bunodids, pseudoniscids, chasmataspidids, eurypterids and arachnids), as well as several basal synziphosurid genera. The clade is defined by the lack of exopods (outer branches) of prosomal appendage II-V in the adult instar, where in contrast the exopods of appendage II-V are well-developed in the non-prosomapod euchelicerates ''Offacolus ''Offacolus'' is an extinct genus of euchelicerate, a group of chelicerate arthropods. Its only species, ''O. kingi'', has been found in deposits from the Silurian period (Homerian epoch) in the Wenlock Series Lagerstätte of Herefordshire, Eng ...'' and '' Dibasterium''. References Middle Ordovician first appearances {{Chelicerata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borchgrevinkium
''Borchgrevinkium'' is an extinct genus of chelicerate arthropod. A fossil of the single and type species, ''B. taimyrensis'', has been discovered in deposits of the Early Devonian period ( Lochkovian epoch) in the Krasnoyarsk Krai, Siberia, Russia. The name of the genus honors Carsten Borchgrevink, an Anglo-Norwegian explorer who participated in many expeditions to Antarctica. ''Borchgrevinkium'' represents a poorly known genus whose affinities are uncertain. It had several unique characteristics that differentiated it from many other arthropods, such as its long parabolic (nearly U-shaped) prosoma (head), its elongated first and second segments and the presence of paired "ridges" in the surface of its third to tenth tergites (dorsal halves of the segments). Furthermore, the opisthosoma (the "trunk") of ''Borchgrevinkium'' was triangular, and its telson (the posteriormost division of its body), short and wedge-shaped. It was a small animal, approximately long. The only known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosomapoda
Prosomapoda is a clade of euchelicerates including the groups Xiphosura (horseshoe crabs) and Planaterga (a group comprising bunodids, pseudoniscids, chasmataspidids, eurypterids and arachnids), as well as several basal synziphosurid genera. The clade is defined by the lack of exopods (outer branches) of prosomal appendage II-V in the adult instar, where in contrast the exopods of appendage II-V are well-developed in the non-prosomapod euchelicerates '' Offacolus'' and ''Dibasterium ''Dibasterium'' is an extinct genus of euchelicerate, a group of chelicerate arthropods. Fossils of the single and type species, ''D. durgae'', have been discovered in the Coalbrookdale Formation of the Middle Silurian period (Homerian age) in ...''. References Middle Ordovician first appearances {{Chelicerata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offacolus
''Offacolus'' is an extinct genus of euchelicerate, a group of chelicerate arthropods. Its only species, ''O. kingi'', has been found in deposits from the Silurian period (Homerian epoch) in the Wenlock Series Lagerstätte of Herefordshire, England. It is the only member of the monotypic family Offacolidae, and classified as a basal ("primitive") genus in the clade Euchelicerata, along with ''Dibasterium'' and Prosomapoda. The genus is named after Offa, a king from the ancient kingdom of Mercia, and ''colus'', a person who dwelled among (this time referring to) the Offa's Dyke. The species name honors Robert Joseph King, a British mineralogist who found the fossils of ''Offacolus''. Similar to ''Dibasterium'', ''Offacolus'' possess limb-like exopods (outer limb branches) on appendage II to V, a character suggest to be plesiomorphic (observable in the putative stem-chelicerate taxon Habeliida) and lost within the prosomapod clade. Classification ''Offacolus'' was originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
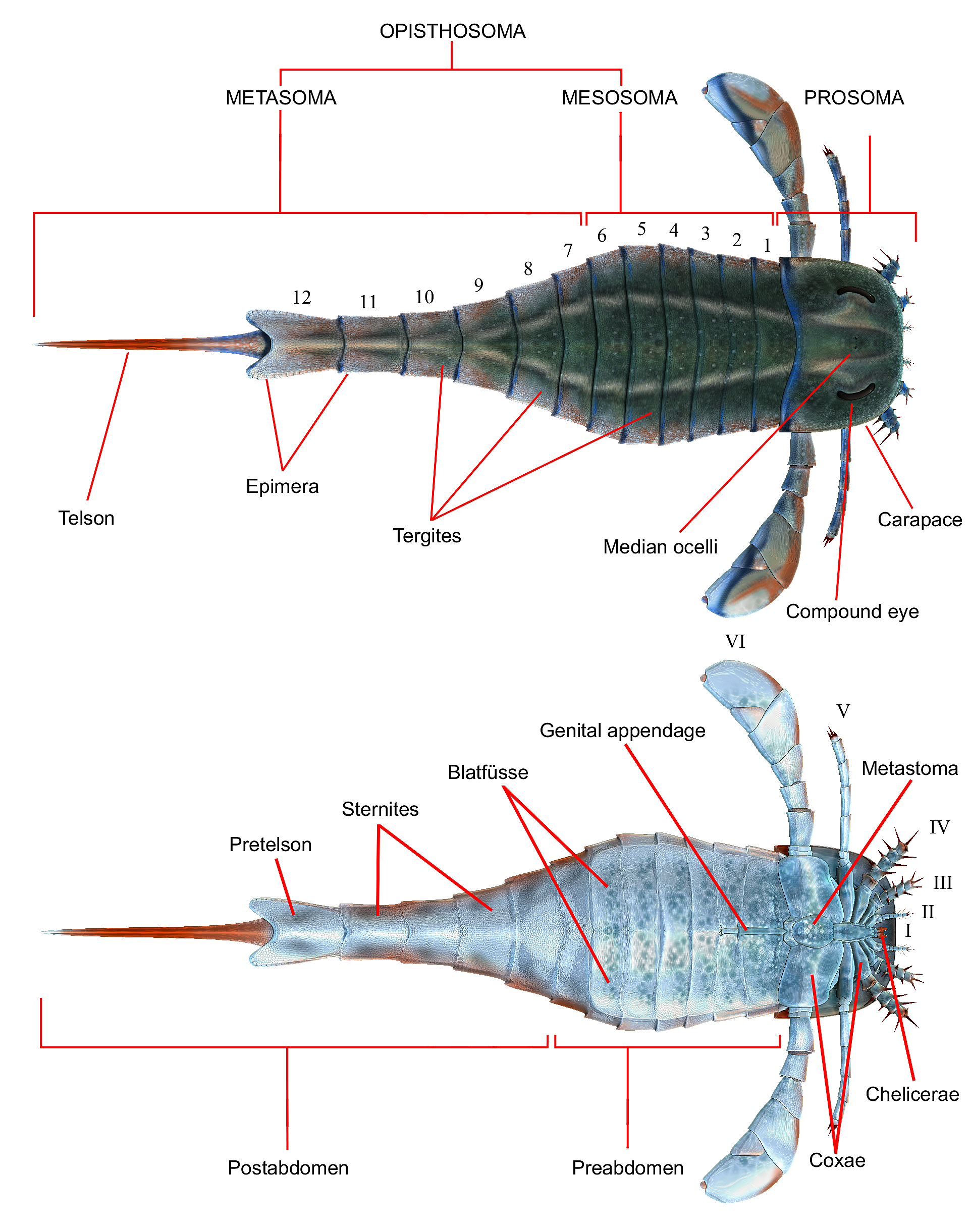
Chelicerata
The subphylum Chelicerata (from New Latin, , ) constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum Arthropoda. It contains the sea spiders, horseshoe crabs, and arachnids (including Opiliones, harvestmen, scorpions, spiders, Solifugae, solifuges, Parasitiformes, ticks, and Acariformes, mites, among many others), as well as a number of extinct lineages, such as the eurypterids (sea scorpions) and chasmataspidids. The Chelicerata originated as marine animals in the Middle Cambrian period; the first confirmed chelicerate fossils, belonging to ''Sanctacaris'', date from Burgess Shale, 508 million years ago. The surviving marine species include the four species of xiphosurans (horseshoe crabs), and possibly the 1,300 species of Pycnogonida, pycnogonids (sea spiders), if the latter are indeed chelicerates. On the other hand, there are over 77,000 well-identified species of air-breathing chelicerates, and there may be about 500,000 unidentified species. Like all arth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camanchia
''Camanchia'' is a genus of synziphosurine, a paraphyletic group of fossil chelicerate arthropods. ''Camanchia'' was regarded as part of the clade Prosomapoda. Fossils of the single and type species, ''C. grovensis'', have been discovered in deposits of the Silurian period in Iowa, in the United States. Alongside '' Venustulus'', ''Camanchia'' is one of the only Silurian synziphosurine with fossil showing evidence of appendages. The prosoma of ''Camanchia'' covered by a smoothly curved subtriangular carapace with broad doublure (ventral thickening run through the margin of carapace). Detail of the 6 prosomal appendage pairs (chelicerae+5 leg pairs) obscure, at least the first leg pair (appendage II) have spur-like terminations. Opisthosoma is externally 10-segmented with tergites possses blunt pleurae (lateral extension). The last 3 opisthosomal segments forming a narrow postabdomen with short pleurae. Telson The telson () is the posterior-most division of the body of an art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legrandella
''Legrandella'' is a genus of synziphosurine, a paraphyletic group of fossil chelicerate arthropods. ''Legrandella'' was regarded as part of the clade Prosomapoda. Fossils of the single and type species, ''L. lombardii'', have been discovered in deposits of the Devonian period in Cochabamba, Bolivia. The prosoma of ''Legrandella'' covered by a vaulted carapace with anterior projection, blunt genal cornua (posterolateral corners), humped cardiac lobe and pairs of radiated grooves. Alongside ''Pseudoniscus roosevelti'', ''Legrandella lombardii'' is one of the few synziphosurine species that confirmed to have lateral compound eyes. The eyes are slit-like, located just below the ophthalmic ridges on each side of the carapace. The opisthosoma is externally 11-segmented, subdivided into a 8-segmented preabdomen and 3-segmented postabdomen. Tergite of the 1st preabdomimal segment is a reduced microtergite while the remaining 7 tergite possess axial nodes and spine-like tergopleurae (lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venustulus
''Venustulus'' is a genus of synziphosurine, a paraphyletic group of fossil chelicerate arthropods. ''Venustulus'' was regarded as part of the clade Prosomapoda. Fossils of the single and type species, ''V. waukeshaensis'', have been discovered in deposits of the Silurian period in Wisconsin, in the United States. ''Venustulus'' is one of the few synziphosurine genera with fossil showing evidence of appendages, the other ones being '' Weinbergina, Anderella'' and ''Camanchia''. Despite often being aligned close to Horseshoe crabs, it has been found that ''Venustulus'' and its relatives form a group made up of various basal euchelicerate arthropods more distant to the xiphosurans. Description ''Venustulus'' is the third largest member of its grouping just behind ''Willwerathia'' and ''Weinbergina'' respectively. This arthropod appears to be blind due to the lack of eyes on its carapace, suggesting it lived either in deep water or buried in the sediments. Unlike modern horseshoe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurypterida
Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct arthropods that form the order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period 467.3 million years ago. The group is likely to have appeared first either during the Early Ordovician or Late Cambrian period. With approximately 250 species, the Eurypterida is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order. Following their appearance during the Ordovician, eurypterids became major components of marine faunas during the Silurian, from which the majority of eurypterid species have been described. The Silurian genus ''Eurypterus'' accounts for more than 90% of all known eurypterid specimens. Though the group continued to diversify during the subsequent Devonian period, the eurypterids were heavily affected by the Late Devonian extinction event. They declined in numbers and diversity until becoming extinct during the Permian–Triassic extinction event (or sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weinbergina
''Weinbergina'' is a genus of synziphosurine, a paraphyletic group of fossil chelicerate arthropods. Fossils of the single and type species, ''W. opitzi'', have been discovered in deposits of the Devonian period in the Hunsrück Slate, Germany. Morphology ''Weinbergina'' is a relatively large synziphosurine, ranging about 7 cm to 10 cm in full body length. The prosoma is covered by a semicircular carapace with blunt genal cornua (posterolateral corners). There is possible evidence of lateral eyes located just below the ophthalmic ridges. The opisthosoma is externally 10-segmented, expressed by tergites that possess blunt tergopleurae (lateral extension) and axial nodes. However, the opisthosoma is most likely 11-segmented in origin, with the first segment being highly reduced (a synapomorphy of euchelicerates) and possibly covered by the preceding carapace. The last 3 segments form a narrow postabdomen and lacking lateral nodes. Compared to other synziphosurines wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anderella
''Anderella'' is a genus of synziphosurine, a paraphyletic group of fossil chelicerate arthropods. ''Anderella'' was regarded as part of the clade Prosomapoda. Fossils of the single and type species, ''A. parva'', have been discovered in deposits of the Carboniferous period in Montana, in the United States. ''Anderella'' is the first and so far (as of 2020) the only Carboniferous synziphosurine being described, making it the youngest member of synziphosurines. ''Anderella'' is also one of the few synziphosurine genera with fossil showing evidence of appendages, but the details are obscure due to their poor preservation. The prosoma of ''Anderella'' possess a suboval carapace slightly longer than the externally 10-segmented opisthosoma (excluding telson). A row of axial nodes run through the opisthosomal tergite A ''tergum'' (Latin for "the back"; plural ''terga'', associated adjective tergal) is the dorsal ('upper') portion of an arthropod segment other than the head. The ante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planaterga
Planaterga is a clade of prosomapod euchelicerates including several synziphosurid genera (mainly bunodids and pseudoniscids) and the group Dekatriata (which in turn includes arachnids, chasmataspidids and eurypterid Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct arthropods that form the Order (biology), order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period 467.3 Myr, million yea ...s). Planaterga is defined by the opisthosoma with tergites broadest at third or fourth and lacking enlarged axial nodes, carapace (prosomal dorsal shield) with reduced genal spines, as well as somite VII (first opisthosomal segment) with reduced appendages and microtergite. References Middle Ordovician first appearances {{Chelicerata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiphosura
Xiphosura () is an order of arthropods related to arachnids. They are more commonly known as horseshoe crabs (a name applied more specifically to the only extant family, Horseshoe crab, Limulidae). They first appeared in the Hirnantian (Late Ordovician). Currently, there are only four living species. Xiphosura contains one suborder, Xiphosurida, and several stem-genera. The group has hardly changed in appearance in hundreds of millions of years; the modern horseshoe crabs look almost identical to prehistoric genera and are considered to be living fossils. The most notable difference between ancient and modern forms is that the abdominal segments in present species are fused into a single unit in adults. Xiphosura were historically placed in the class Merostomata, although this term was intended to encompass also the Eurypterida, eurypterids, whence it denoted what is now known to be an unnatural (paraphyletic) group (although this is a grouping recovered in some recent cladistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_from_the_Waukesha_lagerstätte.jpg)