|
Prolacertoides
''Prolacertoides'' is an extinct genus of archosauromorph reptile from the Early Triassic of China, the type species being ''Prolacertoides jimusarensis''. ''Prolacertoides'' means 'like ''Prolacerta''', in reference to ''Prolacerta'', another genus of archosauromorph which ''Prolacertoides'' was once believed to have been closely related to. ''Prolacertoides'' is known from a single partial skull, IVPP V3233, which was discovered in Xinjiang in northwestern China. The locality of its discovery belongs to the Cangfanggou Group of the Jiucaiyuan Formation, which is dated to the Induan age of the very early Triassic. Description IVPP V3233 is a partially flattened and incomplete skull, with some bones being well preserved and others being badly damaged. The snout is tapering and lacks antorbital fenestrae. The anterodorsal edge of each maxilla is convex, in contrast to the concave edge of other basal archosauromorphs. The ascending process of each maxilla is tall and anteropos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolacertoides Skull Reconstruction
''Prolacertoides'' is an extinct genus of archosauromorph reptile from the Early Triassic of China, the type species being ''Prolacertoides jimusarensis''. ''Prolacertoides'' means 'like ''Prolacerta''', in reference to ''Prolacerta'', another genus of archosauromorph which ''Prolacertoides'' was once believed to have been closely related to. ''Prolacertoides'' is known from a single partial skull, IVPP V3233, which was discovered in Xinjiang in northwestern China. The locality of its discovery belongs to the Cangfanggou Group of the Jiucaiyuan Formation, which is dated to the Induan age of the very early Triassic. Description IVPP V3233 is a partially flattened and incomplete skull, with some bones being well preserved and others being badly damaged. The snout is tapering and lacks antorbital fenestrae. The anterodorsal edge of each maxilla is convex, in contrast to the concave edge of other basal archosauromorphs. The ascending process of each maxilla is tall and anteroposte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
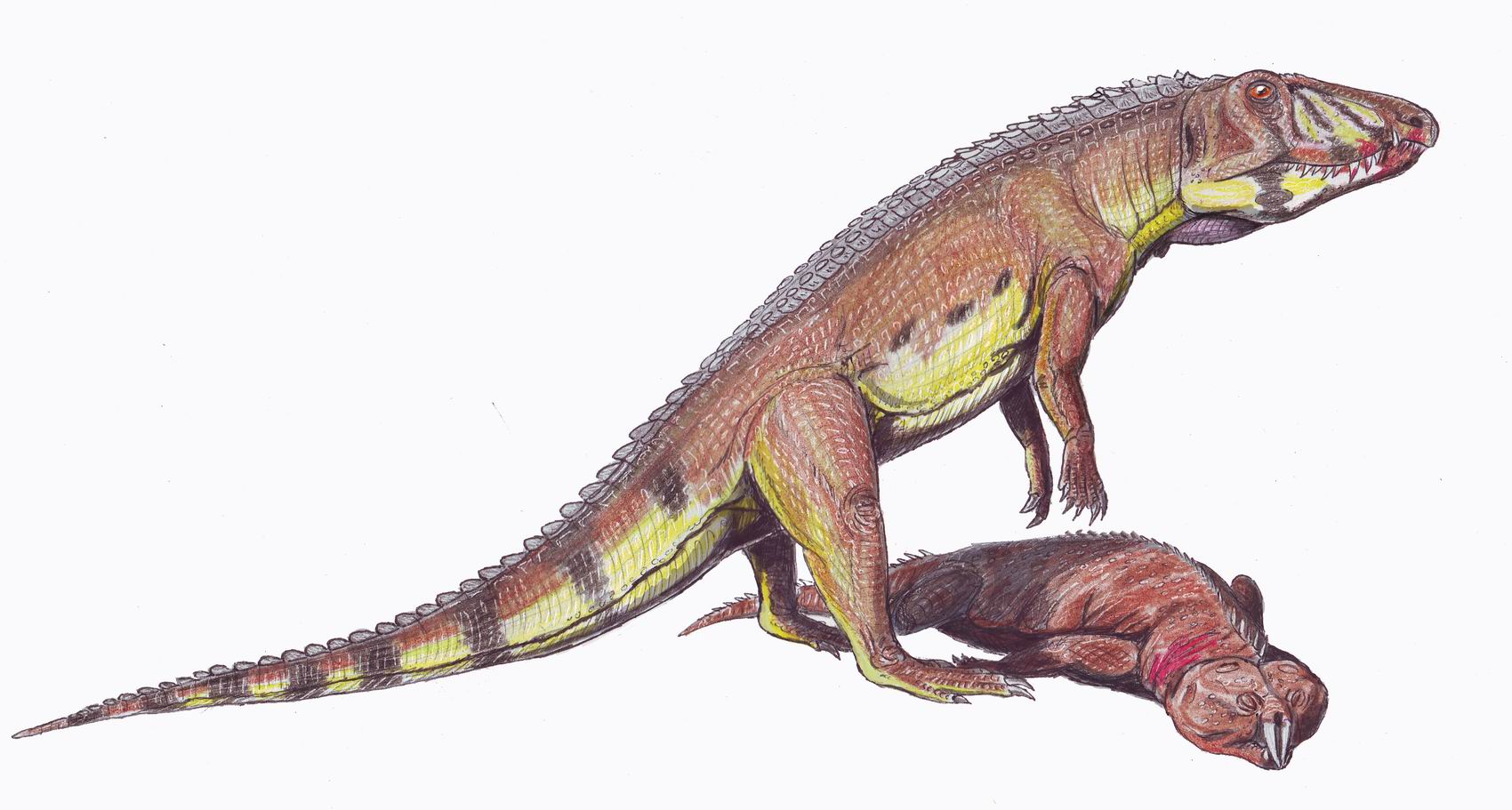
Allokotosauria
Allokotosauria is a clade of early archosauromorph reptiles from the Middle to Late Triassic known from Asia, Africa, North America and Europe. Allokotosauria was first described and named when a new monophyletic grouping of specialized herbivorous archosauromorphs was recovered by Sterling J. Nesbitt, John J. Flynn, Adam C. Pritchard, J. Michael Parrish, Lovasoa Ranivoharimanana and André R. Wyss in 2015. The name Allokotosauria is derived from Greek meaning "strange reptiles" in reference to unexpected grouping of early archosauromorph with a high disparity of features typically associated with herbivory. History Nesbitt ''et al.'' (2015) defined the group as a stem-based taxon containing ''Azendohsaurus madagaskarensis'' and '' Trilophosaurus buettneri'' and all taxa more closely related to them than to ''Tanystropheus longobardicus'', ''Proterosuchus fergusi'', ''Protorosaurus speneri'' or ''Rhynchosaurus articeps''. Therefore, Allokotosauria includes the families Azendoh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauromorph
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) rather than lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including ''Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and ''Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines (turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some authors. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
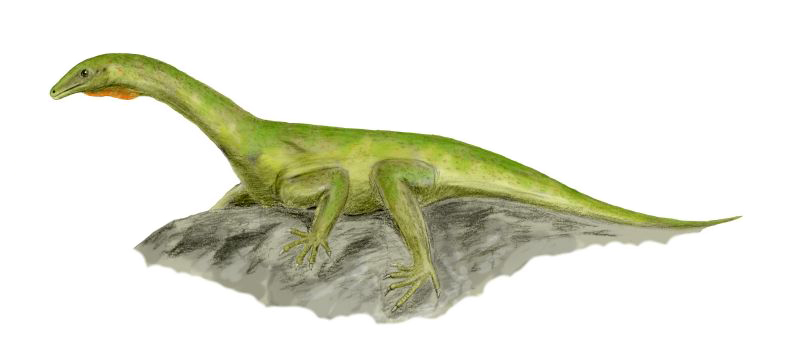
Prolacertidae
Prolacertidae is an extinct family of archosauromorph reptiles that lived during the Early Triassic epoch. It was named in 1935 by the British palaeontologist Francis Rex Parrington to include the species ''Prolacerta broomi'' of South Africa and Antarctica. In 1979 a second species, '' Kadimakara australiensis'', was described from Australia. Several other genera, such as ''Macrocnemus'', ''Pamelaria'' and ''Prolacertoides'', have also been assigned to this family in the past, but these have been placed elsewhere by later studies, leaving ''Prolacerta'' and ''Kadimakara'' as the only well-supported members. The prolacertids were historically placed within the paraphyletic group Prolacertiformes along with other basal, long-necked archosauriforms like ''Protorosaurus'' and the tanystropheids. However, more recent research has shown that the prolacertids were only distantly related to other "prolacertiforms", and were instead among the closest relatives of Archosauriformes. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefrontal Bone
The prefrontal bone is a bone separating the lacrimal and frontal bones in many tetrapod skulls. It first evolved in the sarcopterygian clade Rhipidistia, which includes lungfish and the Tetrapodomorpha. The prefrontal is found in most modern and extinct lungfish, amphibians and reptiles. The prefrontal is lost in early mammaliaforms and so is not present in modern mammals either. In dinosaurs The prefrontal bone is a very small bone near the top of the skull, which is lost in many groups of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs and is completely absent in their modern descendants, the birds. Conversely, a well developed prefrontal is considered to be a primitive feature in dinosaurs. The prefrontal makes contact with several other bones in the skull. The anterior part of the bone articulates with the nasal bone and the lacrimal bone. The posterior part of the bone articulates with the frontal bone and more rarely the palpebral bone The palpebral bone is a small dermal bone found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polytomy
An internal node of a phylogenetic tree is described as a polytomy or multifurcation if (i) it is in a rooted tree and is linked to three or more child subtrees or (ii) it is in an unrooted tree and is attached to four or more branches. A tree that contains any multifurcations can be described as a multifurcating tree. Soft polytomies vs. hard polytomies Two types of polytomies are recognised, soft and hard polytomies. Soft polytomies are the result of insufficient phylogenetic information: though the lineages diverged at different times – meaning that some of these lineages are closer relatives than others, and the available data does not allow recognition of this. Most polytomies are soft, meaning that they would be resolved into a typical tree of dichotomies if better data were available. In contrast, a hard polytomy represents a true divergence event of three or more lineages. Applications Interpretations for a polytomy depend on the individuals, that are represe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systematics
Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: cladograms, phylogenetic trees, phylogenies). Phylogenies have two components: branching order (showing group relationships) and branch length (showing amount of evolution). Phylogenetic trees of species and higher taxa are used to study the evolution of traits (e.g., anatomical or molecular characteristics) and the distribution of organisms (biogeography). Systematics, in other words, is used to understand the evolutionary history of life on Earth. The word systematics is derived from the Latin word '' systema,'' which means systematic arrangement of organisms. Carl Linnaeus used 'Systema Naturae' as the title of his book. Branches and applications In the study of biological systematics, researchers use the different branches to further understand the relationshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Bone
In anatomy, the palatine bones () are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxillae, they comprise the hard palate. (''Palate'' is derived from the Latin ''palatum''.) Structure The palatine bones are situated at the back of the nasal cavity between the maxilla and the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone. They contribute to the walls of three cavities: the floor and lateral walls of the nasal cavity, the roof of the mouth, and the floor of the orbits. They help to form the pterygopalatine and pterygoid fossae, and the inferior orbital fissures. Each palatine bone somewhat resembles the letter L, and consists of a horizontal plate, a perpendicular plate, and three projecting processes—the pyramidal process, which is directed backward and lateral from the junction of the two parts, and the orbital and sphenoidal processes, which surmount the vertical part, and are separated by a dee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterygoid Bone
The pterygoid is a paired bone forming part of the palate of many vertebrates, behind the palatine bone In anatomy, the palatine bones () are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxillae, they comprise the hard palate. (''Palate'' is derived from the Latin ''pa ...s. It is a flat and thin lamina, united to the medial side of the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone, and to the perpendicular lamina of the palatine bone. Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
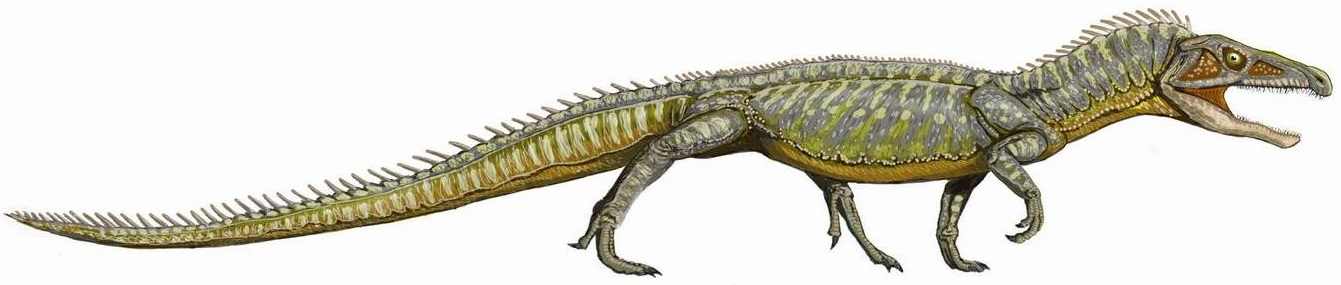
Archosauriformes
Archosauriformes (Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles that developed from archosauromorph ancestors some time in the Latest Permian (roughly 252 million years ago). It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria (the group that contains crocodiles, pterosaurs and dinosaurs bird.html"_;"title="ncluding_bird">ncluding_birds;_Phil_Senter.html" ;"title="bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter">bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing ''Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. These reptiles, which include members of the Family (biology), family Proterosuchidae and more advanced forms, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |