|
Prolacerta Broomi
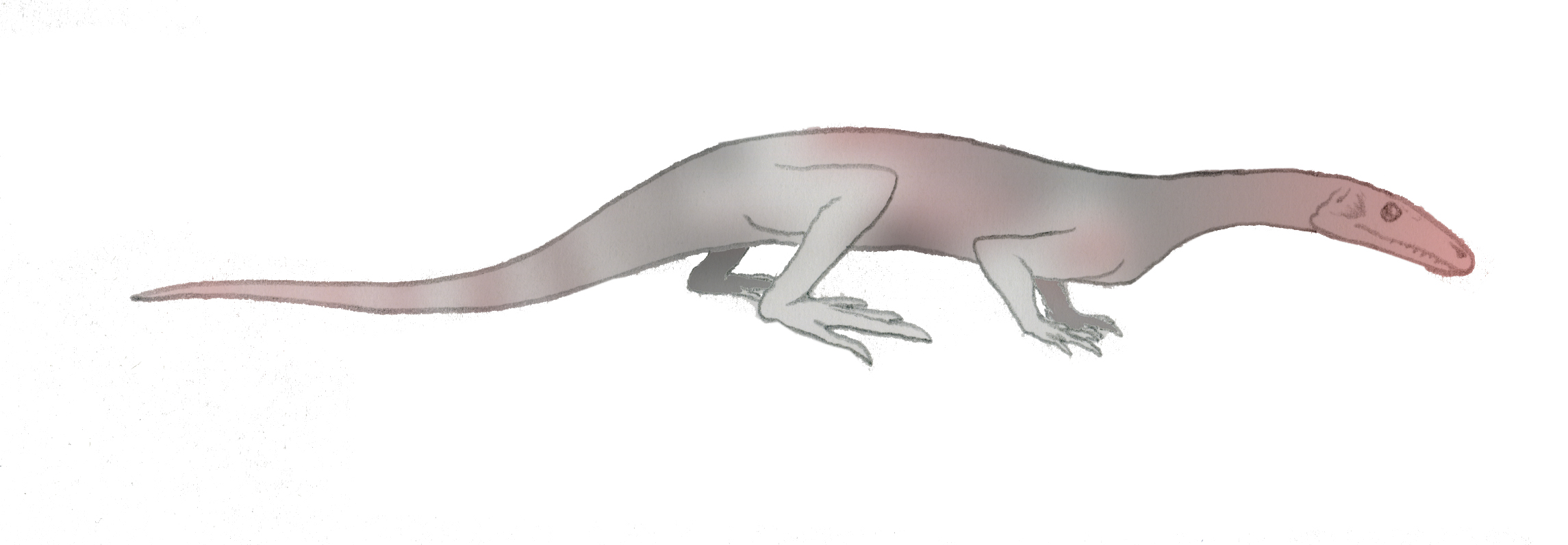
''Prolacerta'' is a genus of archosauromorph from the lower Triassic of South Africa and Antarctica. The only known species is ''Prolacerta broomi''. The generic name ''Prolacerta'' is derived from Latin meaning “before lizard” and its species name ''broomi'' is in commemoration of the famous paleontologist Robert Broom, who discovered and studied many of the fossils found in rocks of the Karoo Supergroup. When first discovered, ''Prolacerta'' was considered to be ancestral to modern lizards, scientifically known as lacertilians. However, a study by Gow (1975) instead found that it shared more similarities with the lineage that would lead to archosaurs such as crocodilians and dinosaurs (including birds). ''Prolacerta'' is considered by modern paleontologists to be among the closest relatives of the Archosauriformes. History of discovery ''Prolacerta'' was first described by Francis Rex Parrington in 1935 from a single skull recovered near the small town, Middelburg, in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Triassic span the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, are among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolacerta Broomi
''Prolacerta'' is a genus of archosauromorph from the lower Triassic of South Africa and Antarctica. The only known species is ''Prolacerta broomi''. The generic name ''Prolacerta'' is derived from Latin meaning “before lizard” and its species name ''broomi'' is in commemoration of the famous paleontologist Robert Broom, who discovered and studied many of the fossils found in rocks of the Karoo Supergroup. When first discovered, ''Prolacerta'' was considered to be ancestral to modern lizards, scientifically known as lacertilians. However, a study by Gow (1975) instead found that it shared more similarities with the lineage that would lead to archosaurs such as crocodilians and dinosaurs (including birds). ''Prolacerta'' is considered by modern paleontologists to be among the closest relatives of the Archosauriformes. History of discovery ''Prolacerta'' was first described by Francis Rex Parrington in 1935 from a single skull recovered near the small town, Middelburg, in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek language, Greek wikt:φυλή, φυλή/wikt:φῦλον, φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, Protein, protein Amino acid, amino acid sequences, or Morphology (biology), morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothesis
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained with the available scientific theories. Even though the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, a scientific hypothesis is not the same as a scientific theory. A working hypothesis is a provisionally accepted hypothesis proposed for further research in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to denote the antecedent of a proposition; thus in the proposition "If ''P'', then ''Q''", ''P'' denotes the hypothesis (or antecedent); ''Q'' can be called a consequent. ''P'' is the assumption in a (possibly counterfactual) ''What If'' question. The adjective ''hypothetical'', meaning "hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lewis Camp
Charles Lewis Camp (March 12, 1893 Jamestown, North Dakota – August 14, 1975 San Jose, California) was a palaeontologist and zoologist, working from the University of California, Berkeley. He took part in excavations at the 'Placerias Quarry', in 1930 and the forty ''Shonisaurus'' skeleton discoveries of the 1960s, in what is now the Berlin-Ichthyosaur State Park. Camp served as the third director of the University of California Museum of Paleontology from 1930 to 1949, and coincidentally as chair of the UC Berkeley Paleontology Department between 1939 and 1949. Camp named a number of species of marine reptiles such as ''Shonisaurus'' and ''Plotosaurus'', as well as the dinosaur '' Segisaurus''. Camp was also an important bibliographer and historian of Western America. This aspect of his career is represented most notably by two works. The first is his biography of American pioneer James Clyman, which Bernard De Voto called "one of the half-dozen classics in the field." The secon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Younginidae
Younginidae is an extinct family of neodiapsid reptiles from the Late Permian and Early Triassic. In a phylogenetic context, younginids are near the base of the clade Neodiapsida. Younginidae includes the species ''Youngina capensis'' from the Late Permian of South Africa and '' Thadeosaurus colcanapi'' from the Late Permian and Early Triassic of Madagascar. ''Heleosuchus griesbachi'' from the Late Permian of South Africa may also be a member of the family. Younginidae was traditionally assigned to Eosuchia, an order containing an assemblage of basal diapsids now thought to represent an evolutionary grade rather than a true clade. In 1945 paleontologist Alfred Romer reclassified Younginidae within a new group, Younginiformes, grouping it with the families Tangasauridae and Prolacertidae. Romer considered Younginidae to include many genera that are no longer classified as younginids: ''Paliguana'', '' Palaegama'', and ''Saurosternon'' are now considered basal lepidosauromorphs, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a phylogenetic tree#Rooted tree, rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, Phylogenetic diversity, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and cladogenesis, diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation tends to exist within any given population as a result of genetic mutation and recombination. Evolution occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection (including sexual selection) and genetic drift act on this variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more common or more rare within a population. The evolutionary pressures that determine whether a characteristic is common or rare within a population constantly change, resulting in a change in heritable characteristics arising over successive generations. It is this process of evolution that has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules. The theory of evolution by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone
The ''Lystrosaurus'' Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone which correlates to the upper Adelaide and lower Tarkastad Subgroups of the Beaufort Group, a fossiliferous and geologically important geological Group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. This biozone has outcrops in the south central Eastern Cape (Middelburg, Queenstown, Aliwal North, Nieu-Bethesda) and in the southern and northeastern Free State (Bethulie, Gariep Dam, Mthatha, Harrismith). The ''Lystrosaurus'' Assemblage Zone is one of eight biozones found in the Beaufort Group, and is considered to be Early Triassic in age. The name of the biozone refers to ''Lystrosaurus'', a small to medium-sized dicynodont therapsid. It is characterized by the appearance of further ''Lystrosaurus'' subspecies which are confined to this biozone. '' Lystrosaurus maccaigi'' and ''Lystrosaurus curvatus'' are the only two species found outside the ''Lystrosaurus'' Assemblage Zone in Upper Permian deposits of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Cape
The Eastern Cape is one of the provinces of South Africa. Its capital is Bhisho, but its two largest cities are East London and Gqeberha. The second largest province in the country (at 168,966 km2) after Northern Cape, it was formed in 1994 out of the Xhosa homelands or bantustans of Transkei and Ciskei, together with the eastern portion of the Cape Province. The central and eastern part of the province is the traditional home of the indigenous Xhosa people. In 1820 this area which was known as the Xhosa Kingdom began to be settled by Europeans who originally came from England and some from Scotland and Ireland. Since South Africa's early years, many Xhosas believed in Africanism and figures such as Walter Rubusana believed that the rights of Xhosa people and Africans in general, could not be protected unless Africans mobilized and worked together. As a result, the Eastern Cape is home to many anti-apartheid leaders such as Robert Sobukwe, Oliver Tambo, Nelson Mandel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |