|
Project Dragonfly (space Study)
Project Dragonfly is the first conceptual design study that assesses the feasibility of a laser-propelled interstellar probe, conducted by the Initiative for Interstellar Studies.Leonard David, "Pushing the Boundaries: Initiative for Interstellar Studies/ref>Next Big Future, "Project Dragonfly is competition to design interstellar laser sail probes that would be technological feasible by 2034 and launched by 2050/ref> Contrary to past unmanned interstellar travel, interstellar mission studies such as Project Daedalus and Project Icarus, the focus is particularly on a small spacecraft. The project was founded in 2013 by the Initiative for Interstellar Studies (i4is). A subsequent design competition was launched in 2014. The objective was to design a spacecraft that is capable of reaching Alpha Centauri within 100 years using existing or near-term technologies and a beam power below . Four teams presented their designs at the final workshop at the British Interplanetary Socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Dragonfly
Project Dragonfly may refer to * Project Dragonfly (space study) Project Dragonfly is the first conceptual design study that assesses the feasibility of a laser-propelled interstellar probe, conducted by the Initiative for Interstellar Studies.Leonard David, "Pushing the Boundaries: Initiative for Interstel ... - the first conceptual design study that assesses the feasibility of a laser-propelled interstellar probe. * Google's development of the Dragonfly search engine intended for use in the People's Republic of China {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, Santa Barbara
The University of California, Santa Barbara (UC Santa Barbara or UCSB) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Santa Barbara County, California, Santa Barbara, California with 23,196 undergraduates and 2,983 graduate students enrolled in 2021–2022. It is part of the University of California 10-university system. Tracing its roots back to 1891 as an independent teachers' college, UCSB joined the University of California system in 1944, and is the third-oldest undergraduate campus in the system, after University of California, Berkeley, UC Berkeley and University of California, Los Angeles, UCLA. Located on a WWII-era Marine air station, UC Santa Barbara is organized into three undergraduate colleges (UCSB College of Letters and Science, College of Letters and Science, UCSB College of Engineering, College of Engineering, College of Creative Studies) and two graduate schools (Gevirtz Graduate School of Education and Bren School of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam-powered Propulsion
Beam-powered propulsion, also known as directed energy propulsion, is a class of aircraft or spacecraft propulsion that uses energy beamed to the spacecraft from a remote power plant to provide energy. The beam is typically either a microwave or a laser beam and it is either pulsed or continuous. A continuous beam lends itself to thermal rockets, photonic thrusters and light sails, whereas a pulsed beam lends itself to ablative thrusters and pulse detonation engines. The rule of thumb that is usually quoted is that it takes a megawatt of power beamed to a vehicle per kg of payload while it is being accelerated to permit it to reach low earth orbit. Other than launching to orbit, applications for moving around the world quickly have also been proposed. Background Rockets are momentum machines; they use mass ejected from the rocket to provide momentum to the rocket. Momentum is the product of mass and velocity, so rockets generally attempt to put as much velocity into their worki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Propulsion
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric entry. Several methods of pragmatic spacecraft propulsion have been developed each having its own drawbacks and advantages. Most satellites have simple reliable chemical thrusters (often monopropellant rockets) or resistojet rockets for orbital station-keeping and some use momentum wheels for attitude control. Soviet bloc satellites have used electric propulsion for decades, and newer Western geo-orbiting spacecraft are starting to use them for north–south station-keeping and orbit raising. Interplanetary vehicles mostly use chemical rockets as well, although a few have used ion thrusters and Hall-effect thrusters (two different types of electric propulsion) to great success. Hypothetical in-space propulsion technologies describe the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
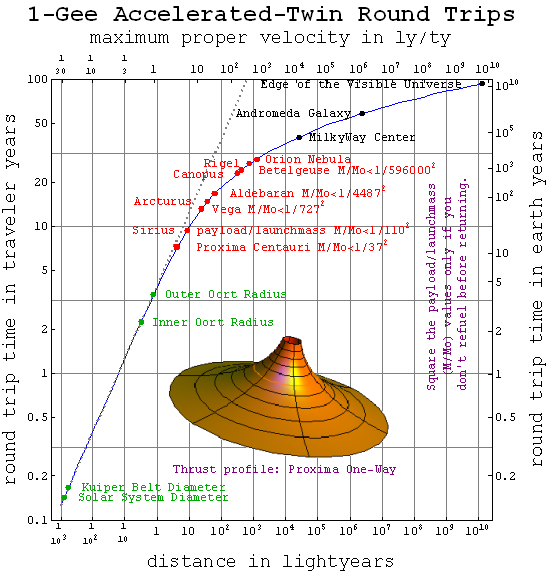
Interstellar Travel
Interstellar travel is the hypothetical travel of spacecraft from one star system, solitary star, or planetary system to another. Interstellar travel is expected to prove much more difficult than interplanetary spaceflight due to the vast difference in the scale of the involved distances. Whereas the distance between any two planets in the Solar System is less than 30 astronomical units (AU), stars are typically separated by hundreds of thousands of AU, causing these distances to typically be expressed instead in light-years. Because of the vastness of these distances, non-generational interstellar travel based on known physics would need to occur at a high percentage of the speed of light; even so, travel times would be long, at least decades and perhaps millennia or longer. As of 2022, five uncrewed spacecraft, all launched and operated by the United States, have achieved the escape velocity required to leave the Solar System as part of missions to explore parts of the out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David A
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the third king of the United Kingdom of Israel. In the Books of Samuel, he is described as a young shepherd and harpist who gains fame by slaying Goliath, a champion of the Philistines, in southern Canaan. David becomes a favourite of Saul, the first king of Israel; he also forges a notably close friendship with Jonathan, a son of Saul. However, under the paranoia that David is seeking to usurp the throne, Saul attempts to kill David, forcing the latter to go into hiding and effectively operate as a fugitive for several years. After Saul and Jonathan are both killed in battle against the Philistines, a 30-year-old David is anointed king over all of Israel and Judah. Following his rise to power, David ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kickstarter
Kickstarter is an American public benefit corporation based in Brooklyn, New York, that maintains a global crowdfunding platform focused on creativity. The company's stated mission is to "help bring creative projects to life". As of July 2021, Kickstarter has received $6.6 billion in pledges from 21 million backers to fund 222,000 projects, such as films, music, stage shows, comics, journalism, video games, board games, technology, publishing, and food-related projects. People who back Kickstarter projects are offered tangible rewards or experiences in exchange for their pledges. This model traces its roots to subscription model of arts patronage, where artists would go directly to their audiences to fund their work. History Kickstarter launched on April 28, 2009, by Perry Chen, Yancey Strickler, and Charles Adler. ''The New York Times'' called Kickstarter "the people's NEA". ''Time'' named it one of the "Best Inventions of 2010" and "Best Websites of 2011". Kickstarter repo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakthrough Initiatives
Breakthrough Initiatives is a science-based program founded in 2015 and funded by Julia and Yuri Milner, also of Breakthrough Prize, to search for extraterrestrial intelligence over a span of at least 10 years. The program is divided into multiple projects. Breakthrough Listen will comprise an effort to search over 1,000,000 stars for artificial radio or laser signals. A parallel project called Breakthrough Message is an effort to create a message "representative of humanity and planet Earth". The project Breakthrough Starshot, co-founded with Mark Zuckerberg, aims to send a swarm of probes to the nearest star at about 20% the speed of light. The project Breakthrough Watch aims to identify and characterize Earth-sized, rocky planets around Alpha Centauri and other stars within 20 light years of Earth. Breakthrough plans to send a mission to Saturn's moon Enceladus, in search for life in its warm ocean, and in 2018 signed a partnership agreement with NASA for the project. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakthrough Starshot
Breakthrough Starshot is a research and engineering project by the Breakthrough Initiatives to develop a Proof of concept, proof-of-concept fleet of light sail interstellar probes named ''Starchip'', to be capable of making the journey to the Alpha Centauri star system 4.37 light-years away. It was founded in 2016 by Yuri Milner, Stephen Hawking, and Mark Zuckerberg. A flyby mission has been proposed to Proxima Centauri b, an Terrestrial planet, Earth-sized exoplanet in the habitable zone of its host star, Proxima Centauri, in the Alpha Centauri system. At a speed between 15% and 20% of the speed of light, it would take between twenty and thirty years to complete the journey, and approximately four years for a return message from the starship to Earth. The conceptual principles to enable this interstellar travel project were described in "A Roadmap to Interstellar Flight", by Philip Lubin of University of California, Santa Barbara, UC Santa Barbara.(file available at University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WARR (TUM)
The Scientific Workgroup for Rocketry and Spaceflight (WARR) (german: Wissenschaftliche Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Raketentechnik und Raumfahrt) is a scientific workgroup situated at Technical University of Munich, composed mainly of its students. It was founded by students in 1962 with the goal to compensate for the lack of a chair for space technology at the university at the time. Since the establishment of such a chair in 1966, the group has conducted practical projects, starting with the first successful development and of a hybrid rocket in Germany. One rocket of this type was launched in 1972, another is on permanent display at Deutsches Museum. WARR has attained some public attention by for its projects in space elevator competitions, small satellites interstellar spaceflight concepts, and for winning all SpaceX Hyperloop pod competitions. Currently, WARR works in the fields of hybrid propulsion, satellite technology, robotics, and transportation technologies. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical University Of Munich
The Technical University of Munich (TUM or TU Munich; german: Technische Universität München) is a public research university in Munich, Germany. It specializes in engineering, technology, medicine, and applied and natural sciences. Established in 1868 by King Ludwig II of Bavaria, the university now has additional campuses in Garching, Freising, Heilbronn, Straubing, and Singapore, with the Garching campus being its largest. The university is organized into eight schools and departments, and is supported by numerous research centers. It is one of the largest universities in Germany, with 50,000 students and an annual budget of €1,770.3 million (including university hospital). A ''University of Excellence'' under the German Universities Excellence Initiative, TUM is considered the top university in Germany according to major rankings as of 2022 and is among the leading universities in the European Union. Its researchers and alumni include 18 Nobel laureates and 23 Leib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstellar Travel
Interstellar travel is the hypothetical travel of spacecraft from one star system, solitary star, or planetary system to another. Interstellar travel is expected to prove much more difficult than interplanetary spaceflight due to the vast difference in the scale of the involved distances. Whereas the distance between any two planets in the Solar System is less than 30 astronomical units (AU), stars are typically separated by hundreds of thousands of AU, causing these distances to typically be expressed instead in light-years. Because of the vastness of these distances, non-generational interstellar travel based on known physics would need to occur at a high percentage of the speed of light; even so, travel times would be long, at least decades and perhaps millennia or longer. As of 2022, five uncrewed spacecraft, all launched and operated by the United States, have achieved the escape velocity required to leave the Solar System as part of missions to explore parts of the out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)