|
Problem Of Apollonius
In Euclidean plane geometry, Apollonius's problem is to construct circles that are tangent to three given circles in a plane (Figure 1). Apollonius of Perga (c. 262 190 BC) posed and solved this famous problem in his work (', "Tangencies"); this work has been lost, but a 4th-century AD report of his results by Pappus of Alexandria has survived. Three given circles generically have eight different circles that are tangent to them (Figure 2), a pair of solutions for each way to divide the three given circles in two subsets (there are 4 ways to divide a set of cardinality 3 in 2 parts). In the 16th century, Adriaan van Roomen solved the problem using intersecting hyperbolas, but this solution does not use only straightedge and compass constructions. François Viète found such a solution by exploiting limiting cases: any of the three given circles can be shrunk to zero radius (a point) or expanded to infinite radius (a line). Viète's approach, which uses simpler limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Apollonius Problem Typical Solution
Apollonius () is a masculine given name which may refer to: People Ancient world Artists * Apollonius of Athens (sculptor) (fl. 1st century BC) * Apollonius of Tralles (fl. 2nd century BC), sculptor * Apollonius (satyr sculptor) * Apollonius (son of Archias), sculptor Historians * Apollonius of Aphrodisias (fl. c. 3rd century BC), historian of Caria * Apollonius of Ascalon, historian mentioned by Stephanus of Byzantium Writers * Apollonius Attaleus, writer on dreams * Apollonius of Acharnae, ancient Greek writer on festivals * Apollonius of Laodicea, writer on astrology * Apollonius of Rhodes (born c. 270 BC), librarian and poet, best known for the ''Argonautica'' * Apollonius (son of Chaeris), ancient Greek writer, mentioned by the scholiast on Aristophanes * Apollonius (son of Sotades), writer Oratory * Apollonius Dyscolus (fl. 2nd century AD), grammarian * Apollonius Eidographus, ancient Greek grammarian * Apollonius Molon (fl. 70 BC), rhetorician * Apo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Joseph Diaz Gergonne
Joseph Diez Gergonne (19 June 1771 at Nancy, France – 4 May 1859 at Montpellier, France) was a French mathematician and logician. Life In 1791, Gergonne enlisted in the French army as a captain. That army was undergoing rapid expansion because the French government feared a foreign invasion intended to undo the French Revolution and restore Louis XVI to the throne of France. He saw action in the major battle of Valmy on 20 September 1792. He then returned to civilian life but soon was called up again and took part in the French invasion of Spain in 1794. In 1795, Gergonne and his regiment were sent to Nîmes. At this point, he made a definitive transition to civilian life by taking up the chair of "transcendental mathematics" at the new École centrale. He came under the influence of Gaspard Monge, the Director of the new École polytechnique in Paris. In 1810, in response to difficulties he encountered in trying to publish his work, Gergonne founded his own mathematics jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Circles Of Apollonius
The circles of Apollonius are any of several sets of circles associated with Apollonius of Perga, a renowned Greek geometer. Most of these circles are found in planar Euclidean geometry, but analogs have been defined on other surfaces; for example, counterparts on the surface of a sphere can be defined through stereographic projection. The main uses of this term are fivefold: # Apollonius showed that a circle can be defined as the set of points in a plane that have a specified ''ratio'' of distances to two fixed points, known as foci. This Apollonian circle is the basis of the Apollonius pursuit problem. It is a particular case of the first family described in #2. # The Apollonian circles are two families of mutually orthogonal circles. The first family consists of the circles with all possible distance ratios to two fixed foci (the same circles as in #1), whereas the second family consists of all possible circles that pass through both foci. These circles form the basis o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Number Theory
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and arithmetic functions. Number theorists study prime numbers as well as the properties of mathematical objects constructed from integers (for example, rational numbers), or defined as generalizations of the integers (for example, algebraic integers). Integers can be considered either in themselves or as solutions to equations (Diophantine geometry). Questions in number theory can often be understood through the study of Complex analysis, analytical objects, such as the Riemann zeta function, that encode properties of the integers, primes or other number-theoretic objects in some fashion (analytic number theory). One may also study real numbers in relation to rational numbers, as for instance how irrational numbers can be approximated by fractions (Diophantine approximation). Number theory is one of the oldest branches of mathematics alongside geometry. One quirk of number theory is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fractal
In mathematics, a fractal is a Shape, geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illustrated in successive magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. This exhibition of similar patterns at increasingly smaller scales is called self-similarity, also known as expanding symmetry or unfolding symmetry; if this replication is exactly the same at every scale, as in the Menger sponge, the shape is called affine geometry, affine self-similar. Fractal geometry lies within the mathematical branch of measure theory. One way that fractals are different from finite geometric figures is how they Scaling (geometry), scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a filled polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the conventional dimension of the filled polygon). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Apollonian Gasket
In mathematics, an Apollonian gasket, Apollonian net, or Apollonian circle packing is a fractal generated by starting with a triple of circles, each tangent to the other two, and successively filling in more circles, each tangent to another three. It is named after Greek mathematician Apollonius of Perga. Construction The construction of the Apollonian gasket starts with three circles C_1, C_2, and C_3 (black in the figure), that are each tangent to the other two, but that do not have a single point of triple tangency. These circles may be of different sizes to each other, and it is allowed for two to be inside the third, or for all three to be outside each other. As Apollonius discovered, there exist two more circles C_4 and C_5 (red) that are tangent to all three of the original circles – these are called ''Apollonian circles''. These five circles are separated from each other by six curved triangular regions, each bounded by the arcs from three pairwise-tangent circles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
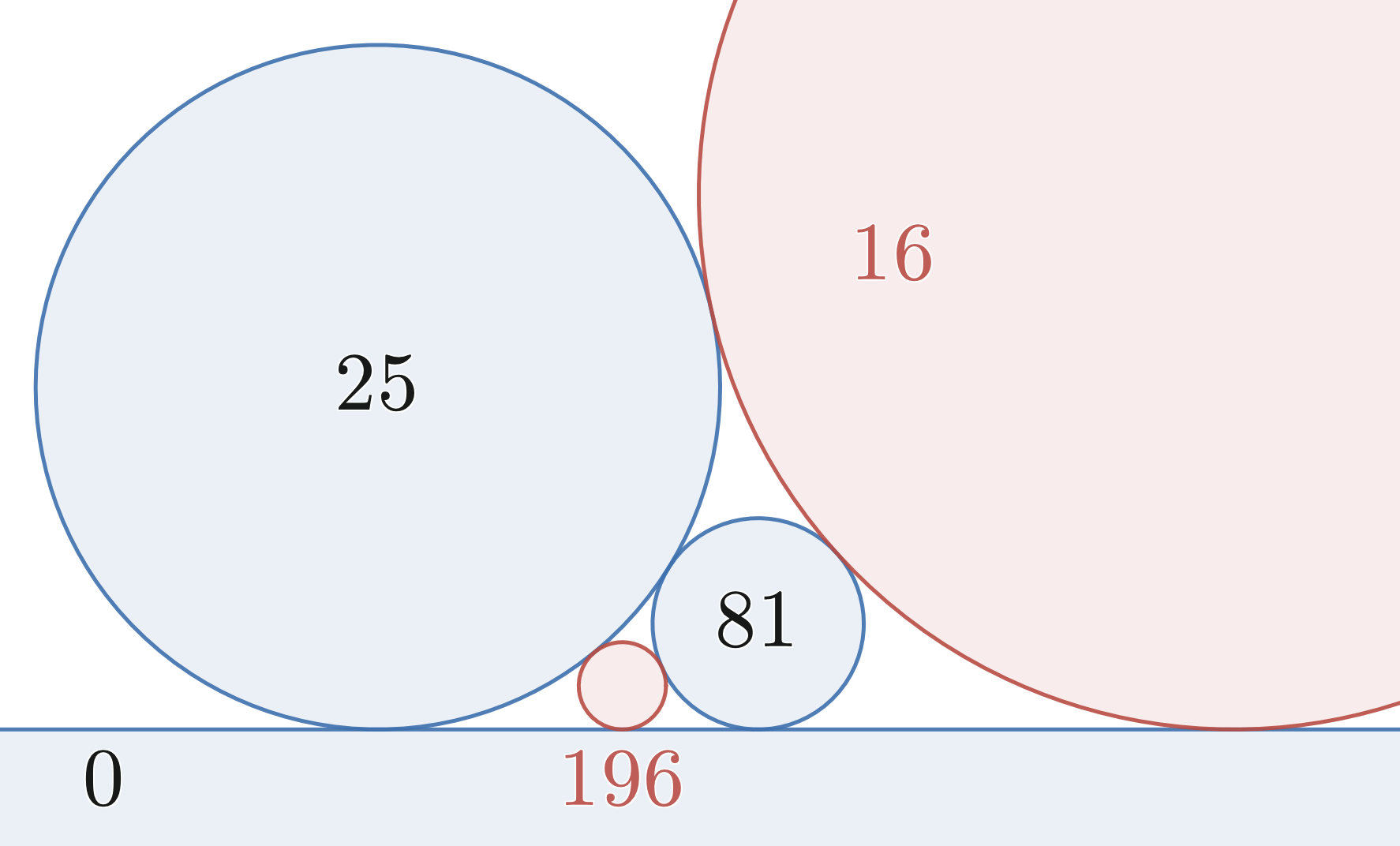
Descartes' Theorem
In geometry, Descartes' theorem states that for every four kissing, or mutually tangent circles, the radii of the circles satisfy a certain quadratic equation. By solving this equation, one can construct a fourth circle tangent to three given, mutually tangent circles. The theorem is named after René Descartes, who stated it in 1643. Frederick Soddy's 1936 poem ''The Kiss Precise'' summarizes the theorem in terms of the ''bends'' (signed inverse radii) of the four circles: Special cases of the theorem apply when one or two of the circles is replaced by a straight line (with zero bend) or when the bends are integers or square numbers. A version of the theorem using complex numbers allows the centers of the circles, and not just their radii, to be calculated. With an appropriate definition of curvature, the theorem also applies in spherical geometry and hyperbolic geometry. In higher dimensions, an analogous quadratic equation applies to systems of pairwise tangent spheres or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
René Descartes
René Descartes ( , ; ; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and Modern science, science. Mathematics was paramount to his method of inquiry, and he connected the previously separate fields of geometry and algebra into analytic geometry. Descartes spent much of his working life in the Dutch Republic, initially serving the Dutch States Army, and later becoming a central intellectual of the Dutch Golden Age. Although he served a Dutch Reformed Church, Protestant state and was later counted as a Deism, deist by critics, Descartes was Roman Catholicism, Roman Catholic. Many elements of Descartes's philosophy have precedents in late Aristotelianism, the Neostoicism, revived Stoicism of the 16th century, or in earlier philosophers like Augustine of Hippo, Augustine. In his natural philosophy, he differed from the Scholasticism, schools on two major point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Higher Dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on itfor example, the point at 5 on a number line. A surface, such as the boundary of a cylinder or sphere, has a dimension of two (2D) because two coordinates are needed to specify a point on itfor example, both a latitude and longitude are required to locate a point on the surface of a sphere. A two-dimensional Euclidean space is a two-dimensional space on the plane. The inside of a cube, a cylinder or a sphere is three-dimensional (3D) because three coordinates are needed to locate a point within these spaces. In classical mechanics, space and time are different categories and refer to absolute space and time. That conception of the world is a four-dimensional space but not the one that was fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |