|
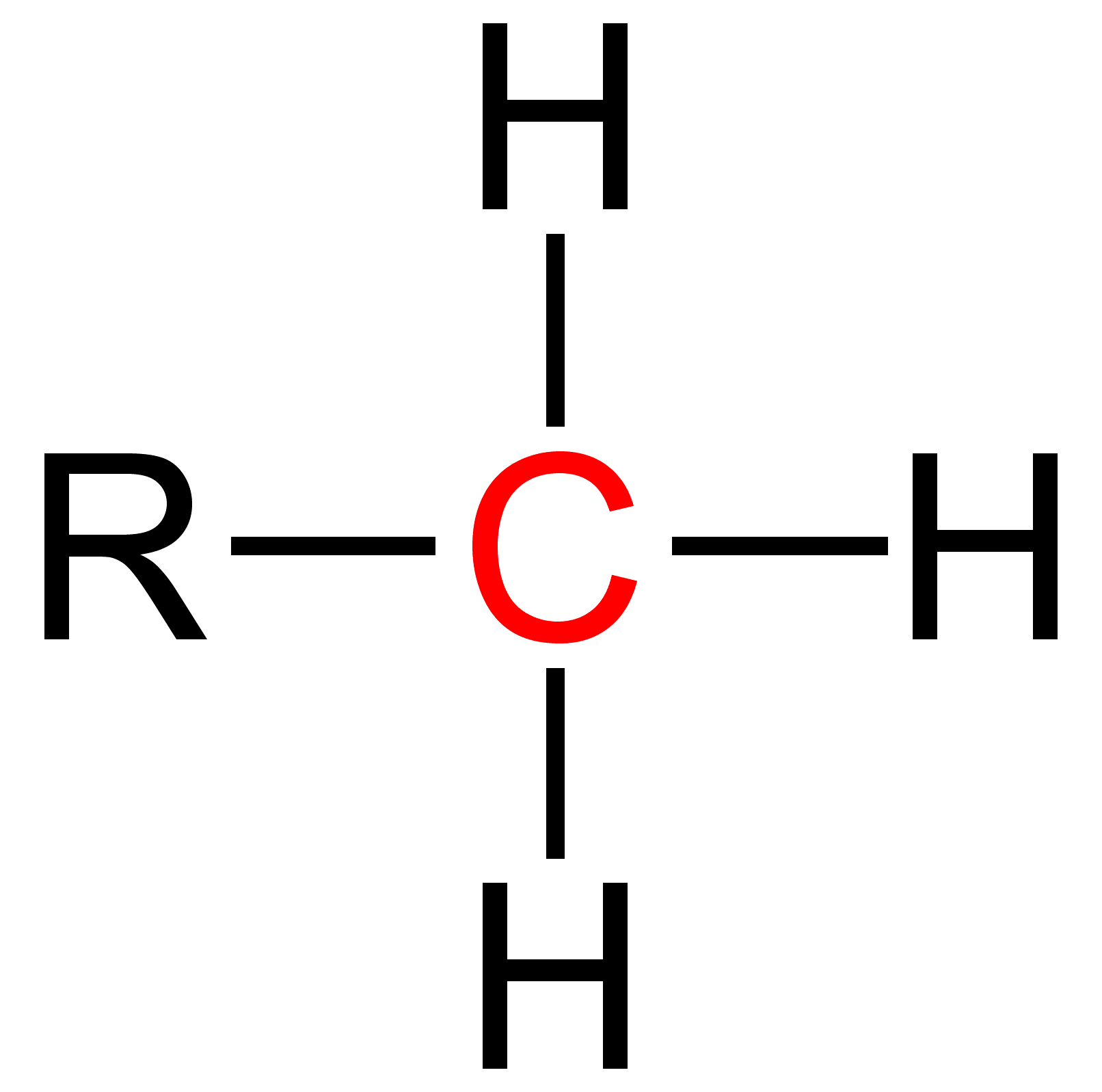
Primary (chemistry)
Primary is a term used in organic chemistry Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clay ... to classify various types of compounds (e.g. alcohols, alkyl halides, amines) or reactive intermediates (e.g. alkyl radicals, carbocations). {{clear See also * Secondary (chemistry) * Tertiary (chemistry) * Quaternary (chemistry) References Chemical nomenclature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Intermediates
In chemistry, a reactive intermediate or an intermediate is a short-lived, high-energy, highly reactive molecule. When generated in a chemical reaction, it will quickly convert into a more stable molecule. Only in exceptional cases can these compounds be isolated and stored, e.g. low temperatures, matrix isolation. When their existence is indicated, reactive intermediates can help explain how a chemical reaction takes place. Most chemical reactions take more than one elementary step to complete, and a reactive intermediate is a high-energy, yet stable, product that exists only in one of the intermediate steps. The series of steps together make a reaction mechanism. A reactive intermediate differs from a reactant or product or a simple reaction intermediate only in that it cannot usually be isolated but is sometimes observable only through fast spectroscopic methods. It is stable in the sense that an elementary reaction forms the reactive intermediate and the elementary reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbocation
A carbocation is an ion with a positively charged carbon atom. Among the simplest examples are the methenium , methanium and vinyl cations. Occasionally, carbocations that bear more than one positively charged carbon atom are also encountered (e.g., ethylene dication ). Until the early 1970s, all carbocations were called ''carbonium ions''. In the present-day definition given by the IUPAC, a carbocation is any even-electron cation with significant partial positive charge on a carbon atom. They are further classified in two main categories according to the coordination number of the charged carbon: three in the carbenium ions and five in the carbonium ions. This nomenclature was proposed by G. A. Olah. Carbonium ions, as originally defined by Olah, are characterized by a three-center two-electron delocalized bonding scheme and are essentially synonymous with so-called ' non-classical carbocations', which are carbocations that contain bridging C–C or C–H σ-bonds. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary (chemistry)
Secondary is a term used in organic chemistry to classify various types of compounds (e. g. alcohols, alkyl halides, amines) or reactive intermediates (e. g. alkyl radicals, carbocations). An atom is considered secondary if it has two 'R' Groups attached to it. An 'R' group is a carbon containing group such as a methyl (CH3 ). A secondary compound is most often classified on an alpha carbon (middle carbon) or a nitrogen. The word secondary comes from the root word 'second' which means two. This nomenclature can be used in many cases and further used to explain relative reactivity. The reactivity of molecules varies with respect to the attached atoms. Thus, a primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary molecule of the same function group will have different reactivities. Secondary Alcohols Secondary alcohols are identified by the groups attached to the central carbon that is bonding with the alcohol (-OH) group. A secondary alcohol is a carbon with four substituents includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary (chemistry)
Tertiary is a term used in organic chemistry to classify various types of compounds (e. g. alcohols, alkyl halides, amines) or reactive intermediates (e. g. alkyl radicals, carbocations). See also * Primary (chemistry) * Secondary (chemistry) * Quaternary (chemistry) References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
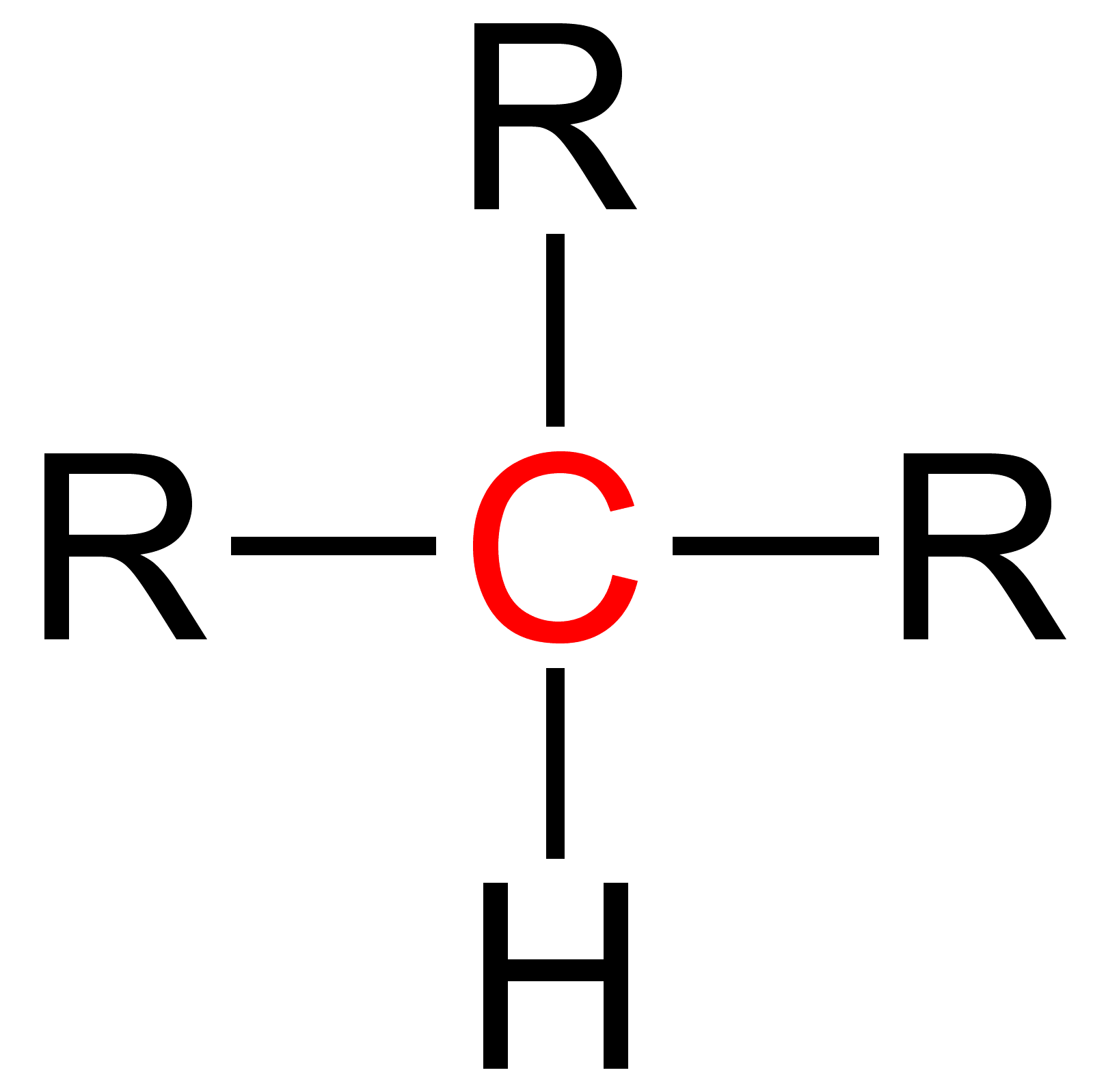
Quaternary (chemistry)
Quaternary is a term used in organic chemistry to classify various types of compounds (e. g. amines and ammonium salts).Paula Yurkanis Bruice: ''Organic Chemistry'', Pearson Education Inc., 2004, 4. Ed., p. 78, 104, 893, and 912, . {{clear See also * Primary (chemistry) Primary is a term used in organic chemistry Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in i ... * Secondary (chemistry) * Tertiary (chemistry) References Chemical nomenclature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkane
In organic chemistry Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clay ..., an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon–carbon bonds are single. Alkanes have the general chemical formula . The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of methane (), where ''n'' = 1 (sometimes called the parent molecule), to arbitrarily large and complex molecules, like Higher alkanes#Nonatetracontane to tetrapentacontane, pentacontane () or 6-ethyl-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl) octane, an isomer of tetradecane (). The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) defines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prim
Prim may refer to: People * Prim (given name) * Prim (surname) Places * Prim, Virginia, unincorporated community in King George County *Dolní Přím, village in the Czech Republic; as Nieder Prim (Lower Prim) site of the Battle of Königgrätz * Saint-Prim, commune in Isère, France *Prim (Neckar), river in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, tributary of the Neckar *Prims, river in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, tributary of the Saar Other *Prim, a type of ''tamburica'' (musical instrument) *Prim or Primost, a Norwegian cheese *Prim, abbreviation for Primitive Methodist *Prim's algorithm for minimum spanning tree, developed by Robert C. Prim *PRIM (watches), a Czech trademark *Graham Street Prims F.C., football club in Derby, England * In computers, a geometric primitive, or prim, is a simple shape used in 3D modeling to build into more complex objects. ** A Sculpted prim, in Second Life, is a 3D parametric object whose 3D shape is determined by a texture, more advanced than the gam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tert
Telomerase reverse transcriptase (abbreviated to TERT, or hTERT in humans) is a catalytic subunit of the enzyme telomerase, which, together with the telomerase RNA component (TERC), comprises the most important unit of the telomerase complex. Telomerases are part of a distinct subgroup of RNA-dependent polymerases. Telomerase lengthens telomeres in DNA strands, thereby allowing senescent cells that would otherwise become postmitotic and undergo apoptosis to exceed the Hayflick limit and become potentially immortal, as is often the case with cancerous cells. To be specific, TERT is responsible for catalyzing the addition of nucleotides in a TTAGGG sequence to the ends of a chromosome's telomeres. This addition of repetitive DNA sequences prevents degradation of the chromosomal ends following multiple rounds of replication. hTERT absence (usually as a result of a chromosomal mutation) is associated with the disorder Cri du chat. Function Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quart
The quart (symbol: qt) is an English unit of volume equal to a quarter gallon. Three kinds of quarts are currently used: the liquid quart and dry quart of the US customary system and the of the British imperial system. All are roughly equal to one liter. It is divided into two pints or (in the US) four cups. Historically, the exact size of the quart has varied with the different values of gallons over time and in reference to different commodities. Name The term comes from the Latin ''quartus'' (meaning one-quarter) via the French '' quart''. However, although the French word '' quart'' has the same root, it frequently means something entirely different. In Canadian French in particular, the quart is called '' pinte'', whilst the pint is called '' chopine''. History Since gallons of various sizes have historically been in use, the corresponding quarts have also existed with various sizes. Definitions and equivalencies US liquid quart In the United States, all tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |