|
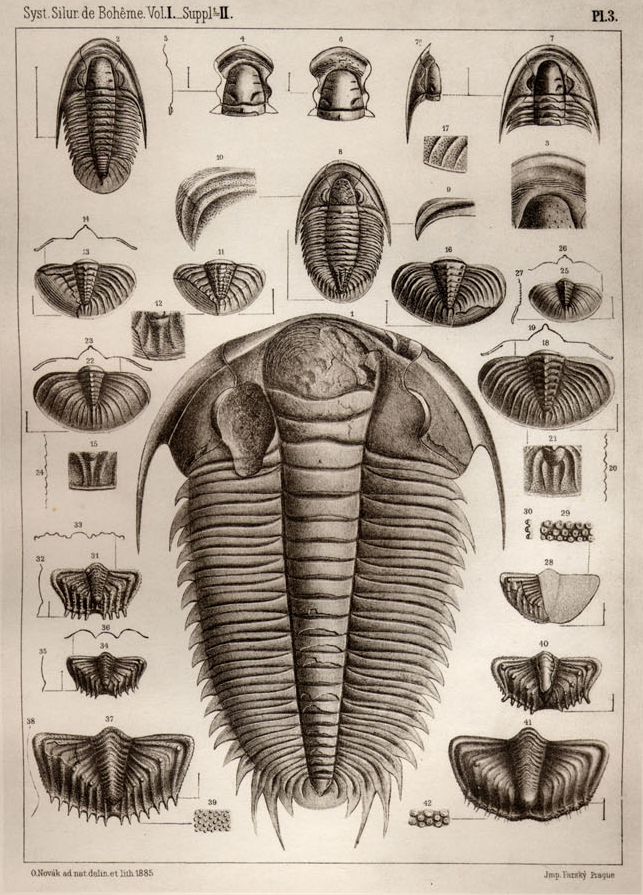
Pricyclopyge Binodosa Eye
''Pricyclopyge'' is a genus of trilobites assigned to the family Cyclopygidae that occurs throughout the Ordovician. ''Pricyclopyge'' had aextratropicaldistribution, and there is evidence that it lived in darker parts of the water column (around 175m deep). ''Pricyclopyge'' has huge eyes, an inverted pear-shaped glabella, six thorax segments, with on the 3rd two small discs.Whittington, H. B. et al. (1997) Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology. Part O, Revised, Volume 1 – Trilobita – Introduction, Order Agnostida, Order Redlichiida. ''Pricyclopyge'' is known from what are today China, the Czech Republic, France, and the United Kingdom.Paleobiology Database Description Like other cyclopygids, ''Pricyclopyge'' lacks genal spines. ''Pricyclopyge'' has six thorax segments of which the third from the front carries two very characteristic round discs that are presumed to have been bioluminescent organs, and if true, this suggests that ''Pricyclopyge'' swam upside down. It ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joachim Barrande
Joachim Barrande (11 August 1799 – 5 October 1883) was a French geologist and palaeontologist. Career Barrande was born at Saugues, Haute Loire, and educated in the École Polytechnique and École Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées at Paris. Although he had received the training of an engineer, his first appointment was that of tutor to the duc de Bordeaux (afterwards known as the comte de Chambord), grandson of Charles X, and when the king abdicated in 1830, Barrande accompanied the royal exiles to England and Scotland, and afterwards to Prague. Settling in that city in 1831, he became occupied in engineering works, and his attention was then attracted to the fossils from the Lower Palaeozoic rocks of Bohemia. The publication in 1839 of ''Murchison's Silurian System'' incited Barrande to carry on systematic researches on the equivalent strata in Bohemia. For ten years (1840–1850) he made a detailed study of these rocks, engaging workmen specially to collect fossils, and in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llanvirn
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same Rock (geology), rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed Stratum, strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Union of Geological Sciences, International Geological Congress. Life continued to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of France
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of The Czech Republic
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of China
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician Trilobites
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambrian Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asaphida Genera
Asaphida is a large, morphologically diverse order of trilobites found in marine strata dated from the Middle Cambrian until their extinction during the Silurian. Asaphida contains six superfamilies (Anomocaroidea, Asaphoidea, Cyclopygoidea, Dikelocephaloidea, Remopleuridoidea and Trinucleioidea), but no suborders. Asaphids comprise some 20% of described fossil trilobites. In 2020, the superfamily Trinucleoidea was proposed to be raised to an order ( Trinucleida) and removed from Asaphida. Morphology The Asaphids generally have cephalon (head) and pygidium (tail) parts similar in size, and most species have a prominent median ventral suture. Heads are often flat, and carapace furrows in the head area are often faint or not visible. Thoracic segments typically number 5 - 12, though some species have as few as two and some as many as 30. They also generally have a wide doublure, or rim, that surrounds the cephalon. This causes some specimens to be described as having a charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton, which are the plant component of the plankton community ("phyto" comes from the Greek word for ''plant''). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding). This means zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food but must eat other plants or animals instead — in particular they eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are generally larger than phytoplankton, most are microscopic, but some (such as jellyfish) are macroscopic and can be seen with the naked eye. Many protozoans (single-celled protists that prey on other microscopic life) are zooplankton, including zooflagellates, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graptolites
Graptolites are a group of colonial animals, members of the subclass Graptolithina within the class Pterobranchia. These filter-feeding organisms are known chiefly from fossils found from the Middle Cambrian (Miaolingian, Wuliuan) through the Lower Carboniferous ( Mississippian). A possible early graptolite, ''Chaunograptus'', is known from the Middle Cambrian. Recent analyses have favored the idea that the living pterobranch ''Rhabdopleura'' represents an extant graptolite which diverged from the rest of the group in the Cambrian. Fossil graptolites and ''Rhabdopleura'' share a colony structure of interconnected zooids housed in organic tubes (theca) which have a basic structure of stacked half-rings (fuselli). Most extinct graptolites belong to two major orders: the bush-like sessile Dendroidea and the planktonic, free-floating Graptoloidea. These orders most likely evolved from encrusting pterobranchs similar to ''Rhabdopleura''. Due to their widespread abundance, plantkonic l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Evolution
Parallel evolution is the similar development of a trait in distinct species that are not closely related, but share a similar original trait in response to similar evolutionary pressure.Zhang, J. and Kumar, S. 1997Detection of convergent and parallel evolution at the amino acid sequence level. ''Mol. Biol. Evol.'' 14, 527-36. Parallel vs. convergent evolution Given a particular trait that occurs in each of two lineages descended from a specified ancestor, it is possible in theory to define parallel and convergent evolutionary trends strictly, and distinguish them clearly from one another. However the criteria for defining convergent as opposed to parallel evolution often are unclear in practice, so that arbitrary diagnosis is common in some cases. When two species are similar in a particular character, evolution is defined as parallel if the ancestors shared that similarity; if they did not, the evolution of that character in those species is defined as convergent. However, thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystisoma
''Cystisoma '' is a genus of amphipod. It is the only member of the family Cystisomatidae within the Hyperiidea. The genus is noted for its nearly completely transparent body, adapted for life in low light waters. Description Gallery ''Cystisoma'' are characterized by unpigmented, transparent bodies which render them essentially invisible in water unless under precisely angled lighting. Only their eyes are pigmented. There is only a single pair of eyes which are large and directed upwards, being spread into a thin sheet on the upper surface of the head. This is likely an adaption of life in the ocean depths, where the only major light source is from above. Marine biologists at Duke University and the Smithsonian analyzed the crustacean's shell and discovered that it was covered in microscopic spheres that significantly reduce reflected light, thus giving the organism an antireflective coating. The spheres are believed to be bacteria due to their morphology and method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphipod
Amphipoda is an order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 9,900 amphipod species so far described. They are mostly marine animals, but are found in almost all aquatic environments. Some 1,900 species live in fresh water, and the order also includes the terrestrial sandhoppers such as ''Talitrus saltator''. Etymology and names The name ''Amphipoda'' comes, via New Latin ', from the Greek roots 'on both/all sides' and 'foot'. This contrasts with the related Isopoda, which have a single kind of thoracic leg. Particularly among anglers, amphipods are known as ''freshwater shrimp'', ''scuds'', or ''sideswimmers''. Description Anatomy The body of an amphipod is divided into 13 segments, which can be grouped into a head, a thorax and an abdomen. The head is fused to the thorax, and bears two pairs of antennae and one pair of se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |