|
Presenter First (software Approach)
Presenter first is a software development approach that combines the ideas of the model–view–presenter (MVP) design pattern, test-driven development, and feature-driven development. Approach Presenter first concentrates on transforming each of a customer's requirements into a well tested, working feature as quickly and with as much correlation to the customer's story language (requirement) as possible. The language of the story or requirement is used to directly guide development of the feature – even naming the modules and function calls. As a consequence, the feature implementation tends to closely represent the customer's desire with little extraneous or unneeded functionality. The language of the source code also corresponds closely to the customer's stories. Presenter first is often applied in graphical user interface applications. It is equally well applied to the development of command-line interfaces. Further, a slight variation of the approach has been used effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model–view–presenter
Model–view–presenter (MVP) is a derivation of the model–view–controller (MVC) architectural pattern, and is used mostly for building user interfaces. In MVP, the ''presenter'' assumes the functionality of the "middle-man". In MVP, all presentation logic is pushed to the presenter. History The model–view–presenter software pattern originated in the early 1990s at Taligent, a joint venture of Apple, IBM, and Hewlett-Packard. MVP is the underlying programming model for application development in Taligent's C++-based CommonPoint environment. The pattern was later migrated by Taligent to Java and popularized in a paper by Taligent CTO Mike Potel. After Taligent's discontinuation in 1998, Andy Bower and Blair McGlashan of Dolphin Smalltalk adapted the MVP pattern to form the basis for their Smalltalk user interface framework. In 2006, Microsoft began incorporating MVP into its documentation and examples for user interface programming in the .NET Framework. The evoluti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
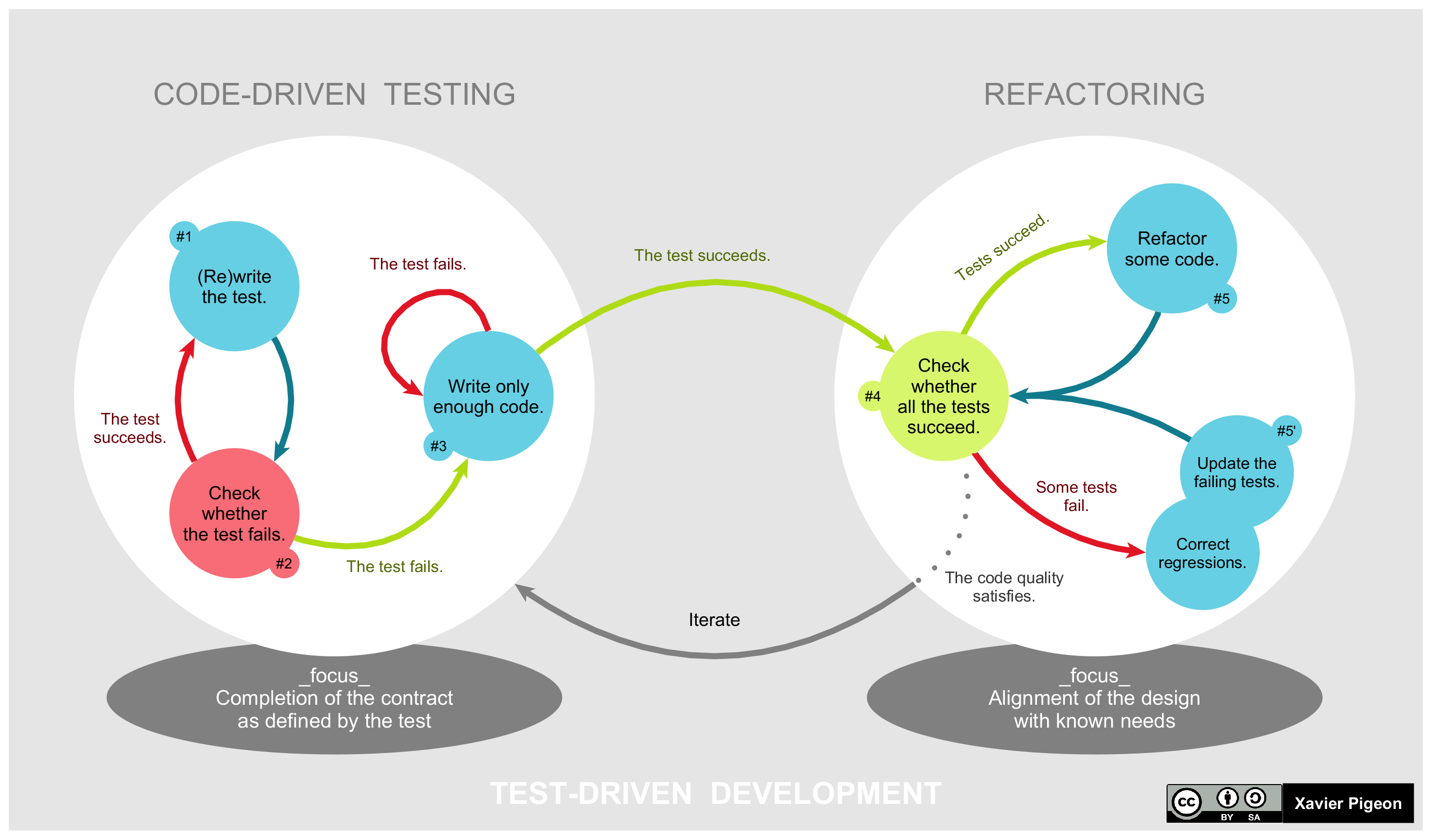
Test-driven Development
Test-driven development (TDD) is a way of writing source code, code that involves writing an test automation, automated unit testing, unit-level test case that fails, then writing just enough code to make the test pass, then refactoring both the test code and the production code, then repeating with another new test case. Alternative approaches to writing automated tests is to write all of the production code before starting on the test code or to write all of the test code before starting on the production code. With TsDD, both are written together, therefore shortening debugging time necessities. TDD is related to the test-first programming concepts of extreme programming, begun in 1999, but more recently has created more general interest in its own right.Newkirk, JW and Vorontsov, AA. ''Test-Driven Development in Microsoft .NET'', Microsoft Press, 2004. Programmers also apply the concept to improving and software bug, debugging legacy code developed with older techniques.Feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feature-driven Development
Feature-driven development (FDD) is an iterative and incremental software development process. It is a lightweight or agile method for developing software. FDD blends several best practices into a cohesive whole. These practices are driven from the perspective of delivering functionality ( features) valued by the client. Its main purpose is to deliver tangible, working software repeatedly in a timely manner in accordance with the Principles behind the agile manifesto. History FDD was initially devised by Jeff De Luca to meet the specific needs of a 15-month, 50-person software development project at a large Singapore bank in 1997. This resulted in a set of five processes that covered the development of an overall model and the listing, planning, design, and building of features. The first process is heavily influenced by Peter Coad's approach to object modeling. The second process incorporates Coad's ideas of using a feature list to manage functional requirements and develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User Story
In software development and product management, a user story is an informal, natural language description of features of a software system. They are written from the perspective of an end user or user of a system, and may be recorded on index cards, Post-it notes, or digitally in specific management software. Depending on the product, user stories may be written by different stakeholders like client, user, manager, or development team. User stories are a type of boundary object. They facilitate sensemaking and communication; and may help software teams document their understanding of the system and its context. History * 1997: Kent Beck introduces user stories at the Chrysler C3 project in Detroit. * 1998: Alistair Cockburn visited the C3 project and coined the phrase "A user story is a promise for a conversation." * 1999: Kent Beck published the first edition of the book ''Extreme Programming Explained'', introducing Extreme Programming (XP), and the usage of user stori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical User Interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based user interface, text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation interface, direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and Distributed control system, industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower-displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embedded Software
Embedded software is computer software, written to control machines or devices that are not typically thought of as computers, commonly known as embedded systems. It is typically specialized for the particular hardware that it runs on and has time and memory constraints. This term is sometimes used interchangeably with firmware. A precise and stable characteristic feature is that no or not all functions of embedded software are initiated/controlled via a human interface, but through machine-interfaces instead. Manufacturers build embedded software into the electronics of cars, telephones, modems, robots, appliances, toys, security systems, pacemakers, televisions and set-top boxes, and digital watches, for example. This software can be very simple, such as lighting controls running on an 8-bit microcontroller with a few kilobytes of memory with the suitable level of processing complexity determined with a Probably Approximately Correct Computation framework (a methodology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Testing
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior. Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the Integration testing, integration or System testing, system level. History Unit testing, as a principle for testing separately smaller parts of large software systems, dates back to the early days of software engineering. In June 1956 at US Navy's Symposium on Advanced Programming Methods for Digital Computers, H.D. Benington presented the Semi-Automatic Ground Environment, SAGE project. It featured a specification-based approach where the coding phase was followed by "parameter testing" to validate component subprograms against their specification, followed then by an "assembly testing" for parts put together. In 1964, a similar approach is described for the software of the Project Mercury, Mercury project, where individual units developed by dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of GUI Testing Tools
GUI testing tools serve the purpose of automating the testing process of software with graphical user interfaces. References {{Software testing GUI Software comparisons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mock Object
In computer science, a mock object is an object that imitates a production object in limited ways. A programmer might use a mock object as a test double for software testing. A mock object can also be used in generic programming. Analogy A mock object can be useful to the software tester like a car designer uses a crash test dummy to simulate a human in a vehicle impact. Motivation In a unit test, mock objects can simulate the behavior of complex, real objects and are therefore useful when a real object is impractical or impossible to incorporate into a unit test. If an object has any of the following characteristics, it may be useful to use a mock object in its place: * it supplies non-deterministic results (e.g. the current time or the current temperature) * it has states that are difficult to create or reproduce (e.g. a network error) * it is slow (e.g. a complete database, which would have to be prepared before the test) * it does not yet exist or may change behavior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agile Software Development
Agile software development is an umbrella term for approaches to software development, developing software that reflect the values and principles agreed upon by ''The Agile Alliance'', a group of 17 software practitioners, in 2001. As documented in their ''Manifesto for Agile Software Development'' the practitioners value: * Individuals and interactions over processes and tools * Working software over comprehensive documentation * Customer collaboration over contract negotiation * Responding to change over following a plan The practitioners cite inspiration from new practices at the time including extreme programming, Scrum (software development), scrum, dynamic systems development method, adaptive software development and being sympathetic to the need for an alternative to documentation driven, heavyweight software development processes. Many software development practices emerged from the agile mindset. These agile-based practices, sometimes called ''Agile'' (with a capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Architecture
Software architecture is the set of structures needed to reason about a software system and the discipline of creating such structures and systems. Each structure comprises software elements, relations among them, and properties of both elements and relations. The ''architecture'' of a software system is a metaphor, analogous to the architecture of a building. It functions as the blueprints for the system and the development project, which project management can later use to extrapolate the tasks necessary to be executed by the teams and people involved. Software architecture is about making fundamental structural choices that are costly to change once implemented. Software architecture choices include specific structural options from possibilities in Software design, the design of the software. There are two fundamental laws in software architecture: # Everything is a trade-off # "Why is more important than how" "Architectural Kata" is a teamwork which can be used to produce an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |