|
Precordillera Terrane
The Precordillera Terrane or Cuyania was an ancient microcontinent or terrane whose history affected many of the older rocks of Cuyo in Argentina. It was separated by oceanic crust from the Chilenia terrane which accreted into it at ~420-390 Ma when Cuyania was already amalgamated with Gondwana. The hypothesized Mejillonia Terrane in the coast of northern Chile is considered by some geologists to be a single block with Cuyania. The San Rafael Block crops out 200 km to the south of the other exposures of Cuyania and is the southern extension of the terrane. The Precordillera has been hypothesised to have been derived from Laurentia, the core of North America, which was attached to the western margin of South America during the Precambrian when virtually all continents formed a "proto- Gondwana" supercontinent known as Pannotia. The Precordillera was then part of a proposed "Texas Plateau", a promontory attached to Laurentia similar to the way the Falkland Plateau is attach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcontinent
Continental crustal fragments, partly synonymous with microcontinents, are pieces of continents that have broken off from main continental masses to form distinct islands that are often several hundred kilometers from their place of origin. Causes Continental fragments and microcontinent crustal compositions are very similar to those of regular continental crust. The rifting process that caused the continental fragments to form most likely impacts their layers and overall thickness along with the addition of mafic intrusions to the crust. Studies have determined that the average crustal thickness of continental fragments is approximately . The sedimentary layer of continental fragments can be up to thick and can overlay two to three crustal layers. Continental fragments have an average crustal density of which is very similar to that of typical continental crust. Strike-slip fault zones cause the fragmentation of microcontinents. The zones link the extensional zones where co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
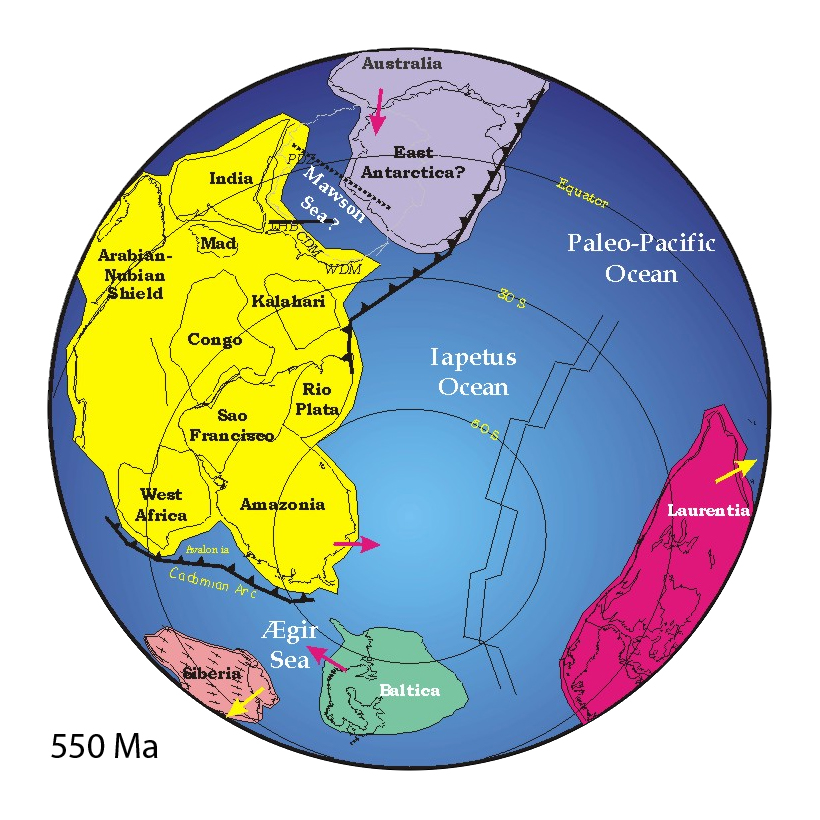
Pannotia
Pannotia (from Greek: '' pan-'', "all", '' -nótos'', "south"; meaning "all southern land"), also known as the Vendian supercontinent, Greater Gondwana, and the Pan-African supercontinent, was a relatively short-lived Neoproterozoic supercontinent that formed at the end of the Precambrian during the Pan-African orogeny (650–500 Ma), during the Cryogenian period and broke apart 560 Ma with the opening of the Iapetus Ocean, in the late Ediacaran and early Cambrian. Pannotia formed when Laurentia was located adjacent to the two major South American cratons, Amazonia and Río de la Plata. The opening of the Iapetus Ocean separated Laurentia from Baltica, Amazonia, and Río de la Plata. In 2022 the whole concept of Pannotia has been put into question by scientists who argue its existence is not supported by geochronology, "the supposed landmass had begun to break up well before it was fully assembled". Origin of concept J. D. A. Piper was probably the first to propose a Proterozoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Continents
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Argentina
The geology of Argentina includes ancient Precambrian basement rock affected by the Grenville orogeny, sediment filled basins from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic as well as newly uplifted areas in the Andes. Geologic history, stratigraphy and tectonics The oldest rocks in Argentina date to the Precambrian. Strontium, oxygen and carbon isotope data from carbonate rocks in the Sierra de Pie de Palo are part of an ophiolite unit related to the Grenville orogeny, formed as cover rock in the Appalachian margin of the continent Laurentia around 720 million years ago. These Neoproterozoic age rocks are believed to have formed above much older Archean craton rock. Throughout the late Proterozoic, sections of Argentina were part of a metamorphic mobile belt adjacent to the Brazilian Shield. Regional metamorphism produced scheelite belts and wolframite in parts of San Luis and Cordoba Provinces. To the north, along the Bolivian border in the Altiplano, drilling has revealed Precambrian Hornblend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Chile
The geology of Chile is a characterized by processes linked to subduction such as volcanism, earthquakes and orogeny. The terrane, buildings blocks of Chile's geology accretion (geology), assembled during the Paleozoic, Paleozoic Era. Chile was by then the southwestern margin of the supercontinent Gondwana. In the Jurassic Gondwana began to split and the ongoing period of crustal deformation and mountain building known as the Andean orogeny began. In the Cenozoic, Late Cenozoic Chile definitely separated from Antarctica, the Andes experienced a great rise accomplained by a cooling climate and the onset of glaciations. The subduction interactions shaped four main wikt:morphostructure, morphostructures of Chile: the Andes; the Chilean Central Valley, Intermediate Depression, the Chilean Coast Range, Coast Range, and the Peru–Chile Trench off the coast. Since Chile is on an active continental margin, it has many volcanoes. Almost the entire country is subject to earthquakes arising ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological History Of The Precordillera Terrane
The Precordillera terrane of western Argentina is a large mountain range located southeast of the main Andes mountain range. The evolution of the Precordillera is noted for its unique formation history compared to the region nearby. The Cambrian- Ordovian sedimentology in the Precordillera terrane has its source neither from old Andes nor nearby country rock, but shares similar characteristics with the Grenville orogeny of eastern North America. This indicates a rift-drift history of the Precordillera in the early Paleozoic. The Precordillera is a moving micro-continent which started from the southeast part of the ancient continent Laurentia (current location: North American plate). The separation of the Precordillera (also named Cuyania) started around the early Cambrian. The mass collided with Gondwana (the ancient supercontinent in the southern hemisphere) around Late Ordovician period. Different models and thinking of rift-drift process and the time of occurrence have been pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Famatinian Orogeny
The Famatinian orogeny ( es, Orogenia de Famatina) is an orogeny that predates the rise of the Andes and that took place in what is now western South America during the Paleozoic, leading to the formation of the Famatinian orogen also known as the Famatinian belt. The Famatinian orogeny lasted from the Late Cambrian to at least the Late Devonian and possibly the Early Carboniferous, with orogenic activity peaking about 490 to 460 million years ago. The orogeny involved metamorphism and deformation in the crust and the eruption and intrusion of magma along a Famatinian magmatic arc that formed a chain of volcanoes. The igneous rocks of the Famatinian magmatic arc are of calc-alkaline character and include gabbros, tonalites and granodiorites. The youngest igneous rocks of the arc are granites. The relationship of the orogeny with the Achala and Cerro Aspero batholiths of central Argentina is not fully understood. These Devonian batholiths are possibly of post-orogenic chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taconic Orogeny
The Taconic orogeny was a mountain building period that ended 440 million years ago and affected most of modern-day New England. A great mountain chain formed from eastern Canada down through what is now the Piedmont of the East coast of the United States. As the mountain chain eroded in the Silurian and Devonian periods, sediments from the mountain chain spread throughout the present-day Appalachians and midcontinental North America. New England and Canada Beginning in Cambrian time, about 550 million years ago, the Iapetus Ocean began to close. The weight of accumulating sediments, in addition to compressional forces in the crust, forced the eastern edge of the North American continent to fold gradually downward. In this manner, shallow-water carbonate deposition that had persisted on the continental shelf margin through Late Cambrian into Early Ordovician time, gave way to fine-grained clastic deposition and deeper water conditions during the Middle Ordovician. In this period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falkland Plateau
Falkland may refer to: * Falkland, British Columbia, a community in Canada * Falkland, Nova Scotia, a community in Canada * Falkland Islands, an archipelago in the south Atlantic Ocean * Falkland, Fife, a former burgh in Fife, Scotland ** Falkland Palace, royal residence of the Kings of Scots in Falkland, Fife, Scotland ** Viscount Falkland, a Scottish peerage title, named after Falkland, Fife, Scotland * Falkland, North Carolina, a town in the United States * Falkland (Redd Shop, Virginia), U.S., a historic plantation house See also * Falkland Ridge, Nova Scotia, a community in Canada * Falkland Sound, a strait separating West Falkland and East Falkland * South Falkland, an English colony on Newfoundland * * * Folkland (other) * Malvinas (other) * Malvina (other) Malvina is a feminine given name derived from the Gaelic, invented by the Scottish poet James Macpherson. Malvina may also refer to: * Malvina, Mississippi * ''Malvina'', an opera by Nico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, although originally it also included the cratonic areas of Greenland and also the northwestern part of Scotland, known as the Hebridean Terrane. During other times in its past, Laurentia has been part of larger continents and supercontinents and itself consists of many smaller terranes assembled on a network of Early Proterozoic orogenic belts. Small microcontinents and oceanic islands collided with and sutured onto the ever-growing Laurentia, and together formed the stable Precambrian craton seen today. The craton is named after the Laurentian Shield, through the Laurentian Mountains, which received their name from the Saint Lawrence River, named after Lawrence of Rome. Interior platform In eastern and central Canada, much of the stable craton is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own distinctive geologic history, which is different from that of the surrounding areas—hence the term "exotic" terrane. The suture zone between a terrane and the crust it attaches to is usually identifiable as a fault. A sedimentary deposit that buries the contact of the terrane with adjacent rock is called an overlap formation. An igneous intrusion that has intruded and obscured the contact of a terrane with adjacent rock is called a stitching pluton. Older usage of ''terrane'' simply described a series of related rock formations or an area having a preponderance of a particular rock or rock groups. Overview A tectonostratigraphic terrane is not necessarily an independent microplate in origin, since it may not contain the full thickness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Rafael Block
The San Rafael Block or San Rafael Massif (Spanish: ''Bloque de San Rafael'' or ''Macizo de San Rafael'') is an uplifted area in central Mendoza Province, Argentina. The San Rafael Block is both a geographic and a tectonic unit. From a tectonostratigraphic view, some geologists consider it an exposure of the Cuyania (Precordillera) terrane being its southern extension. The San Rafael Block crops out to the south of the other exposures of Cuyania. The San Rafael Block forms the northeastern boundary of the Neuquén Basin. See also * North Patagonian Massif The North Patagonian Massif or Somún Cura Massif (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Macizo Norpatagónico'', ''Macizo Nordpatagónico'' or ''Macizo de Somún Cura'') is a massif in northern Patagonia located in the Argentine provinces of Río Negro Pro ... * Reserva Provincial La Payunia * San Rafael orogeny References {{reflist Geology of Mendoza Province Geography of Mendoza Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)