|
PreQ1-II Riboswitch
PreQ1-II riboswitches form a class of riboswitches that specifically bind pre-queuosine1 (PreQ1), a precursor of the modified nucleoside queuosine. They are found in certain species of ''Streptococcus'' and ''Lactococcus'', and were originally identified as a conserved RNA secondary structure called the "COG4708 motif". All known members of this riboswitch class appear to control members of COG4708 genes. These genes are predicted to encode membrane-bound proteins and have been proposed to be a transporter of preQ1, or a related metabolite, based on their association with preQ1-binding riboswitches. PreQ1-II riboswitches have no apparent similarities in sequence or structure to preQ1-I riboswitches, a previously discovered class of preQ1-binding riboswitches. PreQ1 thus joins S-adenosylmethionine ''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional conformational isomerism, form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein protein folding, folds into its three dimensional protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the Amine, amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone chain, backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone Dihedral angle#Dihedral angles of proteins, dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Conservation
In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar sequences in nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) or proteins across species ( orthologous sequences), or within a genome ( paralogous sequences), or between donor and receptor taxa ( xenologous sequences). Conservation indicates that a sequence has been maintained by natural selection. A highly conserved sequence is one that has remained relatively unchanged far back up the phylogenetic tree, and hence far back in geological time. Examples of highly conserved sequences include the RNA components of ribosomes present in all domains of life, the homeobox sequences widespread amongst Eukaryotes, and the tmRNA in Bacteria. The study of sequence conservation overlaps with the fields of genomics, proteomics, evolutionary biology, phylogenetics, bioinformatics and mathematics. History The discovery of the role of DNA in heredity, and observations by Frederick Sanger of variation between animal insulins in 1949, promp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-regulatory Element
''Cis''-regulatory elements (CREs) or ''Cis''-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogenesis, the development of anatomy, and other aspects of embryonic development, studied in evolutionary developmental biology. CREs are found in the vicinity of the genes that they regulate. CREs typically regulate gene transcription by binding to transcription factors. A single transcription factor may bind to many CREs, and hence control the expression of many genes ( pleiotropy). The Latin prefix ''cis'' means "on this side", i.e. on the same molecule of DNA as the gene(s) to be transcribed. CRMs are stretches of DNA, usually 100–1000 DNA base pairs in length, where a number of transcription factors can bind and regulate expression of nearby genes and regulate their transcription rates. They are labeled as ''cis'' because they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riboswitch
In molecular biology, a riboswitch is a regulatory segment of a messenger RNA molecule that binds a small molecule, resulting in a change in production of the proteins encoded by the mRNA. Thus, an mRNA that contains a riboswitch is directly involved in regulating its own activity, in response to the concentrations of its effector molecule. The discovery that modern organisms use RNA to bind small molecules, and discriminate against closely related analogs, expanded the known natural capabilities of RNA beyond its ability to code for proteins, catalyze reactions, or to bind other RNA or protein macromolecules. The original definition of the term "riboswitch" specified that they directly sense small-molecule metabolite concentrations. Although this definition remains in common use, some biologists have used a broader definition that includes other cis-regulatory RNAs. However, this article will discuss only metabolite-binding riboswitches. Most known riboswitches occur in bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queuosine
Queuosine is a modified nucleoside that is present in certain tRNAs in bacteria and eukaryotes. It contains the nucleobase queuine. Originally identified in ''Escherichia coli, E. coli'', queuosine was found to occupy the first anticodon position of tRNAs for histidine, aspartic acid, asparagine and tyrosine. The first anticodon position pairs with the third "wobble base pair, wobble" position in codons, and queuosine improves accuracy of Translation (biology), translation compared to guanosine. Synthesis of queuosine begins with guanosine triphosphate, GTP. In bacteria, three structurally unrelated classes of riboswitch are known to regulate genes that are involved in the synthesis or transport of pre-queuosine1, a precursor to queuosine: PreQ1 riboswitch, PreQ1-I riboswitches, PreQ1-II riboswitches and PreQ1-III riboswitches. Queuosine biosynthesis genes have also been found on phage genomes and may be involved in protection from genome degradation by the host. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive ' (plural ) or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a single axis, so as they grow, they tend to form pairs or chains that may appear bent or twisted. This differs from staphylococci, which divide along multiple axes, thereby generating irregular, grape-like clusters of cells. Most streptococci are oxidase-negative and catalase-negative, and many are facultative anaerobes (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically). The term was coined in 1877 by Viennese surgeon Albert Theodor Billroth (1829–1894), by combining the prefix "strepto-" (from ), together with the suffix "-coccus" (from Modern , from .) In 1984, many bacteria formerly grouped in the genus ''Streptococcus'' were separated out into the genera ''Enterococcus'' and ''Lactococcus''. Currently, over 50 species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactococcus
''Lactococcus'' is a genus of lactic acid bacteria that were formerly included in the genus ''Streptococcus'' Group N1. They are known as homofermenters meaning that they produce a single product, lactic acid in this case, as the major or only product of glucose fermentation. Their homofermentative character can be altered by adjusting environmental conditions such as pH, glucose concentration, and nutrient limitation. They are gram-positive, catalase-negative, non-motile cocci that are found singly, in pairs, or in chains. The genus contains strains known to grow at or below 7˚C. Twelve species of ''Lactococcus'' are currently recognized. They are: *''Lactococcus chungangensis'' *''Lactococcus formosensis'' *''Lactococcus fujiensis'' *''Lactococcus garvieae'' **''L. garvieae subsp. garvieae **''L. garvieae subsp. bovis *''Lactococcus hircilactis'' *''Lactococcus lactis'' **''L. lactis'' subsp. ''cremoris'' **''L. lactis'' subsp. ''hordniae'' **''L. lactis'' subsp. ''lactis'' ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PreQ1 Riboswitch
The PreQ1-I riboswitch is a cis-acting element identified in bacteria which regulates expression of genes involved in biosynthesis of the nucleoside queuosine (Q) from Guanosine triphosphate, GTP. PreQ1 (pre-queuosine1) is an intermediate in the queuosine pathway, and preQ1 riboswitch, as a type of riboswitch, is an RNA element that binds preQ1. The preQ1 riboswitch is distinguished by its unusually small aptamer, compared to other riboswitches. Its atomic-resolution three-dimensional structure has been determined, with thPDB ID 2L1V PreQ1 classification Three subcategories of the PreQ1 riboswitch exist: preQ1-I, preQ1-II, and preQ1-III. PreQ1-I has a distinctly small aptamer, ranging from 25 to 45 nucleotides long, compared to the structures of PreQ1-II riboswitch, PreQ1-II riboswitch and PreQ1-III riboswitch, preQ1-III riboswitch. PreQ1-II riboswitch, only found in ''Lactobacillales'', has a larger and more complex consensus sequence and structure than preQ1-I riboswitch, with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
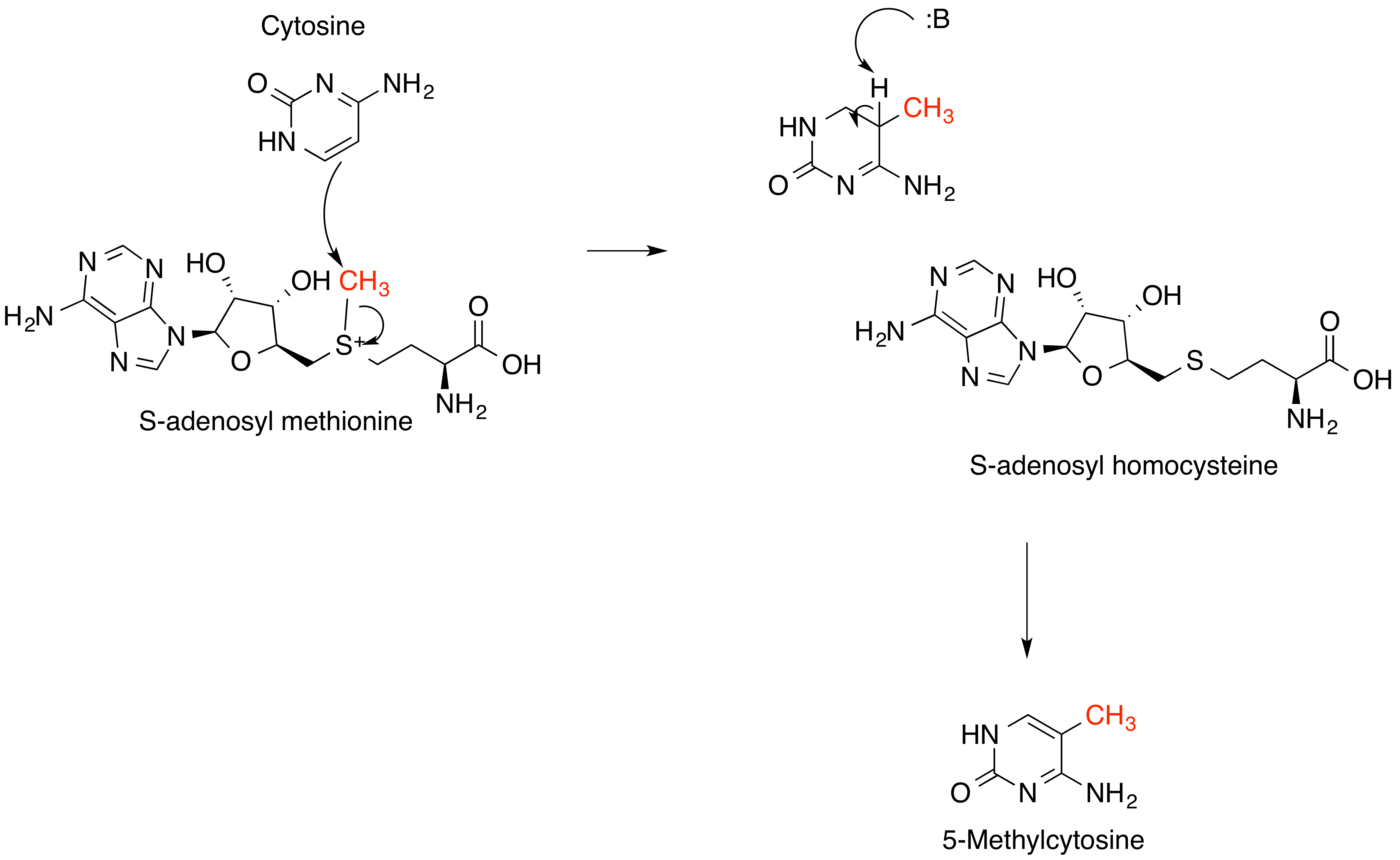
S-adenosylmethionine
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952. In bacteria, SAM is bound by the SAM riboswitch, which regulates genes involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis. In eukaryotic cells, SAM serves as a regulator of a variety of processes including DNA, tRNA, and rRNA methylation; immune response; amino acid metabolism; transsulfuration; and more. In plants, SAM is crucial to the biosynthesis of ethylene, an important plant hormone and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-regulatory RNA Elements
''Cis-acting replication elements'' bring together the 5′ and 3′ ends during replication of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses (for example Picornavirus, Flavivirus, coronavirus, togaviruses, Hepatitis C virus) and double-stranded RNA viruses (for example rotavirus and reovirus). See also *Cis-regulatory element *List of cis-regulatory RNA elements *Enterovirus cis-acting replication element and Enterovirus 5′ cloverleaf cis-acting replication element *Cardiovirus cis-acting replication element (CRE) *Coronavirus SL-III cis-acting replication element (CRE) *Rotavirus cis-acting replication element *Hepatitis C virus cis-acting replication element *Flavivirus 3′ UTR cis-acting replication element (CRE) *Potato virus X cis-acting regulatory element *Human rhinovirus internal cis-acting regulatory element (CRE) Human rhinovirus internal cis-acting regulatory element (CRE) is a CRE from the human rhinoviruses. The CRE is located within the genome segment encoding the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)