|
Portuguese Indian Rupia
The rupia was the currency of Portuguese India sometime after 1668 until 1958. Prior to 1668, the currency unit was ''Xerafim'' (''xerafin'', ''xeraphin''). In 1666, the Portuguese administration struck a silver coin calling it double ''xerafin'' and this was declared equal to a rupia in circulation in India outside of Portuguese possessions. A ''xerafim'' was a convertible subunit of ''rupia'', and it was unique to Portuguese colonies in India. One rupia equalled two xerafims. In decades that followed, the double ''xerafin'' came to be known in Goa and other Portuguese Indian territories simply as rupia (or Portuguese Indian rupia) was subdivided into units such as ''reis'' (''real'') and ''pardao'' that mirrored the currency terms introduced by Portuguese officials in other colonies worldwide. History Before 1871, the rupia was subdivided into 750 ''bazarucos'', 600 ''réis'' (singular: ''real''), 20 ''pardaus'' or 10 ''tangas''. A rupia equaled two ''xerafims''. After 1871, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Issuing Authority
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the currency and monetary policy of a country or monetary union, and oversees their commercial banking system. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the monetary base. Most central banks also have supervisory and regulatory powers to ensure the stability of member institutions, to prevent bank runs, and to discourage reckless or fraudulent behavior by member banks. Central banks in most developed nations are institutionally independent from political interference. Still, limited control by the executive and legislative bodies exists. Activities of central banks Functions of a central bank usually include: * Monetary policy: by setting the official interest rate and controlling the money supply; *Financial stability: acting as a government's banker and as the bankers' bank ("lender of last resort"); * Reserve management: managing a country's fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic History Of Portugal
The economic history of Portugal covers the development of the economy throughout the course of Portuguese history. It has its roots prior to nationality, when Roman occupation developed a thriving economy in Hispania, in the provinces of Lusitania and Gallaecia, as producers and exporters to the Roman Empire. This continued under the Visigoths and then Al-Andalus Moorish rule, until the Kingdom of Portugal was established in 1139. With the end of Portuguese reconquista and integration in the European Middle Age economy, the Portuguese were at the forefront of maritime exploration of the age of discovery, expanding to become the first global empire. Portugal then became the world's main economic power during the Renaissance, introducing most of Africa and the East to European society, and establishing a multi-continental trading system extending from Japan to Brazil. In 1822, Portugal lost its main overseas territory, Brazil. The transition from absolutism to a parliamenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Currencies Of India
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Obsolete Currencies
Modern may refer to: History * Modern history ** Early Modern period ** Late Modern period *** 18th century *** 19th century *** 20th century ** Contemporary history * Moderns, a faction of Freemasonry that existed in the 18th century Philosophy and sociology * Modernity, a loosely defined concept delineating a number of societal, economic and ideological features that contrast with "pre-modern" times or societies ** Late modernity Art * Modernism ** Modernist poetry * Modern art, a form of art * Modern dance, a dance form developed in the early 20th century * Modern architecture, a broad movement and period in architectural history * Modern music (other) Geography *Modra, a Slovak city, referred to in the German language as "Modern" Typography * Modern (typeface), a raster font packaged with Windows XP * Another name for the typeface classification known as Didone (typography) * Modern, a generic font family name for fixed-pitch serif and sans serif fonts (f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Rupia
A port is a maritime law, maritime facility comprising one or more Wharf, wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge Affreightment, cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Port of Hamburg, Hamburg, Port of Manchester, Manchester and Duluth; these access the sea via rivers or canals. Because of their roles as port of entry, ports of entry for immigrants as well as soldiers in wartime, many port cities have experienced dramatic multi-ethnic and multicultural changes throughout their histories. Ports are extremely important to the global economy; 70% of global merchandise trade by value passes through a port. For this reason, ports are also often densely populated settlements that provide the labor for processing and handling goods and related services for the ports. Today by far the greatest growth in port development is in Asia, the continent with some of the World's busiest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental ( native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gold is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to organolead compounds. Like the lighter members of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diu, India
Diu (), also known as ''Dio'' in Indo-Portuguese, is a town in Diu district in the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, India. Diu District is the tenth least populated district of India. The town of Diu lies at the eastern end of Diu Island and is known for its fortress and old Portuguese cathedral. It is a fishing town. The city is one of the hundred Indian cities competing in a national level competition to get funds under Narendra Modi's flagship Smart Cities Mission. Diu will be competing for one of the last 10 spots against 20 cities from across India. In April 2018, it was reported that the Diu Smart City has already become India's first city to run on 100 percent renewable energy during the daytime. History The town and district were historically part of the Saurashtra region of Gujarat and an important port on trade routes of Arabian sea of Indian Ocean. Due to its strategic importance, there was a Battle of Diu in 1509 between Portugal an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banco Nacional Ultramarino
Banco Nacional Ultramarino (, BNU; ; en, National Overseas Bank) is a Macau banking and financial services corporation. It was a Portuguese bank with operations throughout the world, especially in Portugal's former overseas provinces. It ceased existence as an independent legal entity in Portugal following its merger in 2001 with Caixa Geral de Depósitos, the government-owned savings bank. The bank continues operations today under the Banco Nacional Ultramarino brand in Macau, a Chinese Special Administrative Region and former Portuguese colony, where it is also licensed to issue Macanese pataca banknotes. Timeline Banco Nacional Ultramarino (BNU) was established in Lisbon, Portugal, in 1864 as a bank of issue for Portuguese overseas territories. the next year it opened branches in Luanda, Angola and Praia, Cabo Verde. Three years after that, in 1868, BNU opened branches in São Tomé and Príncipe, Goa, and Lourenço Marques, Mozambique. In 1901 BNU lost its banking mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
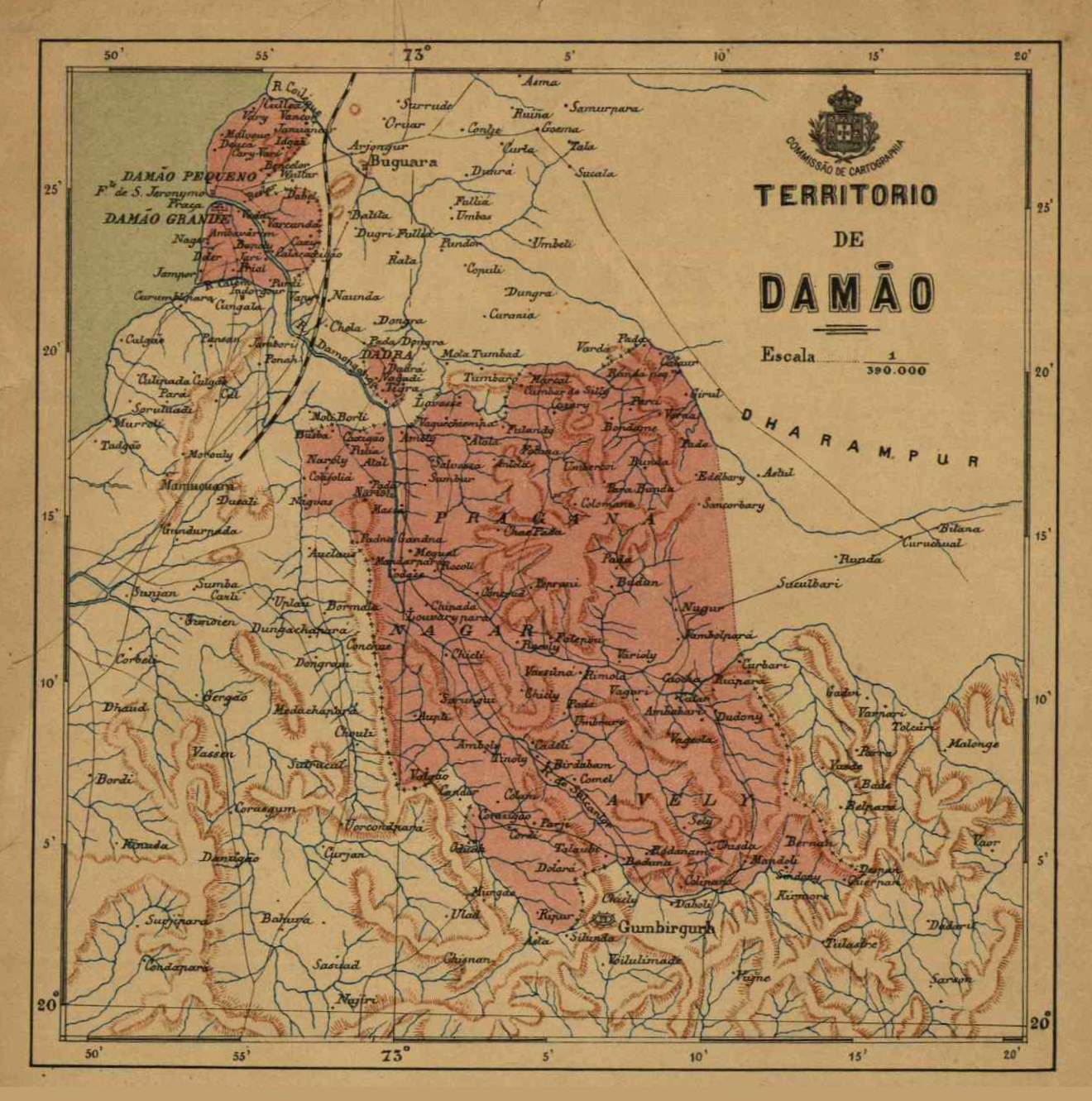
Daman District, India
Daman is one of the three districts of the Indian union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu on the western coast of India, surrounded by Valsad district of Gujarat state on the north, east and south and the Arabian Sea to the west. The district has an area of , and a population of 191,173 at the 2011 census, an increase of 69.256% from the preceding 2001 Census. The district headquarters is Daman. The previous territorial headquarters were in Panjim when it was jointly administered as Goa, Damaon and Diu, until the time of the Goan Opinion Poll. Daman lies at the mouth of the Daman Ganga River. Major industries have units here. The closest railway station is Vapi (7 km). It is also famous for its beach, Portuguese colonial architecture, churches, and for the scenic beauty in the twin towns of Nani-Daman and Moti-Daman, which lie opposite each other across the Daman Ganga. The city of Surat lies to the north, and Mumbai lies approximately 160 km (10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)