|
Portland Company
The Portland Company was established 10 November 1846 by John A. Poor and Norris Locomotive Works engineer Septimus Norris as a locomotive foundry to build railroad equipment for the adjacent Portland terminus of the Atlantic and St. Lawrence Railroad connection between Portland, Maine and Montreal. The shops opened for business in October, 1847. Its first locomotive, the Augusta, emerged from the shops in July 1848 for delivery to the Portland, Saco & Portsmouth (later part of the Boston and Maine Railroad). Over the next several decades, the Company produced in its Fore Street facilities over 600 steam locomotives as well as 160 merchant and naval vessels, railcars, construction equipment, Knox automobiles, and the like. Portland Company built the engines of the civil war side-wheel gunboats and .Switzer, November 1964, p.85 Taking into account its other products, the Company could lay claim to being one of the leading medium-to-heavy steel manufacturers in New England. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John A
Sir John Alexander Macdonald (January 10 or 11, 1815 – June 6, 1891) was the first prime minister of Canada, serving from 1867 to 1873 and from 1878 to 1891. The dominant figure of Canadian Confederation, he had a political career that spanned almost half a century. Macdonald was born in Scotland; when he was a boy his family immigrated to Kingston in the Province of Upper Canada (today in eastern Ontario). As a lawyer, he was involved in several high-profile cases and quickly became prominent in Kingston, which elected him in 1844 to the legislature of the Province of Canada. By 1857, he had become premier under the colony's unstable political system. In 1864, when no party proved capable of governing for long, Macdonald agreed to a proposal from his political rival, George Brown, that the parties unite in a Great Coalition to seek federation and political reform. Macdonald was the leading figure in the subsequent discussions and conferences, which resulted in the Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
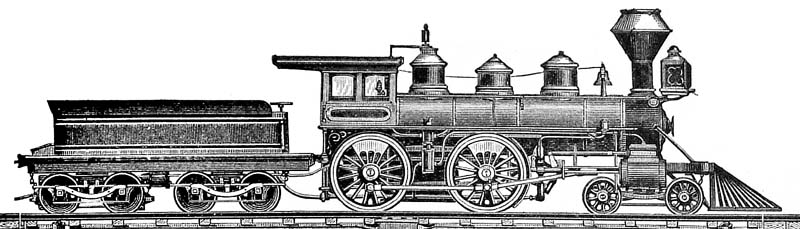
4-4-0
4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and a lack of trailing wheels. Due to the large number of the type that were produced and used in the United States, the 4-4-0 is most commonly known as the American type, but the type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, pp. 46-. Almost every major railroad that operated in North America in the first half of the 19th century owned and operated locomotives of this type. The first use of the name ''American'' to describe locomotives of this wheel arrangement was made by ''Railroad Gazette'' in April 1872. Prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiscasset And Quebec Railroad
Wiscasset is a town in and the seat of Lincoln County, Maine, United States. The municipality is located in the state of Maine's Mid Coast region. The population was 3,742 as of the 2020 census. Home to the Chewonki Foundation, Wiscasset is a tourist destination noted for early architecture. The town is home to the Red's Eats restaurant. History In 1605, Samuel de Champlain is said to have landed here and exchanged gifts with the Indians. Situated on the tidal Sheepscot River, Wiscasset was first settled by Europeans in 1660. The community was abandoned during the French and Indian Wars, and the King Philip's War in 1675 and then resettled around 1730. In 1760, it was incorporated as Pownalborough after Colonial Governor Thomas Pownall. In 1802, it resumed its original Abenaki name, Wiscasset, which means "coming out from the harbor but you don't see where." During the Revolutionary War, the British warship ''Rainbow'' harbored itself in Wiscasset Harbor and held the town a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridgton And Saco River Railroad
The Bridgton and Saco River Railroad (B&SR) was a narrow gauge railroad that operated in the vicinity of Bridgton and Harrison, Maine. It connected with the Portland and Ogdensburg Railroad (later Maine Central Railroad Mountain Division) from Portland, Maine, to St. Johnsbury, Vermont, near the town of Hiram on the Saco River. History B&SR design was based on experience of the Sandy River Railroad. Hinkley Locomotive Works modified their gauge Forney design to run boiler first with an extended frame similar to that installed on Sandy River Railroad #1 following a wreck in early 1882. The successful design of the Bridgton Hinkleys was subsequently repeated for the Monson Railroad and the Franklin and Megantic Railway. Construction began in 1882, and trains were running to Bridgton by early 1883. B&SR used early profits to replace wooden trestles with earthen fills. A granite masonry arch was constructed over Hancock Brook in 1895.''Railroad Commissioners' Report'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiscasset, Waterville And Farmington Railway
The Wiscasset, Waterville and Farmington Railway is a narrow gauge railway. The line was operated as a for-profit company from 1895 until 1933 between the Maine towns of Wiscasset, Albion, and Winslow, but was abandoned in 1936. Today, about of the track in the town of Alna has been rebuilt and is operated by the non-profit Wiscasset, Waterville and Farmington Railway Museum as a heritage railroad offering passenger excursion trains and hauling occasional cargo. History The line began operating to Weeks Mills on February 20, 1895, as the Wiscasset and Quebec Railroad. The line was reorganized in 1901 as the Wiscasset, Waterville and Farmington Railway following the inability to negotiate a crossing of the Belfast and Moosehead Lake Railroad near Burnham Junction. The reorganized WW&F completed a branch line from Weeks Mills to the Kennebec River at Winslow but failed to negotiate a connection with the Sandy River Railroad at Farmington, and therefore never reached Quebec. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandy River Railroad
The Sandy River Railroad was a narrow gauge railway built to serve the towns of Strong and Phillips in the Sandy River valley upstream of Farmington. The Sandy River Railroad was the first narrow gauge common carrier railroad built in the State of Maine. History The railroad was built from Farmington through Strong to Phillips in 1879 using rolling stock of the recently abandoned Billerica and Bedford Railroad. The original Billerica and Bedford equipment consisted of 2 locomotives, 6 flat cars, a baggage car, a coach, a combination car, and 2 box cars rebuilt from open excursion cars. In 1883 the railroad purchased 2 coaches from Laconia Car Company and a third locomotive in anticipation of additional traffic to be generated by the Franklin and Megantic Railroad (F&M) being built from Strong to Kingfield. In 1890 the railroad sold locomotive #2 to the Phillips and Rangeley Railroad (P&R) being built from Phillips to Rangeley, and purchased 2 new locomotives to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandy River And Rangeley Lakes Railroad
The Sandy River & Rangeley Lakes Railroad (SR&RL) was a narrow gauge common carrier railroad that operated approximately of track in Franklin County, Maine. Former equipment from the SR&RL continues to operate in the present day on a revived, short segment of the railway in Phillips, Maine. History Josiah L. Maxey, a Gardiner banker who had recently financed construction of the Kennebec Central Railroad, obtained legislative approval for consolidation of the Sandy River Railroad and Phillips & Rangeley Railroad (P&R) on 10 March 1891. Maxcy purchased controlling stock of the Sandy River Railroad in 1892, and then obtained controlling stock of the Franklin & Megantic Railway (F&M) in 1897. Under Maxey's direction, F&M purchased the Kingfield and Dead River Railway (K&DR) at auction on 2 August 1898; and the F&M, K&DR, and Sandy River railroads operated under common management until formally merged as the SR&RL in January 1908. Under Maxcy's direction, SR&RL purchased the Phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phillips And Rangeley Railroad
The Phillips and Rangeley Railroad was a narrow gauge common carrier railroad in the State of Maine. It connected the towns of Phillips and Rangeley and was built to serve the forestry and resort industries of Franklin County. This railroad pioneered the use of large gauge rolling stock in North America. Earlier freight cars built for the Billerica and Bedford Railroad, the Sandy River Railroad, the Bridgton and Saco River Railroad, the Monson Railroad, the Franklin and Megantic Railroad,''Railroad Commissioners' Report'' State of Maine 1908 p. 135 and the Kennebec Central Railroad had a maximum length of . Phillips and Rangeley Railroad ordered the first cars in 1890 and the subsidiary Eustis Railroad ordered the first cars in 1903. The Portland Company locomotive built in 1890 was 12.5% heavier than any previous gauge locomotive in Maine. The locomotive purchased from Baldwin Locomotive Works the following year was 28% heavier than the Portland locomotive; and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forney Locomotive
The Forney is a type of tank locomotive patented by Matthias N. Forney between 1861 and 1864 and used predominantly in the USA. Forney design Forney locomotives include the following characteristics: * An wheel arrangement, that is four driving wheels followed by a truck with four wheels (though the term has become somewhat generic; many small tank engines of various wheel arrangements have been called Forneys). * No flange on the second pair of driving wheels. * The fuel bunker and water tank placed over the four-wheel truck. History The locomotives were set up to run cab (or bunker) first, effectively as a (or ), though the type achieved popularity for its ability to operate well in either direction. The wheel arrangement, with its three-point suspension, was noted for its good tracking ability, while the flangeless middle wheels allowed the locomotive to round tight curves. Placing the fuel and water over the truck rather than the driving wheels meant the locos had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-4-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-4-4 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles. This type was only used for tank locomotives. In American cities, the type known as a ''Forney locomotive'', was used on the narrow curves of elevated railways and other rapid transit lines. In the UK 0-4-4 tanks were mainly used for suburban or rural passenger duties. Equivalent classifications Other equivalent classifications are: *UIC classification: B2 (also known as German classification and Italian classification) *French classification: 022 *Turkish classification: 24 *Swiss classification: 2/4 *Russian classification: 0-2-2 History Finland The Finnish Steam Locomotive Class F1 entered service with SVR in 1885 were used until 1935. One example is preserved at the Finnish Railway Museum. United Kingdom In the UK the earliest 0-4-4's were well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiscasset, Waterville, And Farmington Railway
The Wiscasset, Waterville and Farmington Railway is a narrow gauge railway. The line was operated as a for-profit company from 1895 until 1933 between the Maine towns of Wiscasset, Albion, and Winslow, but was abandoned in 1936. Today, about of the track in the town of Alna has been rebuilt and is operated by the non-profit Wiscasset, Waterville and Farmington Railway Museum as a heritage railroad offering passenger excursion trains and hauling occasional cargo. History The line began operating to Weeks Mills on February 20, 1895, as the Wiscasset and Quebec Railroad. The line was reorganized in 1901 as the Wiscasset, Waterville and Farmington Railway following the inability to negotiate a crossing of the Belfast and Moosehead Lake Railroad near Burnham Junction. The reorganized WW&F completed a branch line from Weeks Mills to the Kennebec River at Winslow but failed to negotiate a connection with the Sandy River Railroad at Farmington, and therefore never reached Quebec. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennebec Central Railroad
The Kennebec Central Railroad was a narrow gauge railroad operating between Randolph and Togus, Maine. The railroad was built to offer transportation for American Civil War veterans living at Togus to the nearby City of Gardiner.Barney(1986)p.2 Tracks of 25-pound steel rails ran five miles from Randolph, Maine (across the Kennebec River from Gardiner) to the veterans home at Togus. Train service began on 23 July 1890. The Randolph terminal included a small, Queen Anne style station and a long set of stairs up to the covered bridge passengers used to reach Gardiner. Initial rolling stock was six flat cars and two box cars built by W.H.Dyer of Strong, Maine, two passenger coaches and a combination passenger-baggage car built by Jackson & Sharpe, and a 16-ton 0-4-4 Forney locomotive built by Baldwin Locomotive Works. Operational experience during the first summer encouraged purchase of two open, arch-roofed excursion cars from Jackson & Sharp to handle the crowds traveling d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |