|
Porpoise Morbillivirus
Porpoises are a group of fully aquatic marine mammals, all of which are classified under the family Phocoenidae, parvorder Odontoceti (toothed whales). Although similar in appearance to dolphins, they are more closely related to narwhals and belugas than to the true dolphins. There are eight extant species of porpoise, all among the smallest of the toothed whales. Porpoises are distinguished from dolphins by their flattened, spade-shaped teeth distinct from the conical teeth of dolphins, and lack of a pronounced beak, although some dolphins (e.g. Hector's dolphin) also lack a pronounced beak. Porpoises, and other cetaceans, belong to the clade Cetartiodactyla with even-toed ungulates. Porpoises range in size from the vaquita, at in length and in weight, to the Dall's porpoise, at and . Several species exhibit sexual dimorphism in that the females are larger than males. They have streamlined bodies and two limbs that are modified into flippers. Porpoises use echoloca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetacea
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel themselves through the water with powerful up-and-down movement of their tail which ends in a paddle-like fluke, using their flipper-shaped forelimbs to maneuver. While the majority of cetaceans live in marine environments, a small number exclusively reside in brackish water or fresh water. Having a cosmopolitan distribution, they can be found in some rivers and all of Earth's oceans, and many species inhabit vast ranges where they migrate with the changing of the seasons. Cetaceans are famous for their high intelligence and complex social behaviour as well as for the enormous size of some of the group's members, such as the blue whale which reaches a maximum confirmed length of 29.9 meters (98 feet) and a weight of 173 tonnes (190 short to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echolocation (animal)
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological sonar used by several animal species. Echolocating animals emit calls out to the environment and listen to the echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects. Echolocation is used for navigation, foraging, and hunting in various environments. Echolocating animals include some mammals (most notably Laurasiatheria) and a few birds, especially some bat species and odontocetes (toothed whales and dolphins), but also in simpler forms in other groups such as shrews, and two cave-dwelling bird groups, the so-called cave swiftlets in the genus ''Aerodramus'' (formerly ''Collocalia'') and the unrelated oilbird ''Steatornis caripensis''. Early research The term ''echolocation'' was coined in 1938 by the American zoologist Donald Griffin, who, with Robert Galambos, first demonstrated the phenomenon in bats. As Griffin described in his book, the 18th century I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is the world's largest island. It is one of three constituent countries that form the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark and the Faroe Islands; the citizens of these countries are all citizens of Denmark and the European Union. Greenland's capital is Nuuk. Though a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe (specifically Norway and Denmark, the colonial powers) for more than a millennium, beginning in 986.The Fate of Greenland's Vikings , by Dale Mackenzie Brown, ''Archaeological Institute of America'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
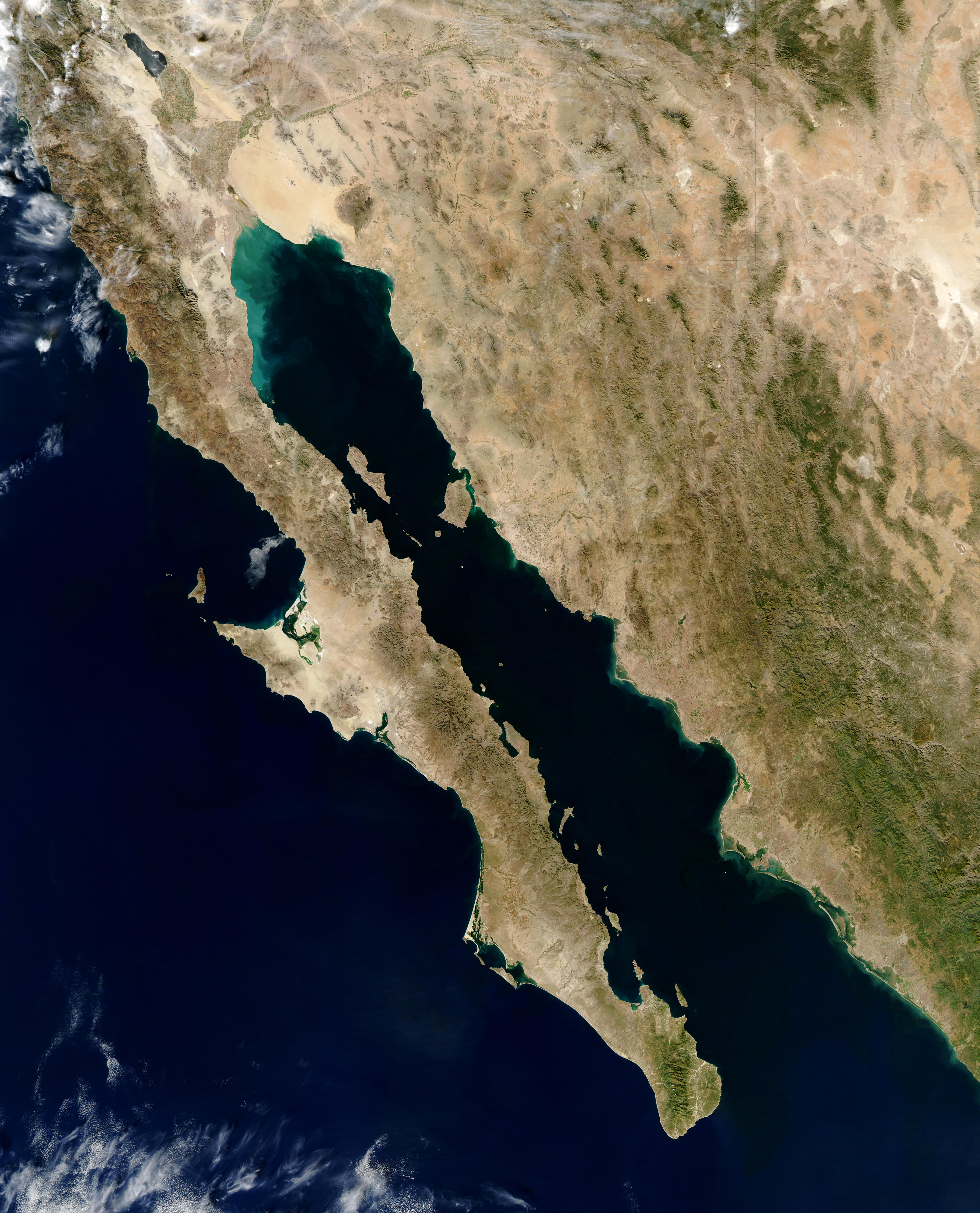
Sea Of Cortez
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexican mainland. It is bordered by the states of Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, and Sinaloa with a coastline of approximately . Rivers that flow into the Gulf of California include the Colorado, Fuerte, Mayo, Sinaloa, Sonora, and the Yaqui. The surface of the gulf is about . Maximum depths exceed because of the complex geology, linked to plate tectonics. The gulf is thought to be one of the most diverse seas on Earth and is home to more than 5,000 species of micro-invertebrates. Parts of the Gulf of California are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography History The marine expeditions of Fortún Ximénez, Hernán Cortés, Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo, Francisco de Ulloa, Hernando de Alarcón, Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectacled Porpoise
The spectacled porpoise (''Phocoena dioptrica'') is a small to midsize porpoise indigenous to the Southern Ocean. It is one of the most poorly studied cetaceans, partly due to its remote range in the southern ocean. What little is known about this porpoise species has been gathered mainly from stranded individuals, and a few observations of living animals made at sea. Description As with other porpoise species, the spectacled porpoise has no beak. It has small pectoral fins with rounded tips positioned far forward on the body, and a triangular dorsal fin. Interestingly, this porpoise species shows obvious sexual dimorphism between adult males and females, as the dorsal fins in the former are much larger and more rounded. Records for female length range up to , while males may reach , which represents the largest specimen documented thus far. The maximum weight for a female was , while a male has been recorded at . The spectacled porpoise has a distinctive colouration. As an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harbour Porpoise
The harbour porpoise (''Phocoena phocoena'') is one of eight extant species of porpoise. It is one of the smallest species of cetacean. As its name implies, it stays close to coastal areas or river estuaries, and as such, is the most familiar porpoise to whale watchers. This porpoise often ventures up rivers, and has been seen hundreds of kilometres from the sea. The harbour porpoise may be polytypic, with geographically distinct populations representing distinct races: ''P. p. phocoena'' in the North Atlantic and West Africa, ''P. p. relicta'' in the Black Sea and Sea of Azov, an unnamed population in the northwestern Pacific and ''P. p. vomerina'' in the northeastern Pacific. Taxonomy The English word porpoise comes from the French (Old French , 12th century), which is from Medieval Latin , which is a compound of ''porcus'' (pig) and (fish). The old word is probably a loan-translation of a Germanic word, compare Danish ''marsvin'' and Middle Dutch ''mereswijn'' (sea swin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finless Porpoise
''Neophocaena'' is a genus of porpoise native to the Indian and Pacific oceans, as well as the freshwater habitats of the Yangtze River basin in China. They are commonly known as finless porpoises. Genetic studies indicate that ''Neophocaena'' is the most basal living member of the porpoise family. There are three species in this genus: Description The finless porpoises are the only porpoises to lack a true dorsal fin A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through conv .... Instead there is a low ridge covered in thick skin bearing several lines of tiny tubercles. In addition, the forehead is unusually steep compared with those of other porpoises. With fifteen to twenty-one teeth in each jaw, they also have, on average, fewer teeth than other porpoises, although there is some over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory System
The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing sensory information. A sensory system consists of sensory neurons (including the sensory receptor cells), neural pathways, and parts of the brain involved in sensory perception. Commonly recognized sensory systems are those for vision, hearing, touch, taste, smell, and balance. Senses are transducers from the physical world to the realm of the mind where people interpret the information, creating their perception of the world around them. The receptive field is the area of the body or environment to which a receptor organ and receptor cells respond. For instance, the part of the world an eye can see, is its receptive field; the light that each rod or cone can see, is its receptive field. Receptive fields have been identified for the visual system, auditory system and somatosensory system. Stimulus :Organisms need information to solve at least three kinds of problems: (a) to maintain an ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Echolocation
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological sonar used by several animal species. Echolocating animals emit calls out to the environment and listen to the echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects. Echolocation is used for navigation, foraging, and hunting in various environments. Echolocating animals include some mammals (most notably Laurasiatheria) and a few birds, especially some bat species and odontocetes (toothed whales and dolphins), but also in simpler forms in other groups such as shrews, and two cave-dwelling bird groups, the so-called cave swiftlets in the genus ''Aerodramus'' (formerly ''Collocalia'') and the unrelated oilbird ''Steatornis caripensis''. Early research The term ''echolocation'' was coined in 1938 by the American zoologist Donald Griffin, who, with Robert Galambos, first demonstrated the phenomenon in bats. As Griffin described in his book, the 18th century I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, colour, markings, or behavioural or cognitive traits. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', which is when both biological sexes are phenotypically indistinguishable from each other. Overview Ornamentation and coloration Common and easily identified types of dimorphism consist of ornamentation and coloration, though not always apparent. A difference in coloration of sexes within a given species is called sexual dichromatism, which is commonly seen in many species of birds and reptiles. Sexual selection leads to the exaggerated dim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dall's Porpoise
Dall's porpoise (''Phocoenoides dalli'') is a species of porpoise endemic to the North Pacific. It is the largest of porpoises and the only member of the genus ''Phocoenoides''. The species is named after American naturalist W. H. Dall. Taxonomy Dall’s porpoise is the only member of the genus ''Phocoenoides''. The ''dalli''- and ''truei''-types were initially described as separate species in 1911, but later studies determined that the available evidence only supported the existence of one species. Currently, these two color morphs are recognized as distinct subspecies, Dall's porpoise (''Phocoenoides dalli dalli'') and True's porpoise (''Phocoenoides dalli truei''). Description Dall's porpoises can be easily distinguished from other porpoises and cetacean species within their range. They have a wide, robust body, a comparatively tiny head, and no distinguished beak. Their flippers are positioned at the front of the body and a triangular dorsal fin sits mid-body. Patterns o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_BHL45850430.jpg)