|
Pop Maynard
George "Pop" Maynard (6 January 187229 November 1962) was an English folk singer and marbles champion. The folk singer Shirley Collins considers Maynard to have been the "finest traditional English singer, matched only by Harry Cox". Life and family George Maynard was born on 6 January 1872 or, as he put it, on Old Christmas Day in Smallfield, Burstow, Surrey, about north of the village of Copthorne, West Sussex, where he lived for his entire life. He was the eleventh of twelve children of James Maynard and his wife Elizabeth (née Skinner), four of whom died in infancy. Maynard was baptised on 3 February 1872 at the Church of St Bartholomew in Burstow, when his father's profession was given as "labourer". Maynard attended school on-and-off until the age of 12. He worked with his father and brothers, in the winter as a woodman cutting wood for the hoop trade, in the summer harvesting, hedging and ditching. He and his family also supplemented their income by poaching rabbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copthorne, West Sussex
Copthorne is a village in the Mid Sussex district of West Sussex, England. It lies close to Gatwick Airport, south of London, north of Brighton, and northeast of the county town of Chichester. Nearby towns include Crawley to the southwest and East Grinstead to the east. It is the most northerly ecclesiastical parish in the Diocese of Chichester in the Church of England, and together with Crawley Down makes up the civil parish of Worth. Etymology The place-name Copthorne is derived from the Old English ''coppede'' + ''þorn'', meaning capped or pollarded thorn tree. (A pollarded tree is one which has had its topmost branches pruned back in order to produce a close head of young shoots.) The name was first recorded as ''Coppethorne'' in 1437. History Lying on the borders between the counties West Sussex and Surrey, has contributed to Copthorne's history. There are stories of smugglers from the south coast stashing their goods in the woods around the village, conscious that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hops
Hops are the flowers (also called seed cones or strobiles) of the hop plant ''Humulus lupulus'', a member of the Cannabaceae family of flowering plants. They are used primarily as a bittering, flavouring, and stability agent in beer, to which, in addition to bitterness, they impart floral, fruity, or citrus flavours and aromas. Hops are also used for various purposes in other beverages and herbal medicine. The hops plants have separate female and male plants, and only female plants are used for commercial production. The hop plant is a vigorous, climbing, herbaceous perennial, usually trained to grow up strings in a field called a hopfield, hop garden (in the South of England), or hop yard (in the West Country and United States) when grown commercially. Many different varieties of hops are grown by farmers around the world, with different types used for particular styles of beer. The first documented use of hops in beer is from the 9th century, though Hildegard of Bingen, 30 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
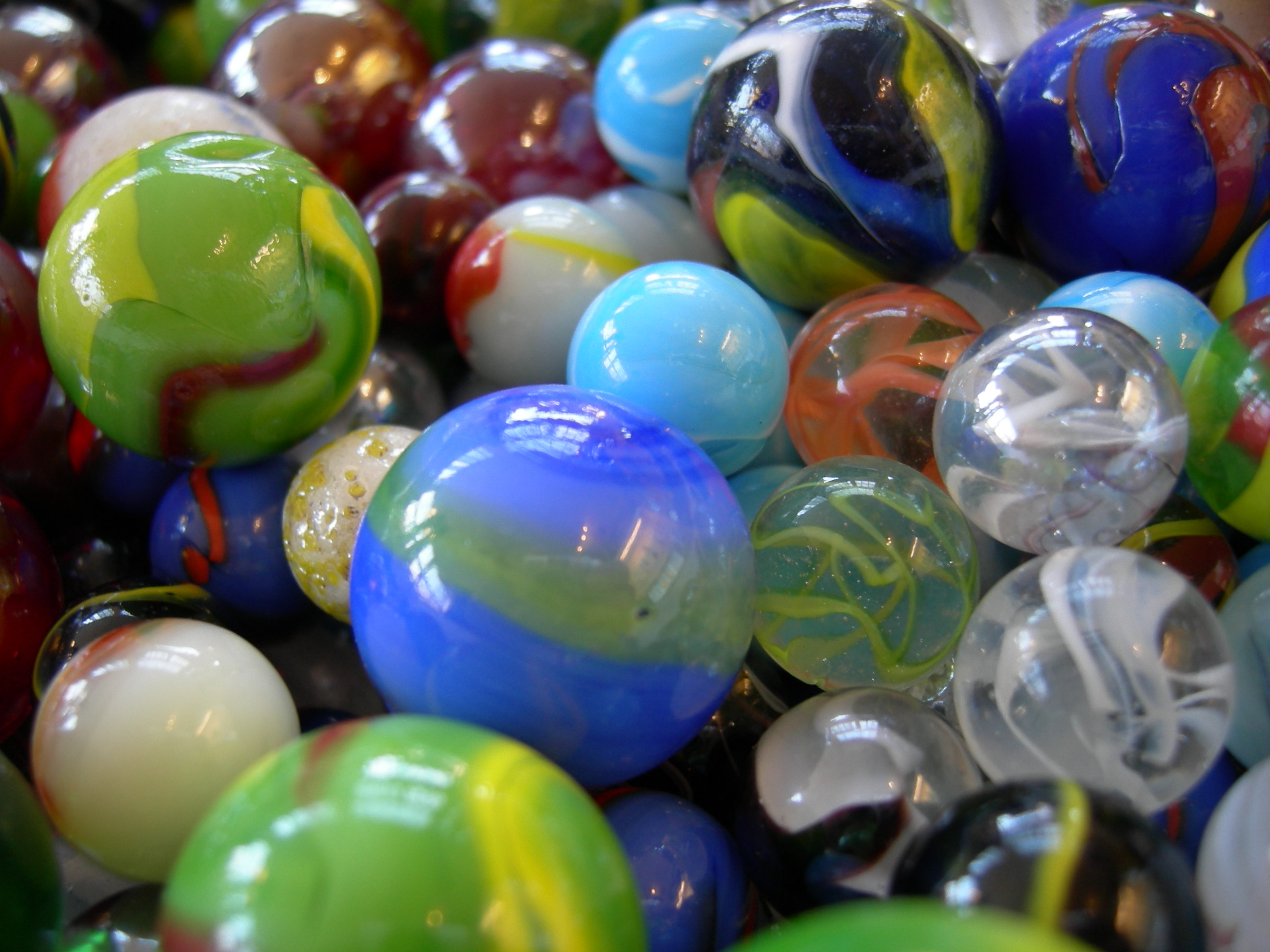
Marbles (game)
A marble is a small spherical object often made from glass, clay, steel, plastic, or agate. They vary in size, and most commonly are about in diameter. These toys can be used for a variety of games called ''marbles'', as well being placed in marble runs or races, or created as a form of art. They are often collected, both for nostalgia and for their aesthetic colors. Sizes may range from less than to over , while some art glass marbles for display purposes are over wide. In the North of England the objects and the game are called "taws", with larger taws being called "bottle washers" after the use of a marble in Codd-neck bottles, which were often collected for play. Games History In the early twentieth century, small balls of stone from about 2500 BCE, identified by archaeologists as marbles, were found by excavation near Mohenjo-daro, in a site associated with the Indus Valley civilization. Marbles are often mentioned in Roman literature, as in Ovid's poem "Nux" (which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darts
Darts or dart-throwing is a competitive sport in which two or more players bare-handedly throw small projectile point, sharp-pointed projectile, missiles known as dart (missile), darts at a round shooting target, target known as a #Dartboard, dartboard. Points can be scored by hitting specific marked areas of the board, though unlike in sports such as archery, these areas are distributed all across the board and do not follow a principle of points increasing towards the bullseye (target), centre of the board. Though a number of similar games using various boards and rules exist, the term "darts" usually now refers to a standardised game involving a specific board design and set of rules. Darts is both a professional shooting sport and a traditional pub game. Darts is commonly played in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, and recreationally enjoyed around the world. History Dartboard The original target in the game is likely to have been a section of a tree trunk, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quoits
Quoits ( or ) is a traditional game which involves the throwing of metal, rope or rubber rings over a set distance, usually to land over or near a spike (sometimes called a hob, mott or pin). The game of quoits encompasses several distinct variations. History From coyte: ‘flat stone thrown in a game’. Probably from Old French coite - ‘flat stone’. Possible derivation of coilte - ‘cushion’. It is not until the 19th century that the game is documented in any detailed way. The official rules first appeared in the April 1881 edition of '' The Field'', having been defined by a body formed from pubs in Northern England.Quoits Online A July 13, 1836 advertisement in the '' |
Skittles (sport)
Skittles is a historical lawn game and target sport of European origin, from which the modern sport of nine-pin bowling is descended. In regions of the United Kingdom and Ireland the game remains as a popular indoor pub game. Playing Skittles is usually played indoors on a bowling alley, with one or more heavy balls, usually spherical but sometimes oblate, and several (most commonly nine) , or small bowling pins. The general object of the game is to use the ball(s) to knock over the skittles, either specific ones or all of them, depending upon game variant. Exact rules vary widely on a regional basis. Rules variations (Note: See Glossary below for explanation of named pins) Front pin first In this variant of the game, pins are counted only if the front pin is knocked over first. If the front pin is missed, any pins that are knocked over are not reset. In Devon Summer League, this rule is played frequently. In Bristol, this is the form of the game played and "all in" skittle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shove Ha'penny
Shove ha'penny (or shove halfpenny), also known in ancestral form as shoffe-grote ['shove- groat' in Modern English], slype groat ['slip groat'], and slide-thrift, is a pub game in the shuffleboard family, played predominantly in the United Kingdom. Two players or teams compete against one another using coins or discs on a tabletop board. Board Shove ha'penny is played on a small, rectangular, smooth board usually made of wood or stone. A number of parallel lines or grooves run horizontally across this board, separated by about one-and-a-half coin diameters. The spaces between the lines (usually nine) are called the "beds". Five British halfpenny coins "ha'pennies" (now obsolete pre-decimalisation coinage, diameter 1 inch; 25mm) or similarly-sized coins or metal discs are placed one-by-one at one end of the board slightly protruding over the edge and are shoved forward toward scoring lines, with a blow from the palm of the hand. In the humorously opinionat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockney
Cockney is an accent and dialect of English, mainly spoken in London and its environs, particularly by working-class and lower middle-class Londoners. The term "Cockney" has traditionally been used to describe a person from the East End, or born within earshot of Bow Bells, although it most commonly refers to the broad variety of English native to London. Estuary English is an intermediate accent between Cockney and Received Pronunciation, also widely spoken in and around London, as well as in wider southeastern England. In multicultural areas of London, the Cockney dialect is, to an extent, being replaced by Multicultural London English—a new form of speech with significant Cockney influence. Words and phrases Etymology of Cockney The earliest recorded use of the term is 1362 in passus VI of William Langland's ''Piers Plowman'', where it is used to mean "a small, misshapen egg", from Middle English ''coken'' + ''ey'' ("a cock's egg"). Concurrently, the mythical land of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
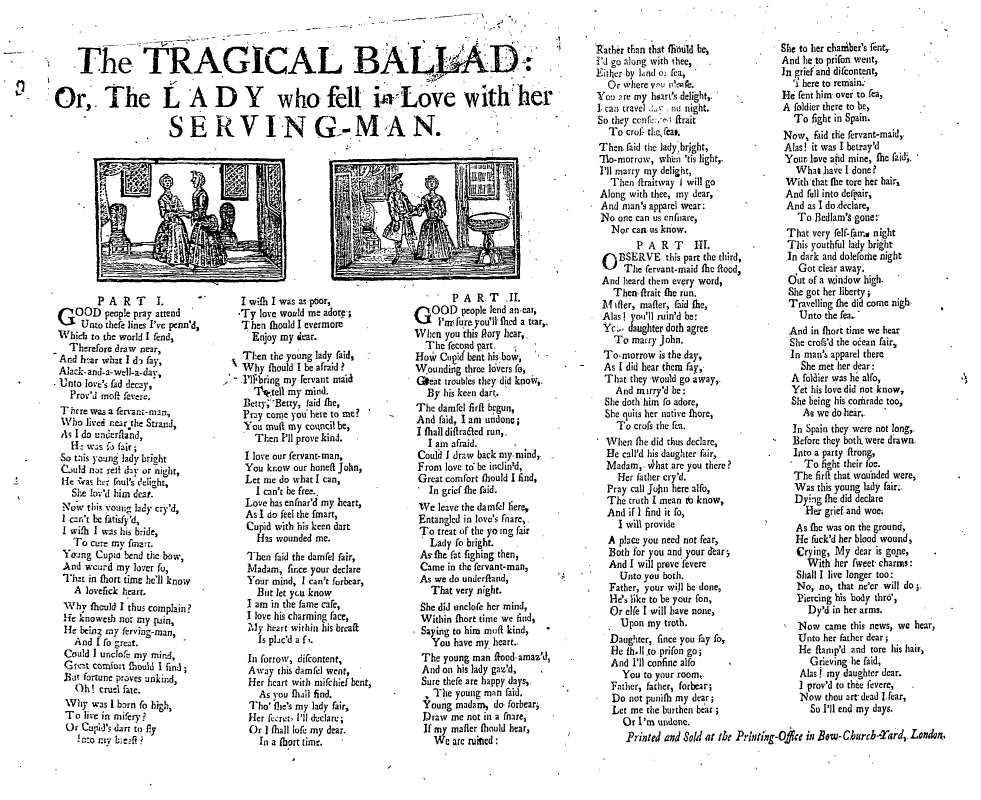
Broadside Ballad
A broadside (also known as a broadsheet) is a single sheet of inexpensive paper printed on one side, often with a ballad, rhyme, news and sometimes with woodcut illustrations. They were one of the most common forms of printed material between the sixteenth and nineteenth centuries, particularly in Britain, Ireland and North America because they are easy to produce and are often associated with one of the most important forms of traditional music from these countries, the ballad. Development of broadsides Ballads developed out of minstrelsy from the fourteenth and fifteenth century. These were narrative poems that had combined with French courtly romances and Germanic legends that were popular at the King’s court, as well as in the halls of lords of the realm. By the seventeenth century, minstrelsy had evolved into ballads whose authors wrote on a variety of topics. The authors could then have their ballads printed and distributed. Printers used a single piece of paper known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Seeds Of Love (folk Song)
"The Sprig of Thyme", "The Seeds of Love", "Maiden’s Lament", "Garners Gay", "Let No Man Steal Your Thyme" or "Rue" () is a traditional British and Irish folk ballad that uses botanical and other symbolism to warn young people of the dangers in taking false lovers. The song was first documented in 1689 and the many variants go by a large number of titles. History In Thomas Dunham Whitaker's ''History of the Parish of Whalley'', it is claimed that around the year 1689, a woman named Mrs. Fleetwood Habergam “undone by the extravagance, and disgraced by the vices of her husband,” wrote of her woes in the symbolism of flowers; however, the folklorist Cecil Sharp doubted this claim. The versions allegedly written by Habergram would have been the "Seeds of Love" variant; The "Sprig of Thyme" / "Let No Man Steal Your Thyme" variant is probably older than the "Seeds of Love" variant; it has a more modal, sad melody with abstract and reflective lyrics. ''The Seeds of Love'', sung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiddingstone
Chiddingstone is a village and civil parish in the Sevenoaks District of Kent, England. The parish is located on the River Eden between Tonbridge and Edenbridge. The village of Chiddingstone Causeway and the hamlet Chiddingstone Hoath are also included in the parish. Chiddingstone is unique in that, apart from the church and Chiddingstone Castle, the entire village is owned by the National Trust, which describes it as "the best example of a Tudor village left in the country". It is an example of a Tudor one-street village. History Chiddingstone is mentioned in the Domesday Book. It was given to Bishop Odo in 1072 after the Norman invasion as part of his Earldom of Kent. The first house was owned by Roger Attwood, constructed in the typical Kent style. Several villagers including Atwood took part in Jack Cade's rebellion of 1450, and were later pardoned. The Castle Inn is a 15th-century building, which became a hostelry in 1730. It was visited by artists John Millais and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The National Archives (United Kingdom)
, type = Non-ministerial department , seal = , nativename = , logo = Logo_of_The_National_Archives_of_the_United_Kingdom.svg , logo_width = 150px , logo_caption = , formed = , preceding1 = , dissolved = , superseding = , jurisdiction = England and Wales, HM Government , headquarters = Kew, Richmond, Greater London TW9 4DU , region_code = GB , coordinates = , employees = 679 , budget = £43.9 million (2009–10) , minister1_name = Michelle Donelan , minister1_pfo = Secretary of State for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport , minister2_name = TBC , minister2_pfo = Parliamentary Under Secretary of State , chief1_name = Jeff James , chief1_position = Chief Executive and Keeper of the Public Records , chief2_name = , chief2_position = , chief3_name = , chief3_position = , chief4_name = , chief4_position = , chief5_name = , chief5_position = , agency_type = , chief6_name = , chief6_position = , chief7_name = , chief7_position = , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(cropped).jpg)






.jpg)
