|
Poor People's March On Washington
The Poor People's Campaign, or Poor People's March on Washington, was a 1968 effort to gain economic justice for poor people in the United States. It was organized by Martin Luther King Jr. and the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC), and carried out under the leadership of Ralph Abernathy in the wake of King's assassination in April 1968. The campaign demanded economic and human rights for poor Americans of diverse backgrounds. After presenting an organized set of demands to Congress and executive agencies, participants set up a 3,000-person protest camp on the Washington Mall, where they stayed for six weeks in the spring of 1968. The Poor People's Campaign was motivated by a desire for economic justice: the idea that all people should have what they need to live. King and the SCLC shifted their focus to these issues after observing that gains in civil rights had not improved the material conditions of life for many African Americans. The Poor People's Campaign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Rights Movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination in the United States, discrimination, and disenfranchisement in the United States, disenfranchisement throughout the United States. The movement had its origins in the Reconstruction era during the late 19th century, although it made its largest legislative gains in the 1960s after years of direct actions and grassroots protests. The social movement's major nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience campaigns eventually secured new protections in federal law for the civil rights of all Americans. After the American Civil War and the subsequent Abolitionism in the United States, abolition of slavery in the 1860s, the Reconstruction Amendments to the United States Constitution granted emancipation and constitutional rights of citizenship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
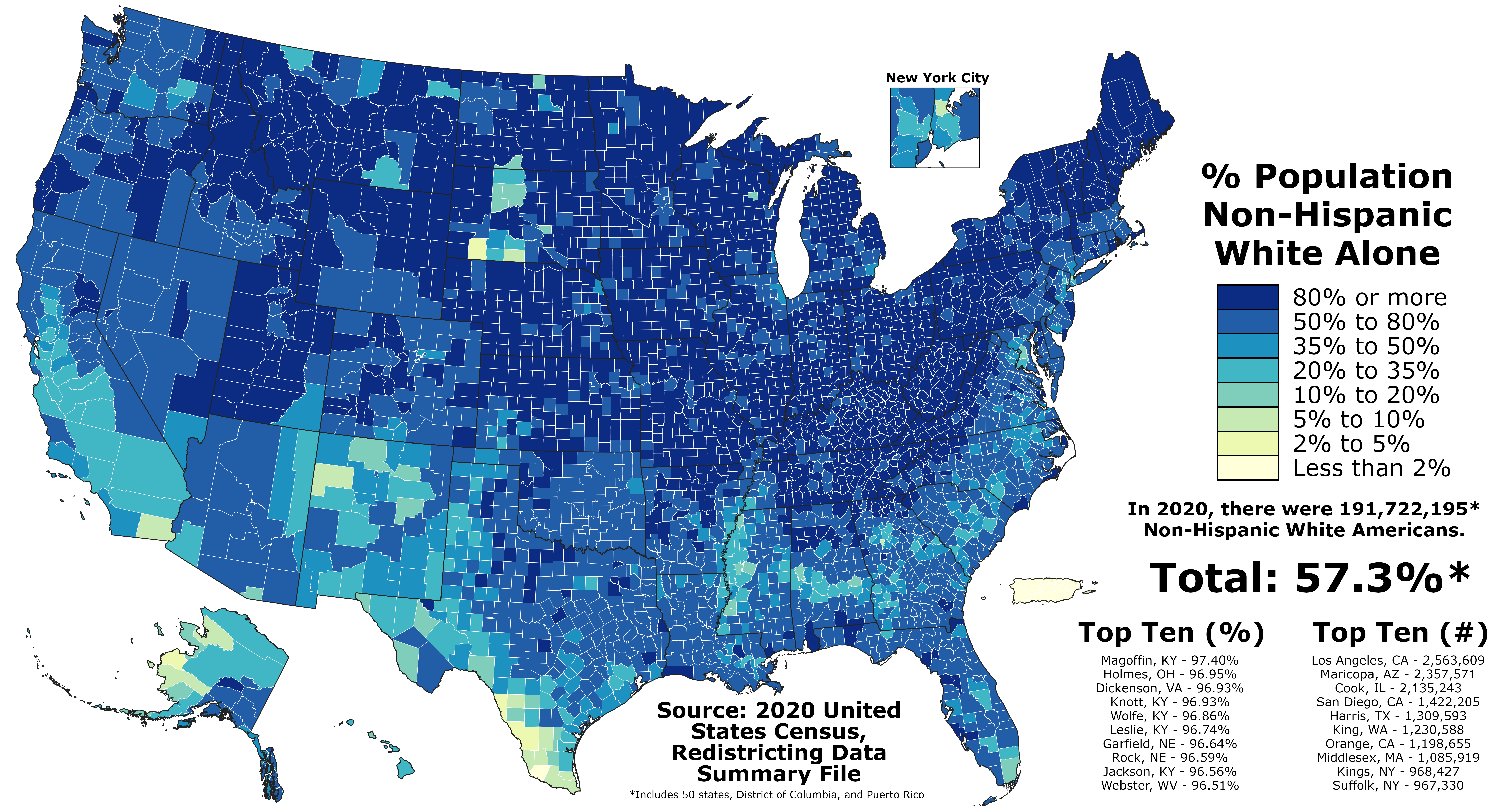
European Americans
European Americans (also referred to as Euro-Americans) are Americans of European ancestry. This term includes people who are descended from the first European settlers in the United States as well as people who are descended from more recent European arrivals. European Americans have been the largest panethnic group in the United States since about the 17th century. The Spaniards are thought to be the first Europeans to establish a continuous presence in what is now the contiguous United States, with Martín de Argüelles ( 1566) in St. Augustine, then a part of Spanish Florida, and the Russians were the first Europeans to settle in Alaska, establishing Russian America. The first English child born in the Americas was Virginia Dare, born August 18, 1587. She was born in Roanoke Colony, located in present-day North Carolina, which was the first attempt, made by Queen Elizabeth I, to establish a permanent English settlement in North America. In the 2016 American Community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1967 Detroit Riot
The 1967 Detroit Riot, also known as the 12th Street Riot or Detroit Rebellion, was the bloodiest of the urban riots in the United States during the "Long, hot summer of 1967". Composed mainly of confrontations between Black residents and the Detroit Police Department, it began in the early morning hours of Sunday July 23, 1967, in Detroit, Michigan. The precipitating event was a police raid of an unlicensed, after-hours bar, known as a ''blind pig'', on the city's Near West Side. It exploded into one of the deadliest and most destructive riots in American history, lasting five days and surpassing the scale of Detroit's 1943 race riot 24 years earlier. Governor George W. Romney ordered the Michigan Army National Guard into Detroit to help end the disturbance. President Lyndon B. Johnson sent in the United States Army's 82nd and 101st Airborne divisions. The riot resulted in 43 deaths, 1,189 injured, over 7,200 arrests, and more than 400 buildings destroyed. The scale of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1967 Newark Riots
The 1967 Newark riots were an episode of violent, armed conflict in the streets of Newark, New Jersey, United States. Taking place over a four-day period (between July 12 and July 17, 1967), the Newark riots resulted in at least 26 deaths and hundreds more serious injuries. Serious property damage, including shattered storefronts and fires caused by arson, left much of the city's built environment damaged or destroyed. At the height of the conflict, the National Guard was called upon to occupy the city with tanks and other military equipment, leading to iconic media depictions that were considered particularly shocking when shared in the national press. In the aftermath of the riots, Newark was quite rapidly abandoned by many of its remaining middle-class and affluent residents, as well as much of its white working-class population. This accelerated flight led to a decades-long period of disinvestment and urban blight, including soaring crime rates and gang activity. The Newar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonviolence
Nonviolence is the personal practice of not causing harm to others under any condition. It may come from the belief that hurting people, animals and/or the environment is unnecessary to achieve an outcome and it may refer to a general philosophy of abstention from violence. It may be based on moral, Religion, religious or spiritual principles, or the reasons for it may be strategic or pragmatic. Failure to distinguish between the two types of nonviolent approaches can lead to distortion in the concept's meaning and effectiveness, which can subsequently result in confusion among the audience. Although both principled and pragmatic nonviolent approaches preach for nonviolence, they may have distinct motives, goals, philosophies, and techniques. However, rather than debating the best practice between the two approaches, both can indicate alternative paths for those who do not want to use violence. These forms of nonviolence approaches (pragmatic and principled) will be discussed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frogmore, South Carolina
Frogmore is an unincorporated community on St. Helena Island in Beaufort County, South Carolina, United States, along U.S. Route 21. Located halfway between Beaufort and Hunting Island State Park, the Frogmore area is primarily rural but is considered to be the commercial center of St. Helena Island. Frogmore is also the name of a plantation that has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The plantation is located off Seaside Road on Frogmore Manor Drive and is significant for its association with Laura Towne and Ellen Murray, the founders of Penn School. Frogmore is renowned for being home to the Penn School Historic District, known as Penn Center, a National Historic Landmark. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. studied and lectured at Penn Center during the formative years of his career as a civil rights leader. The museum at Penn Center is a noted cultural attraction and attracts tourists worldwide who are also interested in learning more about this region of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was United States in the Vietnam War, supported by the United States and other anti-communism, anti-communist Free World Military Forces, allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975. After the French 1954 Geneva Conference, military withdrawal from Indochina in 1954 – following their defeat in the First Indochina War – the Viet Minh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyndon B
Lyndon may refer to: Places * Lyndon, Alberta, Canada * Lyndon, Rutland, East Midlands, England * Lyndon, Solihull, West Midlands, England United States * Lyndon, Illinois * Lyndon, Kansas * Lyndon, Kentucky * Lyndon, New York * Lyndon, Ohio * Lyndon, Pennsylvania * Lyndon, Vermont * Lyndon, Sheboygan County, Wisconsin, a town * Lyndon, Juneau County, Wisconsin, a town Other uses * Lyndon State College, a public college located in Lyndonville, Vermont People * Lyndon (name), given name and surname See also * Lyndon School (other) * Lyndon Township (other) * * Lydon (other) * Lynden (other) * Lindon (other) * Linden (other) {{disambig, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poverty Line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for the average adult.Poverty Lines – Martin Ravallion, in The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, 2nd Edition, London: Palgrave Macmillan The cost of housing, such as the rent for an apartment, usually makes up the largest proportion of this estimate, so economists track the real estate market and other housing cost indicators as a major influence on the poverty line. Individual factors are often used to account for various circumstances, such as whether one is a parent, elderly, a child, married, etc. The poverty threshold may be adjusted annually. In practice, like the definition of poverty, the official or common understanding of the poverty line is significantly higher in developed countries than in developing countries. In October 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War On Poverty
The war on poverty is the unofficial name for legislation first introduced by United States President Lyndon B. Johnson during his State of the Union address on January 8, 1964. This legislation was proposed by Johnson in response to a national poverty rate of around nineteen percent. The speech led the United States Congress to pass the Economic Opportunity Act, which established the Office of Economic Opportunity (OEO) to administer the local application of federal funds targeted against poverty. The forty programs established by the Act were collectively aimed at eliminating poverty by improving living conditions for residents of low-income neighborhoods and by helping the poor access economic opportunities long denied from them. As a part of the Great Society, Johnson believed in expanding the federal government's roles in education and health care as poverty reduction strategies. These policies can also be seen as a continuation of Franklin D. Roosevelt's New Deal, which ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyndon Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice president from 1961 to 1963 under President John F. Kennedy, and was sworn in shortly after Kennedy's assassination. A Democrat from Texas, Johnson also served as a U.S. representative, U.S. senator and the Senate's majority leader. He holds the distinction of being one of the few presidents who served in all elected offices at the federal level. Born in a farmhouse in Stonewall, Texas, to a local political family, Johnson worked as a high school teacher and a congressional aide before winning election to the U.S. House of Representatives in 1937. He won election to the United States Senate in 1948 after a narrow and controversial victory in the Democratic Party's primary. He was appointed to the position of Senate Majority Whip in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of The United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces. The power of the presidency has grown substantially since the first president, George Washington, took office in 1789. While presidential power has ebbed and flowed over time, the presidency has played an increasingly strong role in American political life since the beginning of the 20th century, with a notable expansion during the presidency of Franklin D. Roosevelt. In contemporary times, the president is also looked upon as one of the world's most powerful political figures as the leader of the only remaining global superpower. As the leader of the nation with the largest economy by nominal GDP, the president possesses significant domestic and international hard and soft power. Article II of the Constitution establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |