|
Ponatinib
Ponatinib (trade name Iclusig , previously AP24534) is an oral drug developed by ARIAD Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia chromosome–positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). It is a multi-targeted tyrosine-kinase inhibitor. Some forms of CML, those that have the T315I mutation, are resistant to current therapies such as imatinib. Ponatinib has been designed to be effective against these types of tumors. The United States Food and Drug Administration approved the drug as a candidate in December 2012, but temporarily suspended sales on 31 October 2013 because of "the risk of life-threatening blood clots and severe narrowing of blood vessels". This suspension was partially lifted on Dec. 20, 2013 with ponatinib being issued revised prescribing information, a new "Black Box Warning" and a "Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy" in place to better evaluate the risks and benefits of using the drug. In the US it can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bcr-Abl Tyrosine-kinase Inhibitor
Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKI) are the first-line therapy for most patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). More than 90% of CML cases are caused by a chromosomal abnormality that results in the formation of a so-called Philadelphia chromosome. This abnormality was discovered by Peter Nowell in 1960 and is a consequence of fusion between the Abelson ( Abl) tyrosine kinase gene at chromosome 9 and the break point cluster ( Bcr) gene at chromosome 22, resulting in a chimeric oncogene (Bcr-Abl) and a constitutively active Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase that has been implicated in the pathogenesis of CML. Compounds have been developed to selectively inhibit the tyrosine kinase. Before the 2001 U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of imatinib, no drugs were available to alter the natural progression of CML. Only cytotoxic drugs such as busulfan, hydroxyurea or interferon-alpha (rIFN-α) were utilized. Even though the first Bcr-Abl TK inhibitor was named "the mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bcr-Abl Tyrosine-kinase Inhibitor
Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKI) are the first-line therapy for most patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). More than 90% of CML cases are caused by a chromosomal abnormality that results in the formation of a so-called Philadelphia chromosome. This abnormality was discovered by Peter Nowell in 1960 and is a consequence of fusion between the Abelson ( Abl) tyrosine kinase gene at chromosome 9 and the break point cluster ( Bcr) gene at chromosome 22, resulting in a chimeric oncogene (Bcr-Abl) and a constitutively active Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase that has been implicated in the pathogenesis of CML. Compounds have been developed to selectively inhibit the tyrosine kinase. Before the 2001 U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of imatinib, no drugs were available to alter the natural progression of CML. Only cytotoxic drugs such as busulfan, hydroxyurea or interferon-alpha (rIFN-α) were utilized. Even though the first Bcr-Abl TK inhibitor was named "the mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARIAD Pharmaceuticals
ARIAD Pharmaceuticals, Inc. was an American oncology company, now part of Takeda Oncology, which was founded in 1991 by Harvey J. Berger, M.D. and headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts. ARIAD engaged in the discovery, development, and commercialization of medicines for cancer patients. ARIAD’s most prominent drug discoveries include Iclusig, designed for patients with all forms of Philadelphia chromosome-positive h+chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) or Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who are resistant to or unable to tolerate other tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and brigatinib, a lung cancer drug which has completed its registration trial in ALK fusion driven non-small cell lung cancer as of June 2016 and was approved in the U.S. in April 2017. In January 2017, Takeda announced it would acquire ARIAD for $5.2 billion, expanding the company's oncology and hematology business. On February 16, 2017, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Ltd. announced it had completed its acquisition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
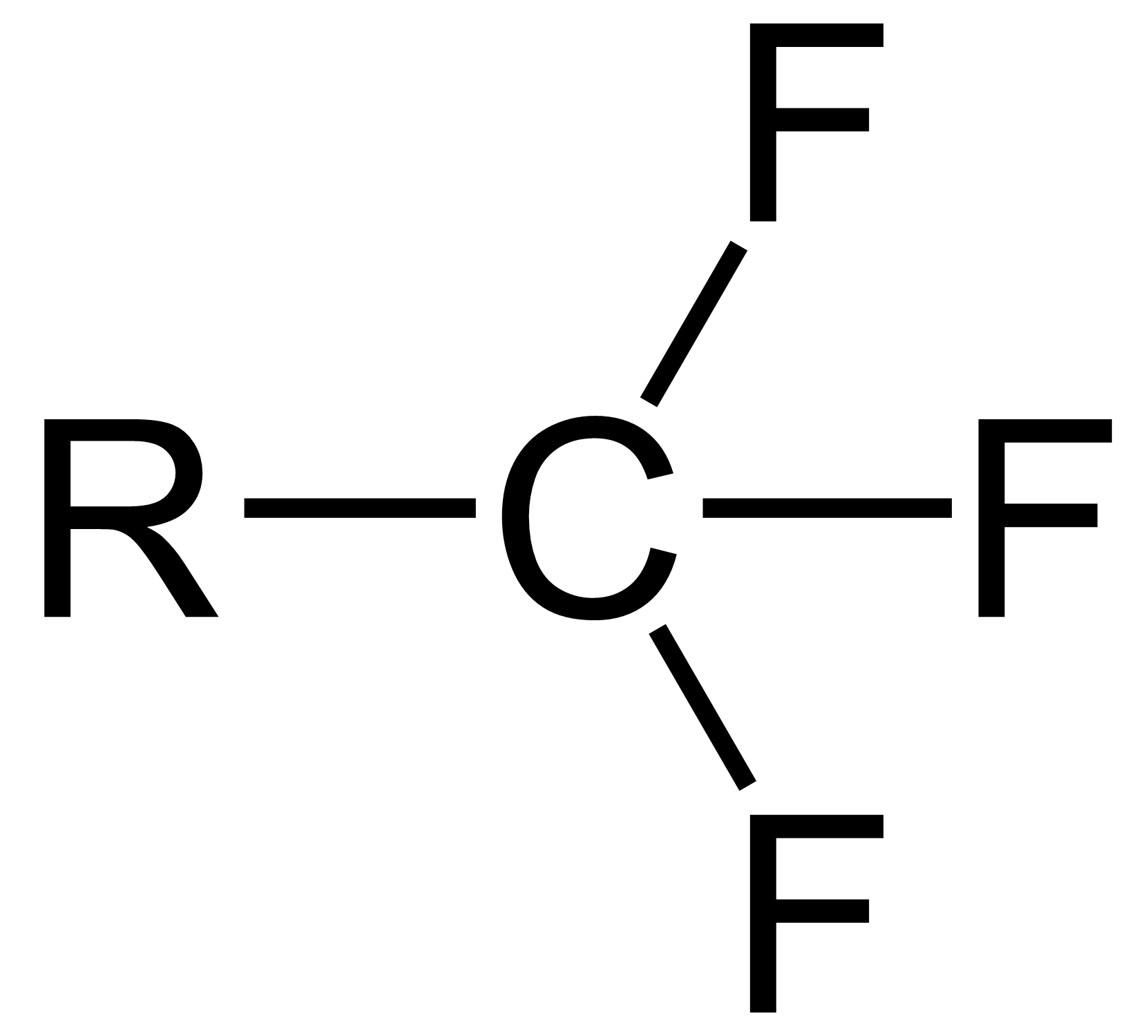
Trifluoromethyl Compounds
The trifluoromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula -CF3. The naming of is group is derived from the methyl group (which has the formula -CH3), by replacing each hydrogen atom by a fluorine atom. Some common examples are trifluoromethane H–, 1,1,1-trifluoroethane –, and hexafluoroacetone –CO–. Compounds with this group are a subclass of the organofluorines. Properties The trifluoromethyl group has a significant electronegativity that is often described as being intermediate between the electronegativities of fluorine and chlorine. For this reason, trifluoromethyl-substituted compounds are often strong acids, such as trifluoromethanesulfonic acid and trifluoroacetic acid. Conversely, the trifluoromethyl group lowers the basicity of compounds like trifluoroethanol. Uses The trifluoromethyl group occurs in certain pharmaceuticals, drugs, and abiotically synthesized natural fluorocarbon based compounds. The medicinal use of the trifloromethyl group dates f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne Derivatives
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 121 picometers is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (134 pm) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. The sigma bond contributes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute For Health And Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas: * the use of health technologies within England's National Health Service (NHS) and NHS Wales (such as the use of new and existing medicines, treatments and procedures) * clinical practice (guidance on the appropriate treatment and care of people with specific diseases and conditions) * guidance for public sector workers on health promotion and ill-health avoidance * guidance for social care services and users. These appraisals are based primarily on evidence-based evaluations of efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness in various circumstances. It serves both the English NHS and the Welsh NHS. It was set up as the National Institute for Clinical Excellence in 1999, and on 1 April 2005 joined with the Health Development Agency to become the new National Institute for Health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Drugs Fund
The Cancer Drugs Fund (CDF) was introduced in England in 2011. It was established in order to provide a means by which National Health Service (NHS) patients in England could get cancer drugs rejected by National Institute for Health and Care Excellence because they were not cost effective. Its establishment was confirmed by the UK government's coalition agreement in 2010, and by the White Paper, Equity and excellence – Liberating the NHS. Starting in April 2011, the fund paid for nearly 100,000 people with cancer to access treatments. It was closed to new drugs from October 2015 to 29 July 2016 in line with the recommendation of the independent Cancer Taskforce report, which called for urgent reform to put the CDF on a more sustainable footing. Objectives Following the reforms in 2016 the objectives were updated. The new arrangements put it on a more sustainable footing with 3 key objectives: *patients have faster access to the most promising new cancer treatments. *taxpayers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purine
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings ( pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purines and their tautomers. They are the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing heterocycles in nature. Dietary sources Purines are found in high concentration in meat and meat products, especially internal organs such as liver and kidney. In general, plant-based diets are low in purines. High-purine plants and algae include some legumes (lentils and black eye peas) and spirulina. Examples of high-purine sources include: sweetbreads, anchovies, sardines, liver, beef kidneys, brains, meat extracts (e.g., Oxo, Bovril), herring, mackerel, scallops, game meats, yeast (beer, yeast extract, nutritional yeast) and gravy. A moderate amount of purine is also contained in red meat, beef, pork, poultry, fish and seafood, asparagus, cauliflo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasatinib
Dasatinib, sold under the brand name Sprycel among others, is a targeted therapy medication used to treat certain cases of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Specifically it is used to treat cases that are Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+). It is taken by mouth. Common adverse effects include low white blood cells, low blood platelets, anemia, swelling, rash, and diarrhea. Severe adverse effects may include bleeding, pulmonary edema, heart failure, and prolonged QT syndrome. Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby. It is a tyrosine-kinase inhibitor and works by blocking a number of tyrosine kinases such as Bcr-Abl and the Src kinase family. Dasatinib was approved for medical use in the United States and in the European Union in 2006. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Dasatinib is used to treat people with chronic myeloid leukemia and people with acute lymphoblastic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilotinib
Nilotinib, sold under the brand name Tasigna marketed worldwide by Novartis, is a medication used to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) which has the Philadelphia chromosome. It may be used both in initial cases of chronic phase CML as well as in accelerated and chronic phase CML that has not responded to imatinib. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects may include low platelets, low white blood cells, anemia, rashes, vomiting, diarrhea, and joint pains. Other serious side effects may include QT prolongation, sudden death, pancreatitis, and liver problems. It is not safe for use during pregnancy. Nilotinib is a Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor and works by interfering with signalling within the cancer cell. Nilotinib was approved for medical use in the United States in 2007. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Nilotinib is used to treat Philadelphia chromosome (Ph+)-positive chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Adverse e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |