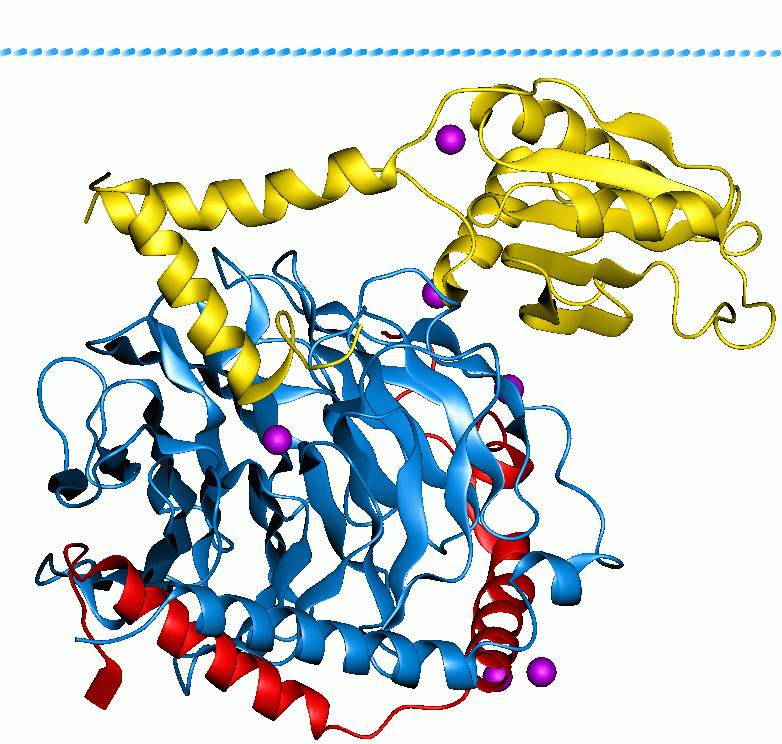
|
Polyphosphate Kinase
In enzymology, a polyphosphate kinase (), or polyphosphate polymerase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of polyphosphate from ATP, with chain lengths of up to a thousand or more orthophosphate moieties. :ATP + (phosphate)n \rightleftharpoons ADP + (phosphate)n+1 Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and polyphosphate phosphate)n whereas its two products are ADP and polyphosphate extended by one phosphate moiety phosphate)n+1 This enzyme is a membrane protein and goes through an intermediate stage during the reaction where it is autophosphorylated with a phosphate group covalently linked to a basic amino acyl residue through an N-P bond. Several enzymes catalyze polyphosphate polymerization. Some of these enzymes couple phosphotransfer to transmembrane transport. These enzyme/transporters are categorized in the Transporter Classification Database (TCDB) under the Polyphosphate Polymerase/YidH SuperfamilyTC# 4.E.1 and are transferases that transfer pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymology
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuoles
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Discovery Contractile vacuoles ("stars") were first observed by Spallanzani (1776) in protozoa, although mistaken for respiratory organs. Dujardin (1841) named these "stars" as ''vacuoles''. In 1842, Schleiden applied the term for plant cells, to distinguish the structure with cell sap from the rest of the protoplasm. In 1885, de Vries named the vacuole membrane as tonoplast. Function The function a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurospora Crassa
''Neurospora crassa'' is a type of red bread mold of the phylum Ascomycota. The genus name, meaning "nerve spore" in Greek, refers to the characteristic striations on the spores. The first published account of this fungus was from an infestation of French bakeries in 1843. ''Neurospora crassa'' is used as a model organism because it is easy to grow and has a haploid life cycle that makes genetic analysis simple since recessive traits will show up in the offspring. Analysis of genetic recombination is facilitated by the ordered arrangement of the products of meiosis in ''Neurospora'' ascospores. Its entire genome of seven chromosomes has been sequenced. ''Neurospora'' was used by Edward Tatum and George Wells Beadle in their experiments for which they won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1958. Beadle and Tatum exposed ''N. crassa'' to x-rays, causing mutations. They then observed failures in metabolic pathways caused by errors in specific enzymes. This led them to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like ''Escherichia coli'' as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation. ''S. cerevisiae'' cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding. Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. ''S. cerevisiae'' is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley bodies present, which are involved in particular secretory pathways. Antibodies against ''S. cerevis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavior of the receiving individuals. There are '' alarm pheromones'', ''food trail pheromones'', '' sex pheromones'', and many others that affect behavior or physiology. Pheromones are used by many organisms, from basic unicellular prokaryotes to complex multicellular eukaryotes. Their use among insects has been particularly well documented. In addition, some vertebrates, plants and ciliates communicate by using pheromones. The ecological functions and evolution of pheromones are a major topic of research in the field of chemical ecology. Background The portmanteau word "pheromone" was coined by Peter Karlson and Martin Lüscher in 1959, based on the Greek φερω ''pheroo'' ('I carry') and ὁρμων ''hormon'' ('stimulating'). Pheromone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of '' alpha'' (α), ''beta'' (β) and ''gamma'' (γ) subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable dimeric complex referred to as the beta-gamma complex . Heterotrimeric G proteins located within the cell ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiamine-triphosphatase
Thiamine-triphosphatase is an enzyme involved in thiamine metabolism. It catalyzes the chemical reaction : thiamine triphosphate + H2O \rightleftharpoons thiamine diphosphate + phosphate This enzyme belongs to the family of acid anhydride hydrolases, specifically those acting on phosphorus-containing anhydrides. Its systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivial ... is thiamine triphosphate phosphohydrolase. Structural studies As of late 2007, only one structure has been solved for this class of enzymes, with the PDB accession code . See also * Thiamine-diphosphate kinase References * EC 3.6.1 Enzymes of known structure {{3.6-enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Barrel
In protein structures, a beta barrel is a beta sheet composed of tandem repeats that twists and coils to form a closed toroidal structure in which the first strand is bonded to the last strand (hydrogen bond). Beta-strands in many beta-barrels are arranged in an antiparallel fashion. Beta barrel structures are named for resemblance to the barrels used to contain liquids. Most of them are water-soluble proteins and frequently bind hydrophobic ligands in the barrel center, as in lipocalins. Others span cell membranes and are commonly found in porins. Porin-like barrel structures are encoded by as many as 2–3% of the genes in Gram-negative bacteria. It has been shown that more than 600 proteins with various function (e.g., oxidase, dismutase, amylase) contain the beta barrel structure. In many cases, the strands contain alternating polar and non-polar (hydrophilic and hydrophobic) amino acids, so that the hydrophobic residues are oriented into the interior of the barrel to form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics. Cofactors typically differ from ligands in that they often derive their function by remaining bound. Cofactors can be divided into two types: inorganic ions and complex organic molecules called coenzymes. Coenzymes are mostly derived from vitamins and other organic essential nutrients in small amounts. (Note that some scientists limit the use of the term "cofactor" for inorganic substances; both types are included here.) Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a "prosthetic group", which consists of a coenzyme that is tightly (or even covalently) and permanently bound to a prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cations
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolyze
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |