|
Polydora Glycymerica
''Polydora glycymerica'' is a species of annelid worm in the family Spionidae, native to the northwestern Pacific Ocean, where it lives commensally in association with a bivalve mollusc, usually ''Glycymeris yessoensis'' but occasionally with another species of clam. The worm intercepts food particles being drawn into the mollusc by its feeding current. Taxonomy This species was first described in 1993 by the Russian marine biologist Vasily I. Radashevsky, who placed it in the genus ''Polydora'' and gave it the specific epithet "''glycymerica''" because of its commensal relationship with the bivalve ''Glycymeris yessoensis''. The new species resembled '' Polydora vulgaris'', a worm from the South China Sea that is also associated with bivalve molluscs, although in this instance, ''Pinctada margaritifera'' and '' Hyotissa hyotis'' are the hosts. Researchers used starch gel electrophoresis to compare the number of isozyme loci and the allozymic variation present in both speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annelid
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments. The Annelids are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate, invertebrate organisms. They also have parapodia for locomotion. Most textbooks still use the traditional division into polychaetes (almost all marine), oligochaetes (which include earthworms) and leech-like species. Cladistic research since 1997 has radically changed this scheme, viewing leeches as a sub-group of oligochaetes and oligochaetes as a sub-group of polychaetes. In addition, the Pogonophora, Echiura and Sipuncula, previously regarded as separate phyla, are now regarded as sub-groups of polycha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules ( DNA, RNA, proteins, etc.) and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size (IEF agarose, essentially size independent) and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge. Nucleic acid molecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the negatively charged molecules through a matrix of agarose or other substances. Shorter molecules move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter molecules migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. This phenomenon is called sieving. Proteins are separated by the charge in agarose because the pores of the gel are too small to sieve proteins. Gel electrophoresis can also be used for the separation of nanoparticles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predation
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it. Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision, hearing, or smell. Many predatory animals, both vertebrate and inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphon (mollusc)
A siphon is an anatomical structure which is part of the body of aquatic molluscs in three classes: Gastropoda, Bivalvia and Cephalopoda (members of these classes include saltwater and freshwater snails, clams, octopus, squid and relatives). Siphons in molluscs are tube-like structures in which water (or, more rarely, air) flows. The water flow is used for one or more purposes such as locomotion, feeding, respiration, and reproduction. The siphon is part of the mantle of the mollusc, and the water flow is directed to (or from) the mantle cavity. A single siphon occurs in some gastropods. In those bivalves which have siphons, the siphons are paired. In cephalopods, there is a single siphon or funnel which is known as a hyponome. In gastropods In some (but not all) sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs, the animal has an anterior extension of the mantle called a siphon, or inhalant siphon, through which water is drawn into the mantle cavity and over the gill for respiration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anadara Broughtonii
Anadara broughtonii is a species of Ark clam. The species was described by Shrenck in 1867. Originally belonging to the genus ''Scapharca'', the genus has merged with ''Anadara'' now. Adult blood clams can reach a shell length of 100 mm and are commercially harvested in China, Japan, and Korea as a source of sashimi. To develop both the scientific research and improve the aquaculture of blood clams, a chromosomal-level genome assembly of the ''S. broughtonii'' genome has been sequenced and assembled, producing a 884.5-Mb genome. Distribution The species is distributed in Far East, from Russia down to Korea, Mainland China, Japan and Taiwan Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort .... References External links {{Taxonbar, from=Q13368000 broughtonii Molluscs describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ark Clam
Ark clam is the common name for a family of small to large-sized saltwater clams or marine bivalve molluscs in the family Arcidae. Ark clams vary both in shape and size. They number about 200 species worldwide. The shells of ark clams are often white or cream, but in some species, the shell is striped with, tinted with, or completely colored, a rich brown. In life the shell of most species has a top shell layer that is thick brown periostracum affixed to the harder calcareous part of the shell. In some species such as '' Barbatia'', this outer horny covering is tufted at the end of the shell into something that resembles a beard, hence the name ''Barbatia'' or bearded one. The group is known as "ark shells" because species such as '' Arca'' have a large flat area between the umbones which, in an undamaged shell, somewhat resembles a deck, with the rest of the shell perhaps illustrating an ancient wooden boat such as Noah's ark is thought to have been. All ark shells have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
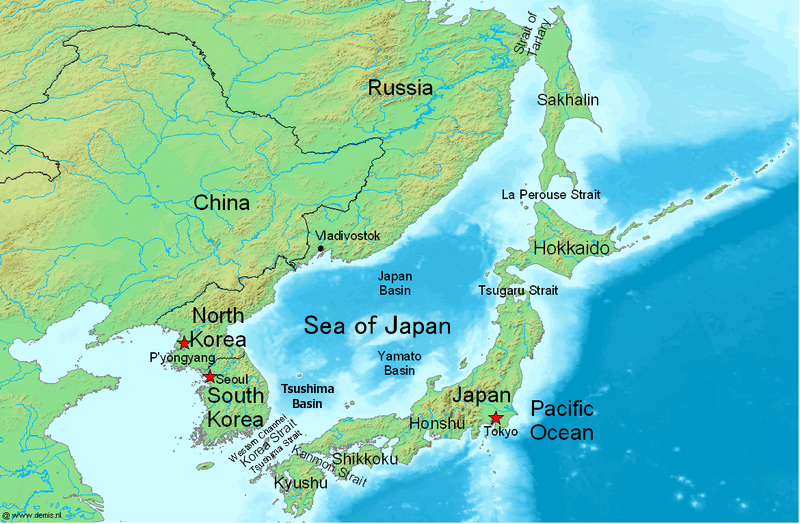
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
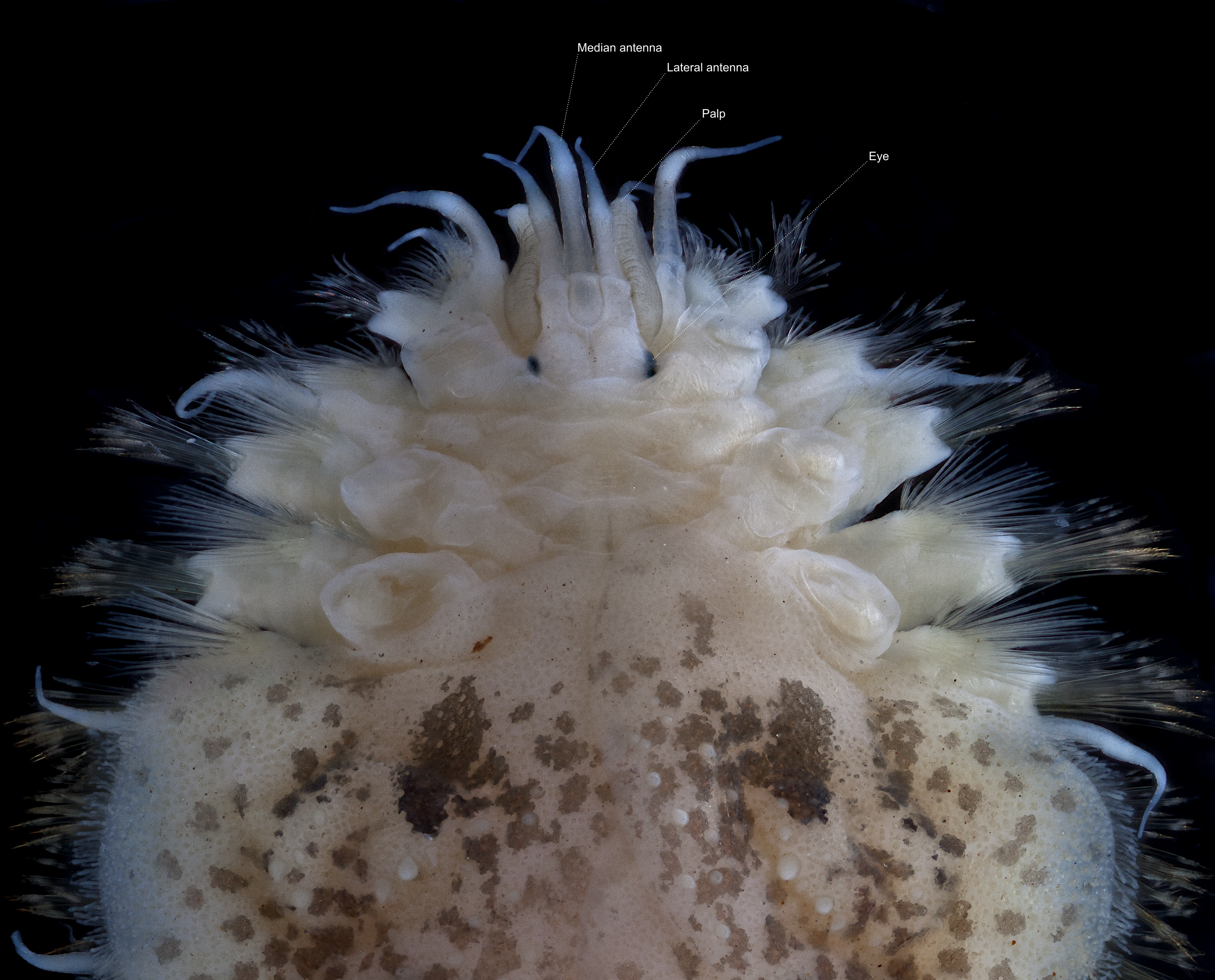
Prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not include) the mouth, being usually a small shelf- or lip-like extension over the dorsal side of the mouth. The prostomium together with the peristomium, which includes the mouth and pharynx, make up the annelid head. Description The prostomium is part of the head and holds at least part of the brain and often bears sensory structures such as the eyes, antennae and palps. It may function like a kind of overlip when the animal is feeding. The prostomium bears many important taxonomic characters and its shape and composition are important for annelid systematics. In addition to the eyes, antennae and palps, the prostomium can possess appendages such as tentacles or cirri. Moreover, some polychaete prostomia have a posterior extension or ridge with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allozyme
Alloenzymes (or also called allozymes) are variant forms of an enzyme which differ structurally but not functionally from other allozymes coded for by different alleles at the same locus. These are opposed to isozymes, which are enzymes that perform the same function, but which are coded by genes located at different loci. Alloenzymes are common biological enzymes that exhibit high levels of functional evolutionary conservation throughout specific phyla and kingdoms. They are used by phylogeneticists as molecular markers to gauge evolutionary histories and relationships between different species. This can be done because allozymes do not have the same structure. They can be separated by capillary electrophoresis. However, some species are monomorphic for many of their allozymes which would make it difficult for phylogeneticists to assess the evolutionary histories of these species. In these instances, phylogeneticists would have to use another method to determine the evolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isozyme
In biochemistry, isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. Isozymes usually have different kinetic parameters (e.g. different ''K''M values), or are regulated differently. They permit the fine-tuning of metabolism to meet the particular needs of a given tissue or developmental stage. In many cases, isozymes are encoded by homologous genes that have diverged over time. Strictly speaking, enzymes with different amino acid sequences that catalyse the same reaction are isozymes if encoded by different genes, or allozymes if encoded by different alleles of the same gene; the two terms are often used interchangeably. Introduction Isozymes were first described by R. L. Hunter and Clement Markert (1957) who defined them as ''different variants of the same enzyme having identical functions and present in the same individual''. This definition encompasses (1) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Honeycomb Oyster
The giant honeycomb oyster (''Hyotissa hyotis'') is a very large saltwater oyster, a marine bivalve mollusk. Species in this family are known as honeycomb oysters or "foam oysters" because under magnification, their shell structure is foam-like. Like most bivalves, the giant honeycomb oyster is a filter feeder. Image:Hyotissa hyotis Mamoudzou.jpg, shallow in Mayotte Image:Hyotissa hyotis (3).jpg, Deeper Image:Hyotissa hyotis (2).jpg, Recently dead specimen Image:Hyotissa hyotis - Kyoto University Museum - DSC06407.JPG Image:Naturalis Biodiversity Center - RMNH.MOL.319515 1 - Hyotissa hyotis (Linnaeus, 1758) - Gryphaeidae - Mollusc shell.jpeg Image:Naturalis Biodiversity Center - ZMA.MOLL.4827 - Hyotissa hyotis (Linnaeus, 1758) - Gryphaeidae - Mollusc shell.jpeg Habitat and range Its native range is in deeper water in the Indo-Pacific Ocean. It has however also been found recently as an accidentally introduced species in the Florida Keys The Florida Keys are a coral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spionidae
Spionidae is a family of marine worms within the Polychaeta. Spionids are selective deposit feeders that use their two grooved palps Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") a ... to locate prey. However, some spionids are capable of interface feeding, i.e. switching between deposit and suspension feeding. Spionids produce tubes by cementing sand grains and detritus material with mucus produced by their glandular pouches. The Spionidae is one of the most studied polychaete families given their biological and commercial importance. Members of this family have been used in regeneration studies and some are capable of boring into calcareous substrate which has destructive implications for commercially important shellfish. References Annelid families Canalipalpata {{a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_with_its_prey.jpg)