|
Poliudie
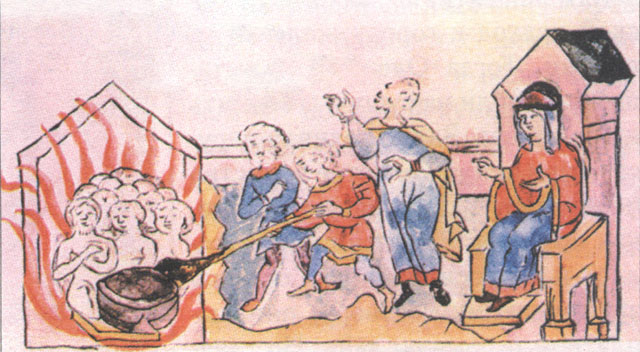
The ''poliudie'' (russian: полюдье) was the practice of gathering tribute by the rulers of Kievan Rus' from vassal East Slavic and Finnic tribes. It was similar to the "right of hospitality" as practised in the Viking lands (where it was known as '' veizla'') and early medieval Poland (where it was known as ''stan''). The ''poliudie'' (Greek: πολύδια) was described in ''De Administrando Imperio'' by the Byzantine emperor Constantine Porphyrogenitus. In winter, the ruler of Kiev went out on rounds, visiting Dregovichs, Krivichs, Drevlians, Severians, and other subordinated tribes. Some paid tribute in money, some in furs or other commodities, and some in slaves. In April, the prince returned to Kiev. The Primary Chronicle suggests Olga of Kiev changed the method of gathering tribute. The chronicle reports that Olga's husband, Igor, was killed by the Drevlians angered at his attempt to collect more tribute than it had been agreed. After his death, Olga appointed her ow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p.14–16.Kievan Rus Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encompassing a variety of polities and peoples, including East Slavic, Norse, and Finnic, it was ruled by the , fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igor I Of Kiev
Igor the Old (Old East Slavic: , ''Igor''; russian: Игорь Рюрикович; uk, Ігор Рюрикович; Old Norse: '; died 945) was a Rurikid ruler of Kievan Rus' from 912 to 945. Biography Information about Igor comes mostly from the ''Primary Chronicle''. This document has Igor as the son of Rurik, the first ruler of Kievan Rus': 6378–6387 (870–879). On his deathbed, Rurik bequeathed his realm to Oleg, who belonged to his kin, and entrusted to Oleg's hands his son Igor', for he was very young. 6388–6390 (880–882). Oleg set forth, taking with him many warriors from among the Varangians, the Chuds, the Slavs, the Merians and all the Krivichians. He thus arrived with his Krivichians before Smolensk, captured the city, and set up a garrison there. Thence he went on and captured Lyubech, where he also set up a garrison. He then came to the hills of Kiev, and saw how Askold and Dir reigned there. He hid his warriors in the boats, left some others behind, and wen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olga Of Kiev
Olga ( orv, Вольга, Volĭga; (); russian: Ольга (); uk, Ольга (). Old Norse: '; Lithuanian language, Lith: ''Alge''; Christian name: ''Elena''; c. 890–925 – 969) was a regent of Kievan Rus' for her son Sviatoslav I of Kiev, Sviatoslav from 945 until 960. Following her baptism, Olga took the name Elenа ( orv, Ѡлена, Olena).''Primary Chronicle'' 82. She is known for her subjugation of the Drevlians, a tribe that had killed her husband Igor of Kiev. Even though it was her grandson Vladimir the Great, Vladimir who converted the entire nation to Christianity, because of her efforts to spread Christianity through Rus', Olga is venerated as a saint in the Eastern Orthodox Church with the epithet "Equal-to-apostles, Equal to the Apostles". Her Calendar of saints, feast day is 11 July. Life Early life While Olga's birthdate is unknown, it could be as early as 890 AD and as late as 925 AD. According to the ''Primary Chronicle,'' Olga was of Varangians, Vara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Prince Takes Tribute By Roerich
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including: *Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries *Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and people of Russia, regardless of ethnicity *Russophone, Russian-speaking person (, ''russkogovoryashchy'', ''russkoyazychny'') *Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages *Russian alphabet *Russian cuisine *Russian culture *Russian studies Russian may also refer to: *Russian dressing *''The Russians'', a book by Hedrick Smith *Russian (comics), fictional Marvel Comics supervillain from ''The Punisher'' series *Russian (solitaire), a card game * "Russians" (song), from the album ''The Dream of the Blue Turtles'' by Sting *"Russian", from the album ''Tubular Bells 2003'' by Mike Oldfield *"Russian", from the album '' '' by Caravan Palace *Nik Russian, the perpetrator of a con committed in 2002 *The South African name for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dregovichs
The Dregoviches or Dregovichi ( Belarusian: дрыгавічы, ''dryhavičy'', ; russian: дреговичи, dregovichi; ua, дреговичі, drehovychi) were one of the tribal unions of Early East Slavs, and inhabited the territories down the stream of the Pripyat River and northern parts of the right bank of the Dnieper river (more exact extents of the tribe's domain are still unknown). The name of the tribe probably derives from the Old Ruthenian word дрегва or дрягва (''drehva'', or ''dryahva'', which means "swamp") because the Dregoviches used to live in the marshlands. The first known reference to the Dregoviches is in the ''Primary Chronicle'', where they are listed among the twelve tribes. However, there is a reference in the ''De Administrando Imperio'' of ''Constantine Porphyrogenitus'' to the 'Drugovichians'. Since the reference appears in a passage describing the Drugovichians as one of the Slavic peoples who pay tribute to the Kievan Rus, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russkaya Pravda
The ''Russkaya Pravda'' (Rus' Justice, Rus' Truth, or Russian Justice; orv, Правда роусьскаꙗ, ''Pravda Rusĭskaya'' (13th century, 1280), Правда Руськая, ''Pravda Rus'kaya'' (second half of the 15th century); russian: Русская правда, ''Russkaya Pravda''; uk, Руська Правда, ) was the legal code of Kievan Rus' and the subsequent Rus' people, Rus' principalities during the times of feudal division. It was written at the beginning of the 12th century and remade during many centuries. The basis of the ''Russkaya Pravda'', Pravda of Yaroslav the Wise, Yaroslav was written at the beginning of the 11th century. The ''Russkaya Pravda'' was a main source of Old Rus' Law. In spite of great influence of Byzantine empire, Byzantine legislation on the contemporary world, and in spite of great cultural and commercial ties between Byzantium and Kievan Rus', the ''Russkaya Pravda'' bore no similarity whatsoever to that of the Byzantine Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentin Yanin
Valentin Lavrentievich Yanin (russian: Валентин Лаврентьевич Янин; 6 February 1929 – 2 February 2020) was a leading Russian historian who authored 700 books and articles. He had also edited a number of important journals and primary sources, including works on medieval Russian law, sphragistics and epigraphy, archaeology and history. His expertise was medieval Rus' especially Novgorod the Great, where he had headed archaeological digs beginning in 1962. Early life Yanin was born in Vyatka. His maternal grandparents were arrested in 1937 and died in a prison camp in 1938. His father was apparently on a list to be executed but escaped this fate and moved with his family to Moscow. Yanin finished his secondary education in 1946, graduating with a Gold Medal; he matriculated at Moscow State University in 1951. Research In 1954, he defended his Kandidat thesis on the monetary systems of pre-Mongol Rus. This was published as ''The Monetary and Weight Syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ''Primary Chronicle'', as well as also, after the author it has traditionally been ascribed to, '' Nestor's Chronicle'', is an Old East Slavic chronicle (letopis) of Kievan Rus' from about 850 to 1110, originally compiled in Kiev around 1113. The work’s name originates from the opening sentence of the text, which reads: “These are the narratives of bygone years regarding the origin of the land of Rus’ (Old East Slavic: Рѹсь), the first princes of Kyiv, and from what source the land of Rus’ had its beginning.” The work has long been considered to be a fundamental source in the interpretation of the history of the East Slavs. The ''Chronicle's'' content is known today from several surviving editions and codices that have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severians
The Severians or Severyans or Siverians ( be, Севяране; bg, Севери; russian: Северяне; uk, Сiверяни, translit=Siveriany) were a tribe or tribal confederation of early East Slavs occupying areas to the east of the middle Dnieper River and southeast of the Danube River. They are mentioned by the Bavarian Geographer (9th century), Emperor Constantine VII (956–959), the Khazar ruler Joseph (c. 955), and in the Primary Chronicle (1113). Ethnonym The etymology of the name "Severian" is uncertain. The name of the Severia region originated from the Slavic tribes. One theory proposes derivation from the Slavic word for "north" (''sěver''; men of the north), but the Severians never were the northernmost tribe of Slavs. Another theory proposes an Iranic derivation, from the name of the Sarmatian ''Seuer'' tribe (''seu'' meaning "black"). Some scholars have argued that Jews called this tribe the ''Sawarta,'' based on the ''Kievan Letter'' (c. 930), written in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drevlians
The Drevlians ( uk, Древляни, Drevliany, russian: Древля́не, Drevlyane) were a tribe of Early East Slavs between the 6th and the 10th centuries, which inhabited the territories of Polesia and right-bank Ukraine, west of the eastern Polans and along the lower reaches of the rivers Teteriv, Uzh, Ubort, and Stsviha. To the west, the Drevlians' territories reached the Sluch River, where the Volynians (related to the territory of Volynia) and Buzhans (related to the name of Southern Bug river) lived. To the north, the Drevlians' neighbors were the Dregovichs. Ethnonym Their name is derived from Slavic ''drevo/древо'' or ''derevo/дерево'', meaning "wood" and "tree", because they lived in the forests. Their name may be rendered "the dwellers in the forest". They possibly were mentioned as ''Forsderen-Liudi'' by Bavarian Geographer in the 9th century. Nestor the Chronicler (1056–1114) mentioned that those Slavs who settled in open fields had been called ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krivichs
The Krivichs (Kryvichs) ( be, крывічы, kryvičý, ; rus, кри́вичи, p='krʲivʲɪtɕɪ, kríviči) were a tribal union of Early East Slavs The early Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies who lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately the 5th to the 10th centuries AD) in Central and Eastern Europe and established the foundations for the Slav ... between the 6th and the 12th centuries. It is suggested that originally the Krivichi were native to the area around Pskov. They migrated to the mostly Volga Finns, Finnic areas in the upper reaches of the Volga, Dnieper, Western Dvina, Dvina, areas south of the lower reaches of river Velikaya River, Velikaya and parts of the Neman River, Neman drainage basin, basin. In some variants of Belarusiphile Anti-Normanism, anti-normanist history, the city, and later principality of Polotsk is linked to Krivichians, much like Kyiv is linked to Polianians, however, based on most modern evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by population within city limits, seventh-most populous city in Europe. Kyiv is an important industrial, scientific, educational, and cultural center in Eastern Europe. It is home to many High tech, high-tech industries, higher education institutions, and historical landmarks. The city has an extensive system of Transport in Kyiv, public transport and infrastructure, including the Kyiv Metro. The city's name is said to derive from the name of Kyi, one of its four legendary founders. During History of Kyiv, its history, Kyiv, one of the oldest cities in Eastern Europe, passed through several stages of prominence and obscurity. The city probably existed as a commercial center as early as the 5th century. A Slavs, Slavic settlement on the great trade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.jpg)
.jpg)