|
Pokhari, Sagarmatha
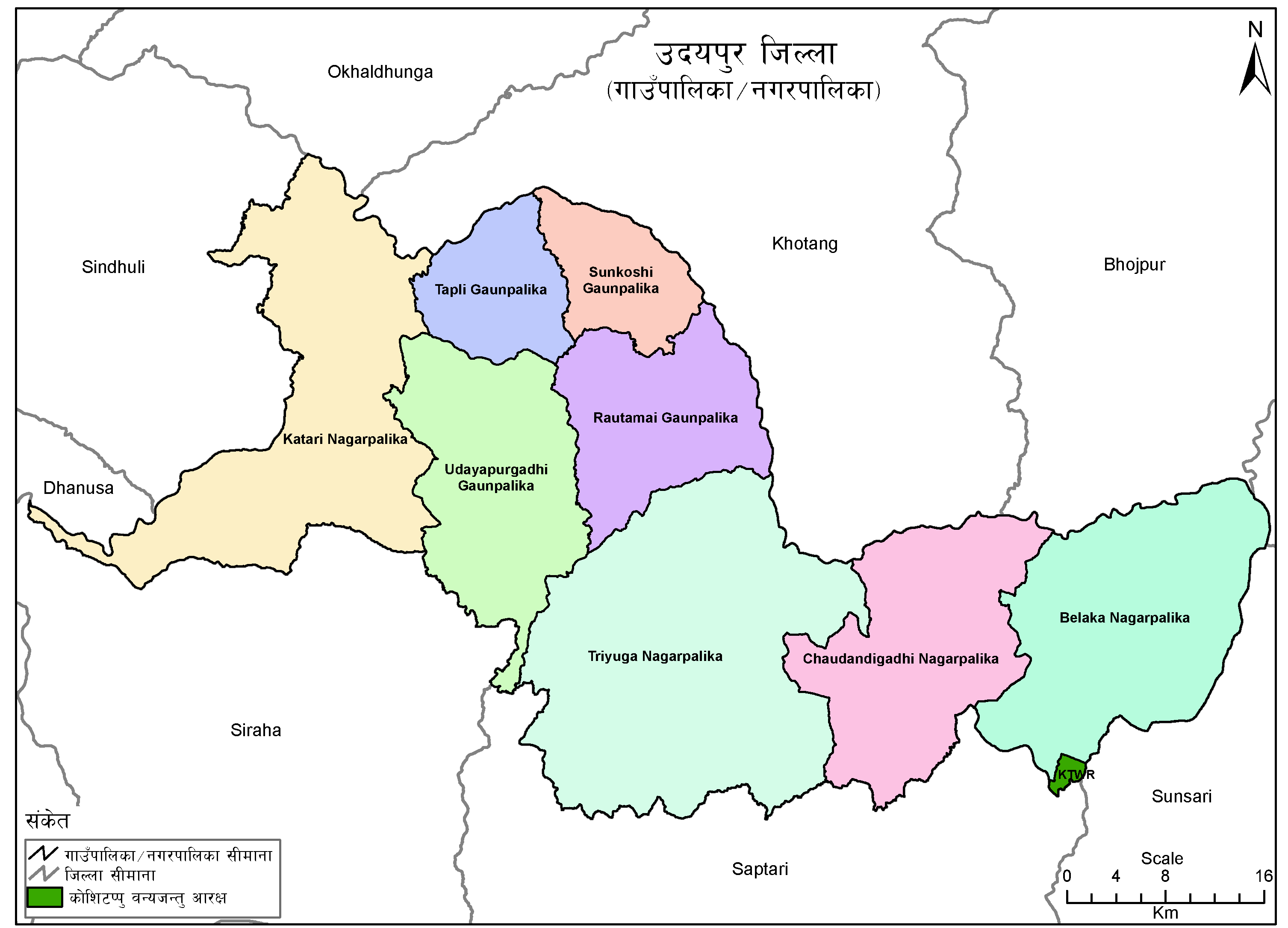
Pokhari was a village development committee in Udayapur District in the Sagarmatha Zone of Eastern Development Region of Nepal. It became part of Rautamai Rural Municipality after reconstruction of administration in Nepal. Fulfilling the requirement of the new constitution of Nepal in 2015, all old municipalities and villages (which were more than 3900 in number) were restructured into 753 new units. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census The 1991 Nepal census was a widespread national census conducted by the Nepal Central Bureau of Statistics. Working with Nepal's Village Development Committees at a district level, they recorded data from all the main towns and villages of each ... it had a population of 2550 people living in 454 individual households. References External linksUN map of the municipalities of Udayapur District Populated places in Udayapur District Rautamai {{Udayapur-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neighborhood
A neighbourhood (British English, Irish English, Australian English and Canadian English) or neighborhood (American English; see spelling differences) is a geographically localised community within a larger city, town, suburb or rural area, sometimes consisting of a single street and the buildings lining it. Neighbourhoods are often social communities with considerable face-to-face interaction among members. Researchers have not agreed on an exact definition, but the following may serve as a starting point: "Neighbourhood is generally defined spatially as a specific geographic area and functionally as a set of social networks. Neighbourhoods, then, are the spatial units in which face-to-face social interactions occur—the personal settings and situations where residents seek to realise common values, socialise youth, and maintain effective social control." Preindustrial cities In the words of the urban scholar Lewis Mumford, "Neighbourhoods, in some annoying, inchoate fashi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
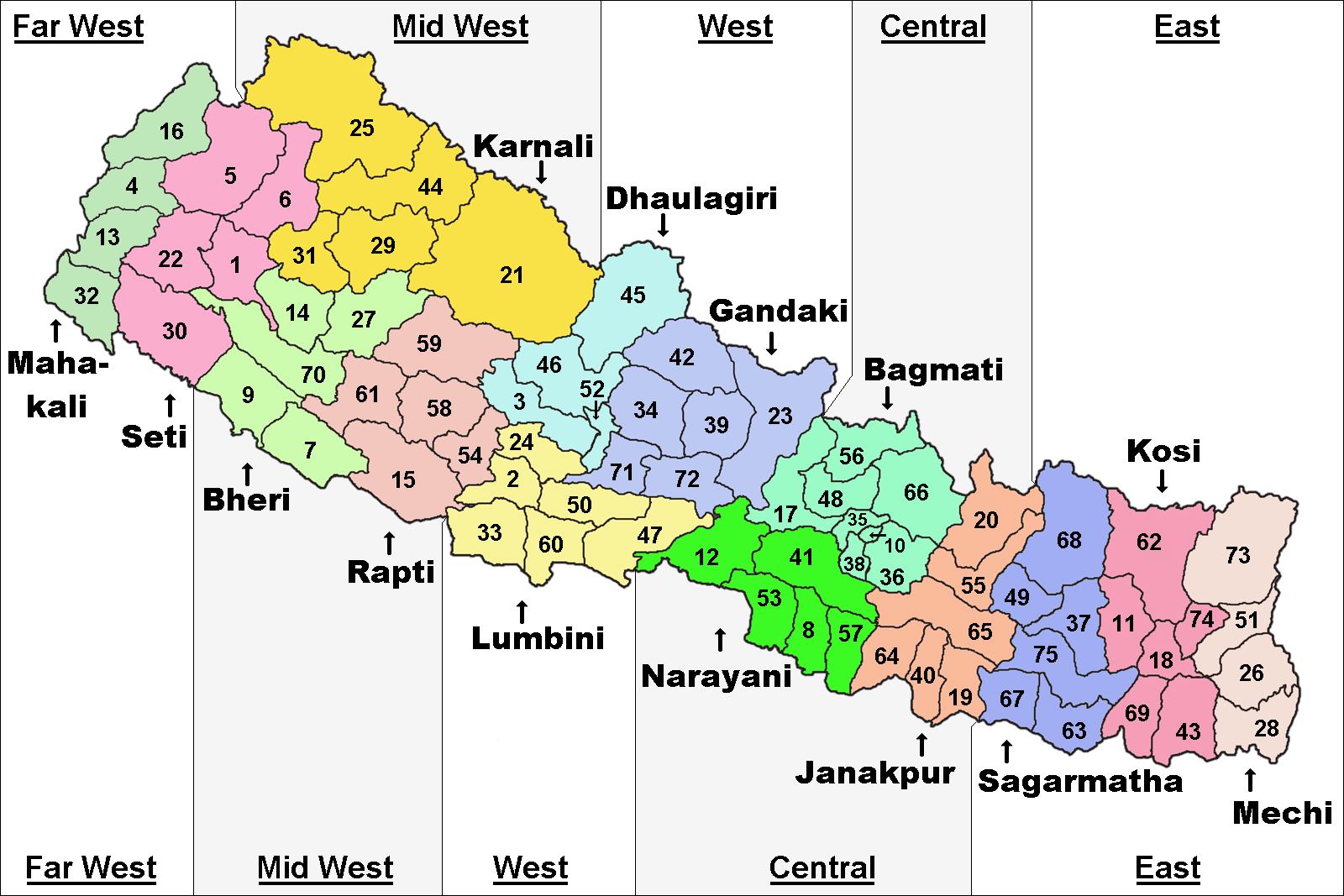
Sagarmatha Zone
Sagarmāthā Zone ( ne, सगरमाथा अञ्चल) or Sagarmatha Anclal ( ne, सगरमाथा अञ्चल) was one of the fourteen zones of Nepal until the restructuring of zones into provinces. The headquarters of Sagarmatha is Rajbiraj. ''Sagarmāthā'' is a Nepali word derived from सगर (sagar) meaning "sky" and माथा (māthā) meaning "head". It includes mountain districts of the Himalayas (including the world's highest peak Mount Everest) in the north, hill districts in the center, and valley districts of the Terai in the south. It is bordered by China to the north, India to the south, the Koshi Zone to the east and the Janakpur Zone to the west. Administrative subdivisions Sagarmāthā was divided into six districts; since 2015 the four northern districts have been redesignated as part of Province No. 1, while the two southernmost districts have been resigned as part of Province No. 2. The main city of the Sagarmāthā Zone was Rajbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Himalaya
The Digital Himalaya project was established in December 2000 by Mark Turin, Alan Macfarlane, Sara Shneiderman, and Sarah Harrison. The project's principal goal is to collect and preserve historical multimedia materials relating to the Himalaya, such as photographs, recordings, and journals, and make those resources available over the internet and offline, on external storage media. The project team have digitized older ethnographic collections and data sets that were deteriorating in their analogue formats, so as to protect them from deterioration and make them available and accessible to originating communities in the Himalayan region and a global community of scholars. The project was founded at the Department of Anthropology of the University of Cambridge, moved to Cornell University in 2002 (when a collaboration with the University of Virginia was initiated), and then back to the University of Cambridge in 2005. From 2011 to 2014, the project was jointly hosted between the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1991 Nepal Census
The 1991 Nepal census was a widespread national census conducted by the Nepal Central Bureau of Statistics. Working with Nepal's Village Development Committees at a district level, they recorded data from all the main towns and villages of each district of the country. The data included statistics on population size, households, sex and age distribution, place of birth, residence characteristics, literacy, marital status, religion, language spoken, caste/ethnic group, economically active population, education, number of children, employment status, and occupation. This census was followed by the 2001 Nepal census. References See also * List of village development committees of Nepal (Former) * 2001 Nepal census * 2011 Nepal census Censuses in Nepal Nepal Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne, सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kantipur Publication
Kantipur Publications Pvt. Ltd. ( ne, कान्तिपुर पब्लिकेशन्स प्रा. लि.) is a media firm based in Kathmandu, Nepal. The company operates five widely circulated print publications. It is the first media organization in Nepal to gain membership to the World Association of Newspapers and News Publishers (WAN). It was founded by Shyam Goenka in 1993 AD. Mr. Kailash Sirohiya is the chairman of the company. History In February 1993, exactly two years after Nepal's constitution was amended to permit a free press, ''Kantipur'' and ''The Kathmandu Post'' were founded by Shyam Goenka, when he was 29 years old. In fact, he had taken the initiative to start the newspapers, with very limited resources, when just about everybody dismissed his efforts to start a private media house as a bad business move. However, Kantipur defied all naysayers and went on to write a history of its own – perhaps the greatest success story for a corporate in Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Himalayan Times
''The Himalayan Times'' is an English-language broadsheet newspaper published and distributed daily in Nepal Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne, सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mai .... Rajan Pokhrel is the acting editor. In the annual newspaper classification report published by Press Council Nepal,it was placed in the A+ category, the highest possible rank. The newspaper was founded on 23 November 2001. It is based in Maharajgunj, Kathmandu. It is owned by International Media Network Nepal (Pvt) Ltd which in turn is owned by a Nepali investors. The paper's competitors tried to organise and lobby against the entry of foreign-owned newspaper in the country, but were not successful. At the time of its founding, it published in 12 pages, six of them coloured, and was priced as Rs 2. Within a year, it had b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne, सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, bordering the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, and India in the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a diverse geography, including fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious and multi-cultural state, with Nepali as the official language. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and the largest city. The name "Nepal" is first recorded in texts from the Vedic period of the India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Development Region, Nepal
The Eastern Development Region ( Nepali: पुर्वाञ्चल विकास क्षेत्र, ''Purwānchal Bikās Kshetra'') was one of Nepal's five development regions. It is also known as Kirata region. It was located at the eastern end of the country with its headquarters at Dhankuta. The town of Dhankuta was the headquarter of the Eastern Region, as well as the headquarter of the Dhankuta District. History On April 13, 1961 Mahendra, the king of Nepal, divided the existing 35 districts into 75 districts and grouped them into 14 administrative zones. In 1972, the King of Nepal grouped 14 zones into total 4 development regions, thus Eastern Development Region came into existence. On 20 September 2015, Eastern Development Region including all other development regions of Nepal were abolished, when the new Constitution of Nepal-2015 was proclaimed. The total area of the region was 28,456 km². Administrative divisions The region administratively was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village Development Committee (Nepal)
A village development committee ( ne, गाउँ विकास समिति; ''gāum̐ vikās samiti'') in Nepal was the lower administrative part of its Ministry of Federal Affairs and Local Development. Each district had several VDCs, similar to municipalities but with greater public-government interaction and administration. There were 3,157 village development committees in Nepal. Each village development committee was further divided into several wards ( ne, वडा) depending on the population of the district, the average being nine wards. Purpose The purpose of village development committees is to organise village people structurally at a local level and creating a partnership between the community and the public sector for improved service delivery system. A village development committee has status as an autonomous institution and authority for interacting with the more centralised institutions of governance in Nepal. In doing so, the village development co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Nepal
The provinces of Nepal ( ne, नेपालका प्रदेशहरू, translit=Nepālkā Pradeśharū) were formed on 20 September 2015 in accordance with Schedule 4 of the Constitution of Nepal. The seven provinces were formed by grouping the existing List of districts in Nepal, districts. The current system of seven provinces replaced an earlier system where Nepal was divided into 14 List of zones of Nepal, administrative zones which were grouped into five Development regions of Nepal, development regions. History A committee was formed to restructure administrative divisions of Nepal on 23 December 1956 and in two weeks, a report was submitted to the government. In accordance with The ''Report On Reconstruction Of Districts Of Nepal, 2013'' (), the country was first divided into total 7 ''Kshetras'' (area). # (Unnamed) # Madesh Kshetra # Bagmati Kshetra # Gandaki Kshetra # Lumbini Kshetra # Karnali Kshetra # Mahakali Kshetra In 1962, all ''Kshetras'' were dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal Time
Nepal Standard Time (NPT) is the time zone for Nepal. With a time offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) of UTC+05:45 all over Nepal, it is one of only three time zones with a 45-minute offset from UTC.The others are Chatham Island Standard Time, with an offset of UTC+12:45, and the unofficial Australian Central Western Time, with an offset of UTC+08:45. NPT is an approximation of Kathmandu mean time, which is 5:41:16 ahead of UTC. The standard meridian passes through the peak of Gaurishankar mountain about east of Kathmandu. Nepal used local solar time until 1920, in Kathmandu UTC+05:41:16. In 1920, Nepal adopted Indian Standard Time, UTC+05:30. In 1986 Nepal advanced their clocks by 15 minutes, giving them a time zone of UTC+05:45. See also *Date and time notation in Nepal Nepal uses both the DMY and YMD format when writing dates, and uses 12-hour format for time. Date YYYY-MM-DD is official date format for the Bikram Sambat calendar used in Nep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rautamai
Rautamai Rural Municipality ( ne, रौतामाई गाउँपालिका) is a rural municipality in Udayapur district of Province No. 1 in Nepal. There are 4 rural municipalities in Udayapur district. There are 8 wards in this municipality. According to 2011 census of Nepal, the total population of the municipality is 23,481 and total area is 204 km². The headquarter of the municipality is in Bhuttar The rural municipality was established on March 10, 2017 when Ministry of Federal Affairs and Local Development dissolved the existing village development committees and announced the establishment of this new local body. Nametar, Bhuttar Bhuttar was a village development committee in Udayapur District in the Sagarmatha Zone of Eastern Development Region of Nepal. It became part of Rautamai Rural Municipality after reconstruction of administration in Nepal. It is now municipal h ..., Laphagaun, Pokhari, Rauta and Aaptar VDCs were merged to form the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |