|
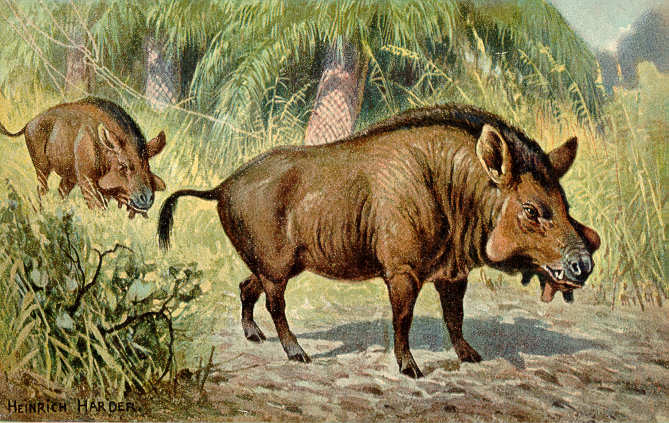
Poabromylus
''Poabromylus'' is an extinct genus of small artiodactyl, of the family Protoceratidae, endemic to North America. They lived during the Late Eocene 40.4—33.9 Ma, existing for approximately . They resembled deer but were more closely related to camelids. Fossil distribution Fossils have been recovered from: *Big Red Horizon, Chambers Tuff Formation, Presidio County, Texas *Titus Canyon, Titus Canyon Formation, Inyo County, California *Titanothere Quarry, Duchesne River Formation, Uintah County, Utah *Badwater Locality, Wagon Bed Formation The Wagon Bed Formation is a geologic formation in Wyoming. It preserves fossils dating back to the Paleogene period. See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Wyoming * Paleontology in Wyoming Paleontology in Wyoming includes r ..., Natrona County, Wyoming References Eocene even-toed ungulates Priabonian genus extinctions Eocene mammals of North America Fossil taxa described in 1931 Prehistoric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoceratidae
Protoceratidae is an extinct family of herbivorous North American artiodactyls (even-toed ungulates) that lived during the Eocene through Pliocene at around 46.2—4.9 Mya, existing for about 41 million years. Classification Protoceratidae was erected by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1891, with the type genus ''Protoceras'' and assigned to the Artiodactyla. It was later assigned to Pecora, and more recently to Ruminantia or Tylopoda. However, recently a relationship to chevrotains in the infraorder Tragulina has been proposed. Morphology When alive, protoceratids would have resembled deer, though they were not directly related. Protoceratids ranged from 1 to 2 m in length, from about the size of a roe deer to an elk. Unlike many modern ungulates, they lacked cannon bones in their legs. Their dentition was similar to that of modern deer and cattle, suggesting they fed on tough grasses and similar foods, with a complex stomach similar to that of camels. At least some forms are beli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchesne River Formation
The Duchesne River Formation is a geologic formation in the Uintah Basin of northeastern Utah Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it .... It was originally named the Duchesne Formation by Carnegie Museum paleontologist OA Peterson, and modified to the Duchesne River Formation by Carnegie Museum paleontologist JL Kay because Duschesne Formation was previously used for a Jurassic limestone. In naming the formation, no type section was given, only that it is named for the Duchesne River, which flows roughly southeast and east to join the Green River. The formation consists of over 3000 feet (915 m) of fluvial conglomerate, sandstone and fine-grained sedimentary rocks. It is subdivided into four members (below), whose sediments are thought to have eroded from the rising Uinta M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Mammals Of North America
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priabonian Genus Extinctions
The Priabonian is, in the ICS's geologic timescale, the latest age or the upper stage of the Eocene Epoch or Series. It spans the time between . The Priabonian is preceded by the Bartonian and is followed by the Rupelian, the lowest stage of the Oligocene. Stratigraphic definition The Priabonian Stage was introduced in scientific literature by Ernest Munier-Chalmas and Albert de Lapparent in 1893. The stage is named after the small hamlet of Priabona in the community of Monte di Malo, in the Veneto region of northern Italy. The base of the Priabonian Stage is at the first appearance of calcareous nannoplankton species ''Chiasmolithus oamaruensis'' (which forms the base of nanoplankton biozone NP18). An official GSSP was ratified in 2020, and was placed in the Alano di Piave section in Alano di Piave, Belluno, Italy. The top of the Priabonian Stage (the base of the Rupelian Stage and Oligocene Series) is at the extinction of foram genus ''Hantkenina''. Sometimes local rock s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Even-toed Ungulates
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and end of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natrona County, Wyoming
Natrona County is a county in the U.S. state of Wyoming. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 79,955, making it the second-most populous county in Wyoming. Its county seat is Casper. Natrona County comprises the Casper, WY Metropolitan Statistical Area. In 2010, the center of population of Wyoming was in Natrona County, near Alcova. History Prior to Wyoming's settlement by European-based populations, the area's stretches played host to nomadic tribes such as Cheyenne, Arapaho, Shoshone, and Sioux. New York investor John Jacob Astor established the settlement of Astoria on the Columbia River, and sent Robert Stuart eastward to blaze a trail and lay the foundation of a string of trading posts. Stuart documented the South Pass Route through the Continental Divide, near the SW corner of present-day Natrona County. Stuart's company erected the first hut in the area in 1812, near present-day Bessemer Bend. In 1840, Father Pierre-Jean De Smet began preachin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wagon Bed Formation
The Wagon Bed Formation is a geologic formation in Wyoming. It preserves fossils dating back to the Paleogene period. See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Wyoming * Paleontology in Wyoming Paleontology in Wyoming includes research into the prehistoric life of the U.S. state of Wyoming as well as investigations conducted by Wyomingite researchers and institutions into ancient life occurring elsewhere. The fossil record of the US stat ... References * Paleogene geology of Wyoming {{Paleogene-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uintah County, Utah
Uintah County ( ) is a county in the U.S. state of Utah. As of the 2020 United States Census the population was 35,620. Its county seat and largest city is Vernal. The county was named for the portion of the Ute Indian tribe that lived in the basin. Uintah County is the largest natural gas producer in Utah, with 272 billion cubic feet produced in 2008. The Vernal, UT Micropolitan Statistical Area includes all of Uintah County. History Archeological evidence suggests that portions of the Uinta Basin have been inhabited by Archaic peoples and Fremont peoples. By the time of recorded history, its inhabitants were the Ute people. The first known traverse by non-Indians was made by Fathers Domínguez and Escalante (1776), as they sought to establish a land route between California and Spanish America. The region was claimed by the Spanish Empire as the Alta California division of New Spain (1521-1821) and was later under Mexican control (1821-1848). By the early nine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inyo County, California
Inyo County () is a county in the eastern central part of the U.S. state of California, located between the Sierra Nevada and the state of Nevada. In the 2020 census, the population was 19,016. The county seat is Independence. Inyo County is on the east side of the Sierra Nevada and southeast of Yosemite National Park in Central California. It contains the Owens River Valley; it is flanked to the west by the Sierra Nevada and to the east by the White Mountains and the Inyo Mountains. With an area of 10,192 square miles (26,397 km2), Inyo County is the second-largest county by area in California, after San Bernardino County. Almost one-half of that area is within Death Valley National Park. However, with a population density of 1.8 people per square mile, it also has the second-lowest population density in California, after Alpine County. History Present-day Inyo county has been the historic homeland for thousands of years of the Mono, Timbisha, Kawaiisu, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artiodactyla
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |