|
Plaxton Derwent 3000
The Plaxton Derwent 3000 was a step entrance single-decker bus body built by Plaxton. It was introduced in 1986, and is not related to the earlier body which was built between 1962 and 1977, with the same name. Around 250 were built, almost four times as many as its predecessor, the Plaxton Bustler, over a similar number of years. It was built mainly on mid-engined chassis, although a small number of Scania K93 -engined chassis were also bodied. The most common chassis was the Leyland Tiger, largely due to orders from the UK military for over a hundred, some of which were left-hand drive. Other chassis were the Volvo B10M (including short wheelbase examples); some of the last Bedford Y series to enter service; Dennis Javelin; and around fifteen secondhand Leyland Leopard chassis being rebodied. The Derwent 3000 was superseded by the Plaxton Verde from 1991. Body numbering In the pre-1989 system of body numbers, the Derwent 3000 initially took the code D1B. This later be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leyland Tiger
The Leyland Tiger, also known as the B43, was a mid-engine design, mid-engined bus and coach (bus), coach chassis manufactured by Leyland Bus, Leyland between 1981 and 1992. This name had previously been used for a front-engined bus built between 1927 and 1968. It replaced the Leyland Leopard, which had been in production for over 20 years. History The Leyland Tiger was released in 1981. Initially, only one engine was offered, the turbocharged Leyland TL11, which could be rated up to 260 hp. The Leopard had enjoyed huge success as a bus in Scotland, usually with the Alexander Y-type body, but had lost some Scottish Bus Group orders to Seddon Atkinson, Seddon's Seddon Pennine 7, Pennine 7, owing to Leyland's unwillingness to offer a L Gardner and Sons Ltd, Gardner engine in the Leopard. When Leyland launched the Tiger, it continued this same unwillingness, just as Dennis was developing the Gardner-engined Dennis Dorchester, which similarly had the potential to win Scotti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coachwork
A coachbuilder or body-maker is someone who manufactures bodies for passenger-carrying vehicles.Construction has always been a skilled trade requiring a relatively lightweight product with sufficient strength. The manufacture of necessarily fragile, but satisfactory wheels by a separate trade, a wheelwright, held together by iron or steel tyres, was always most critical. From about AD 1000 rough vehicle construction was carried out by a ''wainwright'', a wagon-builder. Later names include ''cartwright'' (a carpenter who makes carts, from 1587); ''coachwright''; and ''coachmaker'' (from 1599). Subtrades include ''wheelwright'', ''coachjoiner'', etc. The word ''coachbuilder'' first appeared in 1794. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' 2011 Coachwork is the body of an automobile, bus, horse-drawn carriage, or railway carriage. The word "coach" was derived from the Hungarian town of Kocs. Coachbuilt body is the British English name for the coachbuilder's product. ''Custom body'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaxton Buses
Plaxton is an English builder of bus and coach vehicle bodies based in Scarborough. Founded in 1907 by Frederick William Plaxton, it became a subsidiary of Alexander Dennis in May 2007. In 2019, the maker was acquired by Canadian bus manufacturer New Flyer which then became NFI Group. History Beginnings The business was founded as a joinery workshop, and expanded into building contracting. As a building contractor, Plaxtons built a number of notable buildings in Scarborough. Soon after World War I Plaxtons diversified and began to build charabanc bodies on Ford Model T chassis. Of more importance at the time was the construction of automobile bodywork. This included bodywork for Rolls-Royce, Sunbeam and Daimler, but principally for Crossley car chassis. This activity continued through the 1920s, but the depression of 1929–1933 created difficulties for manufacture of luxury automobiles. As a result, the manufacture of charabanc, and later coach bodies became more impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Buses ...
Year refers to the first year introduced. A range of years is the period the bus was manufactured. # A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Š See also * Bus spotting * Coach (used for long-distance travel) * Dollar van * List of fictional buses * List of Leyland buses * List of AEC buses * Multi-axle bus * Trackless train * Tram * Single decker buses References {{South American bus builders 01 * * Bus A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaxton Paramount
The Plaxton Paramount was a design of coach bodywork built by Plaxton. It first appeared at the 1982 British Motor Show and was built until 1992. In its more common single deck form it replaced the Supreme V and Viewmaster IV, and was replaced by the Premiere and Excalibur. Design Structurally the new Paramount was similar its predecessor the Supreme, utilising 25mm square tubing to form the frame. The rear end was similar to that used on the Supreme V and VI, but otherwise the styling was entirely new. The Paramount had a squarer profile than the Supreme, with cleaner lines, a flatter roof line and square-cornered side windows. The window line at the bottom of the foremost passenger windows (over the front wheelarch) sloped down to meet the deeper windscreen, and immediately aft of this was a small "feature window" (with white screen printing lines) on most bodies. The feature window was omitted on bodies shorter than 10 metres, and some operators (notably Excelsior of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakers Dolphin 57 (XJI5457)
A baker is a tradesperson who bakes and sometimes sells breads and other products made of flour by using an oven or other concentrated heat source. The place where a baker works is called a bakery. History Ancient history Since grains have been a staple food for millennia, the activity of baking is a very old one. Control of yeast, however, is relatively recent.Wayne Gisslen, ''Professional Baking'' (4th ed.: John Wiley & Sons, 2005), p. 4. By the fifth and sixth centuries BCE, the ancient Greeks used enclosed ovens heated by wood fires; communities usually baked bread in a large communal oven. Greeks baked dozens and possibly hundreds of types of bread; Athenaeus described seventy-two varieties. In ancient Rome several centuries later, the first mass production of breads occurred, and "the baking profession can be said to have started at that time." Ancient Roman bakers used honey and oil in their products, creating pastries rather than breads. In ancient Rome, bakers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedford Y Series
The Bedford Y series was a family of single-decker bus and single-decker coach chassis manufactured by Bedford from 1970 to 1986, when Bedford ceased bus and truck production. History Announced in September 1970, the Bedford YRQ was a 10-metre (33 ft) coach chassis intended to replace the Bedford VAM. The engine was mounted centrally under the floor. In 1972 an 11-metre (36 ft) version, the YRT, entered production as a replacement for the twin-steer Bedford VAL. New more powerful engines were introduced in 1975 with the YLQ (10m) and YMT (11m). The 1980 YNT was a development of the YMT with a turbocharged engine, while the YLQ became the YMQ and then the YMP. The 12-metre YNV Venturer with air suspension was the final development of the Y series, announced in 1984. Bus and truck production by Bedford ceased in 1986. Chassis summary The Y series was produced in four different lengths; 8m, 10m, 11m and 12m. The majority were bodied as coaches, though the 8m, 10m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
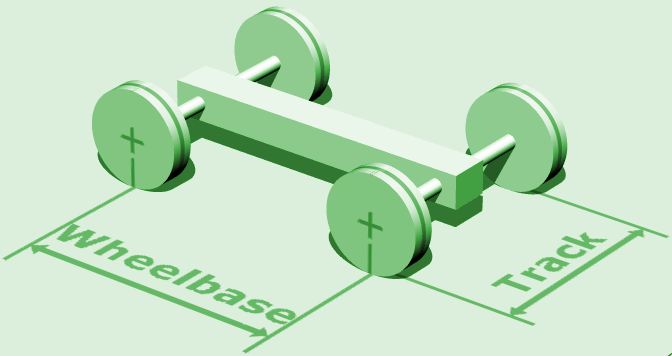
Wheelbase
In both road and rail vehicles, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front) axle and the centerpoint of the driving axle group. In the case of a tri-axle truck, the wheelbase would be the distance between the steering axle and a point midway between the two rear axles. Vehicles The wheelbase of a vehicle equals the distance between its front and rear wheels. At equilibrium, the total torque of the forces acting on a vehicle is zero. Therefore, the wheelbase is related to the force on each pair of tires by the following formula: :F_f = mg :F_r = mg where F_f is the force on the front tires, F_r is the force on the rear tires, L is the wheelbase, d_r is the distance from the center of mass (CM) to the rear wheels, d_f is the distance from the center of mass to the front wheels (d_f + d_r = L), m is the mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving On The Left Or Right
Driving is the controlled operation and movement of a vehicle, including cars, motorcycles, trucks, buses, and bicycles. Permission to drive on public highways is granted based on a set of conditions being met and drivers are required to follow the established road and traffic laws in the location they are driving. The word driving, has etymology dating back to the 15th century and has developed as what driving has encompassed has changed from working animals in the 15th to automobiles in the 1800s. Driving skills have also developed since the 15th century with physical, mental and safety skills being required to drive. This evolution of the skills required to drive have been accompanied by the introduction of driving laws which relate to not only the driver but the driveability of a car. Etymology The origin of the term ''driver'', as recorded from the 15th century, refers to the occupation of driving working animals, especially pack horses or draft horses. The verb ' ''to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Defence (United Kingdom)
The Ministry of Defence (MOD or MoD) is the department responsible for implementing the defence policy set by His Majesty's Government, and is the headquarters of the British Armed Forces. The MOD states that its principal objectives are to defend the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and its interests and to strengthen international peace and stability. The MOD also manages day-to-day running of the armed forces, contingency planning and defence procurement. The expenditure, administration and policy of the MOD are scrutinised by the Defence Select Committee, except for Defence Intelligence which instead falls under the Intelligence and Security Committee of Parliament. History During the 1920s and 1930s, British civil servants and politicians, looking back at the performance of the state during the First World War, concluded that there was a need for greater co-ordination between the three services that made up the armed forces of the United Kingdom: t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rear-engine Design
In automobile design, a rear-engine design layout places the engine at the rear of the vehicle. The center of gravity of the engine itself is behind the rear axle. This is not to be confused with the center of gravity of the whole vehicle, as an imbalance of such proportions would make it impossible to keep the front wheels on the ground. Rear-engined vehicles almost always have a rear-wheel drive car layout, but some are four wheel drive. This layout has the following features: *Packaging: since there is no need for a transmission tunnel, the floor can be flat. *Rear traction: having the engine located over the driven wheels increases downward pressure, which is helpful for grip on loose surfaces, although can be prone to oversteer. *Simplicity of manufacture: the engine is near the driven wheels, and the transmission can be merged with the differential to save space. This layout was once popular in small, inexpensive cars and light commercial vehicles. Today most car makers have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_(Tony_Radakin_cropped).jpg)
