|
Platinum Diselenide
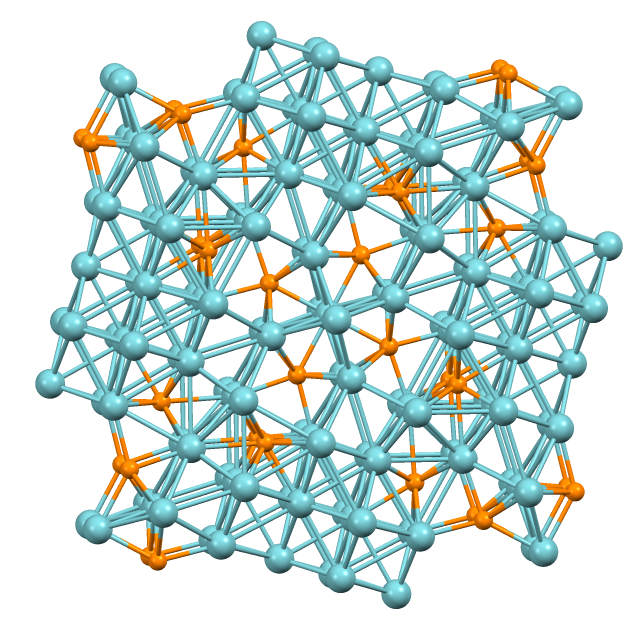
Platinum diselenide is a transition metal dichalcogenide with the formula PtSe2. It is a layered substance that can be split into layers down to three atoms thick. PtSe2 can behave as a metalloid or as a semiconductor depending on the thickness. Synthesis Minozzi was the first to report synthesising platinum diselenide from the elements in 1909. Platinum diselenide can be formed by heating thin foils of platinum in selenium vapour at 400 °C. A platinum 111 surface exposed to selenium vapour at 270 °C forms a monolayer of PtSe2. In addition to these selenization methods, PtSe2 can be made by precipitation in water solution of Pt(IV) treated with hydrogen selenide, or by heating platinum tetrachloride with elemental selenium. Natural occurrence Platinum diselenide occurs naturally as the mineral Sudovikovite. It was named after Russian petrologist, N.G. Sudovikov who lived from 1903 to 1966. The mineral's hardness is 2 to 2. Sudovikovite was found in the Srednyaya Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudovikovite
Platinum diselenide is a transition metal dichalcogenide with the formula PtSe2. It is a layered substance that can be split into layers down to three atoms thick. PtSe2 can behave as a metalloid or as a semiconductor depending on the thickness. Synthesis Minozzi was the first to report synthesising platinum diselenide from the elements in 1909. Platinum diselenide can be formed by heating thin foils of platinum in selenium vapour at 400 °C. A platinum 111 surface exposed to selenium vapour at 270 °C forms a monolayer of PtSe2. In addition to these selenization methods, PtSe2 can be made by precipitation in water solution of Pt(IV) treated with hydrogen selenide, or by heating platinum tetrachloride with elemental selenium. Natural occurrence Platinum diselenide occurs naturally as the mineral Sudovikovite. It was named after Russian petrologist, N.G. Sudovikov who lived from 1903 to 1966. The mineral's hardness is 2 to 2. Sudovikovite was found in the Srednyaya Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year for use primarily in the production of fertilizers. At higher temperatures it is a reddish-brown gas. It can be fatal if inhaled in large quantities. Nitrogen dioxide is a paramagnetic, bent molecule with C2v point group symmetry. It is included in the NOx family of atmospheric pollutants. Properties Nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas with a pungent, acrid odor above , becomes a yellowish-brown liquid below , and converts to the colorless dinitrogen tetroxide () below . The bond length between the nitrogen atom and the oxygen atom is 119.7 pm. This bond length is consistent with a bond order between one and two. Unlike ozone, O3, the ground electronic state of nitrogen dioxide is a doublet state, since nitrogen has one unpaired electron, which decreases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Dichalcogenides
:image:Cadmium sulfide.jpg, 220px, Cadmium sulfide, a prototypical metal chalcogenide, is used as a yellow pigment. A chalcogenide is a chemical compound consisting of at least one chalcogen anion and at least one more electropositive element. Although all group 16 elements of the periodic table are defined as chalcogens, the term chalcogenide is more commonly reserved for sulfides, selenides, Telluride (chemistry), tellurides, and polonides, rather than oxides. Many metal ores exist as chalcogenides. photoconductivity, Photoconductive chalcogenide glasses are used in xerography. Some pigments and catalysts are also based on chalcogenides. The metal dichalcogenide Molybdenum disulfide, MoS2 is a common solid lubricant. Alkali metal and alkaline earth chalcogenides Alkali metal and alkaline earth monochalcogenides are salt-like, being colourless and often water-soluble. The sulfides tend to undergo hydrolysis to form derivatives containing bisulfide (SH−) anions. The alkali metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. "Carbon nanostructures for electromagnetic shielding applications", Mohammed Arif Poothanari, Sabu Thomas, et al., ''Industrial Applications of Nanomaterials'', 2019. "Carbon nanostructures include various low-dimensional allotropes of carbon including carbon black (CB), carbon fiber, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), fullerene, and graphene." The name is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, reflecting the fact that the allotrope of carbon contains numerous double bonds. Each atom in a graphene sheet is connecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Effect Transistor
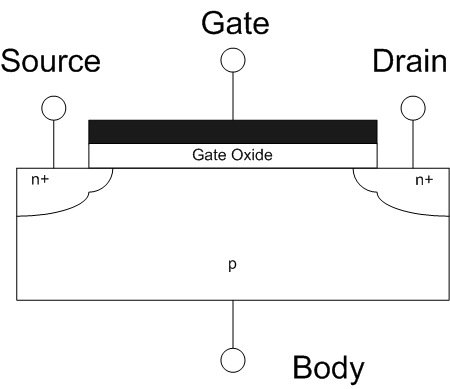
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platinum Disulfide
Platinum disulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula Pt S2. It is a black, semiconducting solid, which is insoluble in all solvents. The compound adopts the cadmium iodide structure, being composed of sheets of octahedral Pt and pyramidal sulfide centers. Single crystals are grown by chemical vapor transport In chemistry, a chemical transport reaction describes a process for purification and crystallization of non- volatile solids. The process is also responsible for certain aspects of mineral growth from the effluent of volcanoes. The technique ... using phosphorus as the transport agent. A related compound is platinum(II) sulfide, PtS. References {{Sulfides Sulfides Sulfides,2 Transition metal dichalcogenides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palladium Ditelluride
Merenskyite is a rare telluride / bismuthinide mineral with the chemical formula . It is an opaque white to light gray metallic mineral that occurs as inclusions within other minerals such as chalcopyrite. It crystallizes in the trigonal crystal system. Merenskyite was first described in 1966 for an occurrence in the Merensky Reef of the Western Bushveld Igneous Complex, South Africa, and named for South African geologist Hans Merensky Hans Merensky (16 March 1871 – 21 October 1952) was a South African geologist, prospector, scientist, conservationist and philanthropist. He discovered the rich deposit of alluvial diamonds at Alexander Bay in Namaqualand, vast platinum ... (1871–1952). References {{Reflist Telluride minerals Bismuthide minerals Palladium minerals Platinum minerals Trigonal minerals Minerals in space group 164 Minerals described in 1966 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold, hence the well-known nickname of ''fool's gold''. The color has also led to the nicknames ''brass'', ''brazzle'', and ''Brazil'', primarily used to refer to pyrite found in coal. The name ''pyrite'' is derived from the Greek language, Greek (), 'stone or mineral which strikes fire', in turn from (), 'fire'. In ancient Roman times, this name was applied to several types of stone that would create sparks when struck against steel; Pliny the Elder described one of them as being brassy, almost certainly a reference to what we now call pyrite. By Georgius Agricola's time, , the term had become a generic term for all of the pyrite group, sulfide minerals. Pyrite is usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spintronics
Spintronics (a portmanteau meaning spin transport electronics), also known as spin electronics, is the study of the intrinsic spin of the electron and its associated magnetic moment, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid-state devices. The field of spintronics concerns spin-charge coupling in metallic systems; the analogous effects in insulators fall into the field of multiferroics. Spintronics fundamentally differs from traditional electronics in that, in addition to charge state, electron spins are exploited as a further degree of freedom, with implications in the efficiency of data storage and transfer. Spintronic systems are most often realised in dilute magnetic semiconductors (DMS) and Heusler alloys and are of particular interest in the field of quantum computing and neuromorphic computing. History Spintronics emerged from discoveries in the 1980s concerning spin-dependent electron transport phenomena in solid-state devices. This includes the observa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rashba Effect
The Rashba effect, also called Bychkov–Rashba effect, is a momentum-dependent splitting of spin bands in bulk crystalsMore specifically, uniaxial noncentrosymmetric crystals. and low-dimensional condensed matter systems (such as heterostructures and surface states) similar to the splitting of particles and anti-particles in the Dirac Hamiltonian. The splitting is a combined effect of spin–orbit interaction and asymmetry of the crystal potential, in particular in the direction perpendicular to the two-dimensional plane (as applied to surfaces and heterostructures). This effect is named in honour of Emmanuel Rashba, who discovered it with Valentin I. Sheka in 1959 for three-dimensional systems and afterward with Yurii A. Bychkov in 1984 for two-dimensional systems.Yu. A. Bychkov and E. I. Rashba, Properties of a 2D electron gas with a lifted spectrum degeneracy, Sov. Phys. - JETP Lett. 39, 78-81 (1984) Remarkably, this effect can drive a wide variety of novel physical phenomen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrosymmetric
In crystallography, a centrosymmetric point group contains an inversion center as one of its symmetry elements. In such a point group, for every point (x, y, z) in the unit cell there is an indistinguishable point (-x, -y, -z). Such point groups are also said to have ''inversion'' symmetry. Point reflection is a similar term used in geometry. Crystals with an inversion center cannot display certain properties, such as the piezoelectric effect. The following space groups have inversion symmetry: the triclinic space group 2, the monoclinic 10-15, the orthorhombic 47-74, the tetragonal 83-88 and 123-142, the trigonal 147, 148 and 162-167, the hexagonal 175, 176 and 191-194, the cubic 200-206 and 221-230. Point groups lacking an inversion center (non-centrosymmetric) can be ''polar'', ''chiral'', both, or neither. A ''polar'' point group is one whose symmetry operations leave more than one common point unmoved. A polar point group has no unique origin because each of those unmoved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |