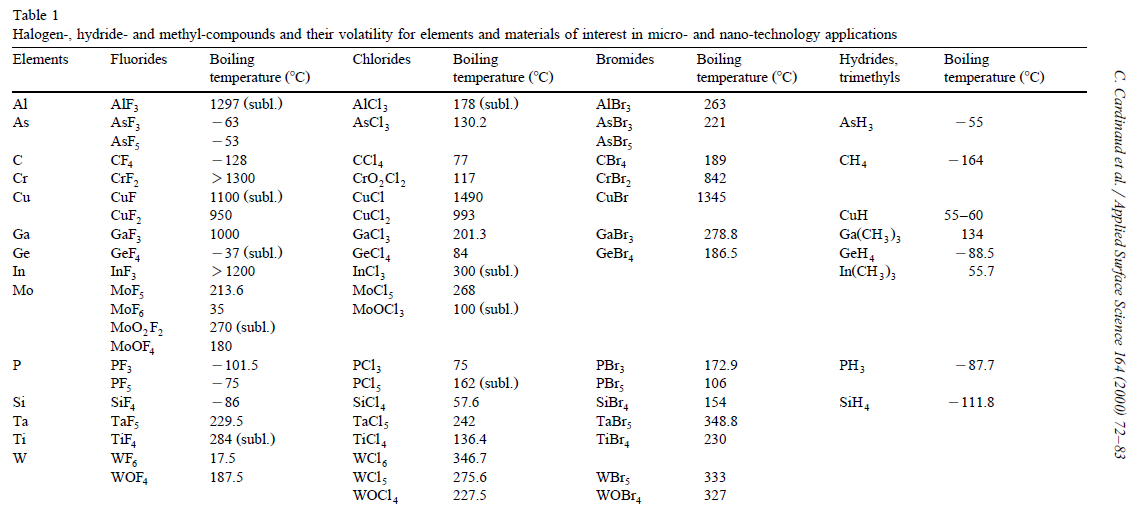
|
Plasma Ashing
In semiconductor manufacturing plasma ashing is the process of removing the photoresist (light sensitive coating) from an etched wafer. Using a plasma source, a monatomic (single atom) substance known as a reactive species is generated. Oxygen or fluorine are the most common reactive species. Other gases used are N2/H2 where the H2 portion is 2%. The reactive species combines with the photoresist to form ash which is removed with a vacuum pump. Typically, monatomic oxygen plasma is created by exposing oxygen gas (O2) at a low pressure to high power radio waves, which ionise it. This process is done under vacuum in order to create a plasma. As the plasma is formed, many free radical A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing. Ageing Ailments of unknown cause Biogerontology Biological processes Causes of death Cellular processes Gerontology Life extension Metabo ...s are created which could damage the wafer. Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoresist
A photoresist (also known simply as a resist) is a light-sensitive material used in several processes, such as photolithography and photoengraving, to form a patterned coating on a surface. This process is crucial in the electronic industry. The process begins by coating a substrate with a light-sensitive organic material. A patterned mask is then applied to the surface to block light, so that only unmasked regions of the material will be exposed to light. A solvent, called a developer, is then applied to the surface. In the case of a positive photoresist, the photo-sensitive material is degraded by light and the developer will dissolve away the regions that were exposed to light, leaving behind a coating where the mask was placed. In the case of a negative photoresist, the photosensitive material is strengthened (either polymerized or cross-linked) by light, and the developer will dissolve away only the regions that were not exposed to light, leaving behind a coating in areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etching (microfabrication)
Etching is used in microfabrication to chemically remove layers from the surface of a wafer during manufacturing. Etching is a critically important process module, and every wafer undergoes many etching steps before it is complete. For many etch steps, part of the wafer is protected from the etchant by a "masking" material which resists etching. In some cases, the masking material is a photoresist which has been patterned using photolithography. Other situations require a more durable mask, such as silicon nitride. Orientation-Dependent Etching * KOH pellets dissolved in water (self-heating) * Etch Rate > >> ** KOH has a slower etching orientation for the planes ** You cannot use this KOH photoresist as a etching mask, because the oxide attacks too slowly, so this resist will not survive * Photoresist can be used a etching mask, and the best photoresist for etching is nitride * For example, the etch rate of Si in KOH Depends on Crystallographic Plane * At low temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma (physics)
Plasma ()πλάσμα , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek English Lexicon'', on Perseus is one of the four fundamental states of matter. It contains a significant portion of charged particles – ions and/or s. The presence of these charged particles is what primarily sets plasma apart from the other fundamental states of matter. It is the most abundant form of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monatomic
In physics and chemistry, "monatomic" is a combination of the words "mono" and "atomic", and means "single atom". It is usually applied to gases: a monatomic gas is a gas in which atoms are not bound to each other. Examples at standard conditions of temperature and pressure include all the noble gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon), though all chemical elements will be monatomic in the gas phase at sufficiently high temperature (or very low pressure). The thermodynamic behavior of a monatomic gas is much simpler when compared to polyatomic gases because it is free of any rotational or vibrational energy. Noble gases The only chemical elements that are stable single atoms (so they are not molecules) at standard temperature and pressure (STP) are the noble gases. These are helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. Noble gases have a full outer valence shell making them rather non-reactive species. While these elements have been described histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reactive, as it reacts with all other elements except for the light inert gases. Among the elements, fluorine ranks 24th in universal abundance and 13th in terrestrial abundance. Fluorite, the primary mineral source of fluorine which gave the element its name, was first described in 1529; as it was added to metal ores to lower their melting points for smelting, the Latin verb meaning 'flow' gave the mineral its name. Proposed as an element in 1810, fluorine proved difficult and dangerous to separate from its compounds, and several early experimenters died or sustained injuries from their attempts. Only in 1886 did French chemist Henri Moissan isolate elemental fluorine using low-temperature electrolysis, a process still employed for moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Pump
A vacuum pump is a device that draws gas molecules from a sealed volume in order to leave behind a partial vacuum. The job of a vacuum pump is to generate a relative vacuum within a capacity. The first vacuum pump was invented in 1650 by Otto von Guericke, and was preceded by the suction pump, which dates to antiquity. History Early pumps The predecessor to the vacuum pump was the suction pump. Dual-action suction pumps were found in the city of Pompeii. Arabic engineer Al-Jazari later described dual-action suction pumps as part of water-raising machines in the 13th century. He also said that a suction pump was used in siphons to discharge Greek fire. The suction pump later appeared in medieval Europe from the 15th century. Donald Routledge Hill (1996), ''A History of Engineering in Classical and Medieval Times'', Routledge, pp. 143 & 150-2 Donald Routledge Hill, "Mechanical Engineering in the Medieval Near East", ''Scientific American'', May 1991, pp. 64-69 ( cf. Donald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Cleaning
Plasma cleaning is the removal of impurities and contaminants from surfaces through the use of an energetic plasma or dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma created from gaseous species. Gases such as argon and oxygen, as well as mixtures such as air and hydrogen/nitrogen are used. The plasma is created by using high frequency voltages (typically kHz to >MHz) to ionise the low pressure gas (typically around 1/1000 atmospheric pressure), although atmospheric pressure plasmas are now also common. Methods In plasma, gas atoms are excited to higher energy states and also ionized. As the atoms and molecules 'relax' to their normal, lower energy states they release a photon of light, this results in the characteristic “glow” or light associated with plasma. Different gases give different colors. For example, oxygen plasma emits a light blue color. A plasma’s activated species include atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, free radicals, metastables, and photons in the short wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing. Ageing Ailments of unknown cause Biogerontology Biological processes Causes of death Cellular processes Gerontology Life extension Metabolic disorders Metabolism Old age Time in life Wikipedia categories named after diseases and disorders {{CatAutoTOC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Etching
Plasma etching is a form of plasma processing used to fabricate integrated circuits. It involves a high-speed stream of glow discharge ( plasma) of an appropriate gas mixture being shot (in pulses) at a sample. The plasma source, known as etch species, can be either charged ( ions) or neutral (atoms and radicals). During the process, the plasma generates volatile etch products at room temperature from the chemical reactions between the elements of the material etched and the reactive species generated by the plasma. Eventually the atoms of the shot element embed themselves at or just below the surface of the target, thus modifying the physical properties of the target. Mechanisms Plasma generation A plasma is a high energetic condition in which a lot of processes can occur. These processes happen because of electrons and atoms. To form the plasma electrons have to be accelerated to gain energy. Highly energetic electrons transfer the energy to atoms by collisions. Three differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Device Fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuit (IC) chips such as modern computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips such as NAND flash and DRAM that are present in everyday electrical and electronics, electronic devices. It is a multiple-step sequence of Photolithography, photolithographic and chemical processing steps (such as surface passivation, thermal oxidation, planar process, planar diffusion and p–n junction isolation, junction isolation) during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer (electronics), wafer made of pure semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications. The entire manufacturing process takes time, from start to packaged chips ready for shipment, at least six to eight weeks (tape-out only, not including the circuit design) and is performed in highly specialized semiconduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |