|
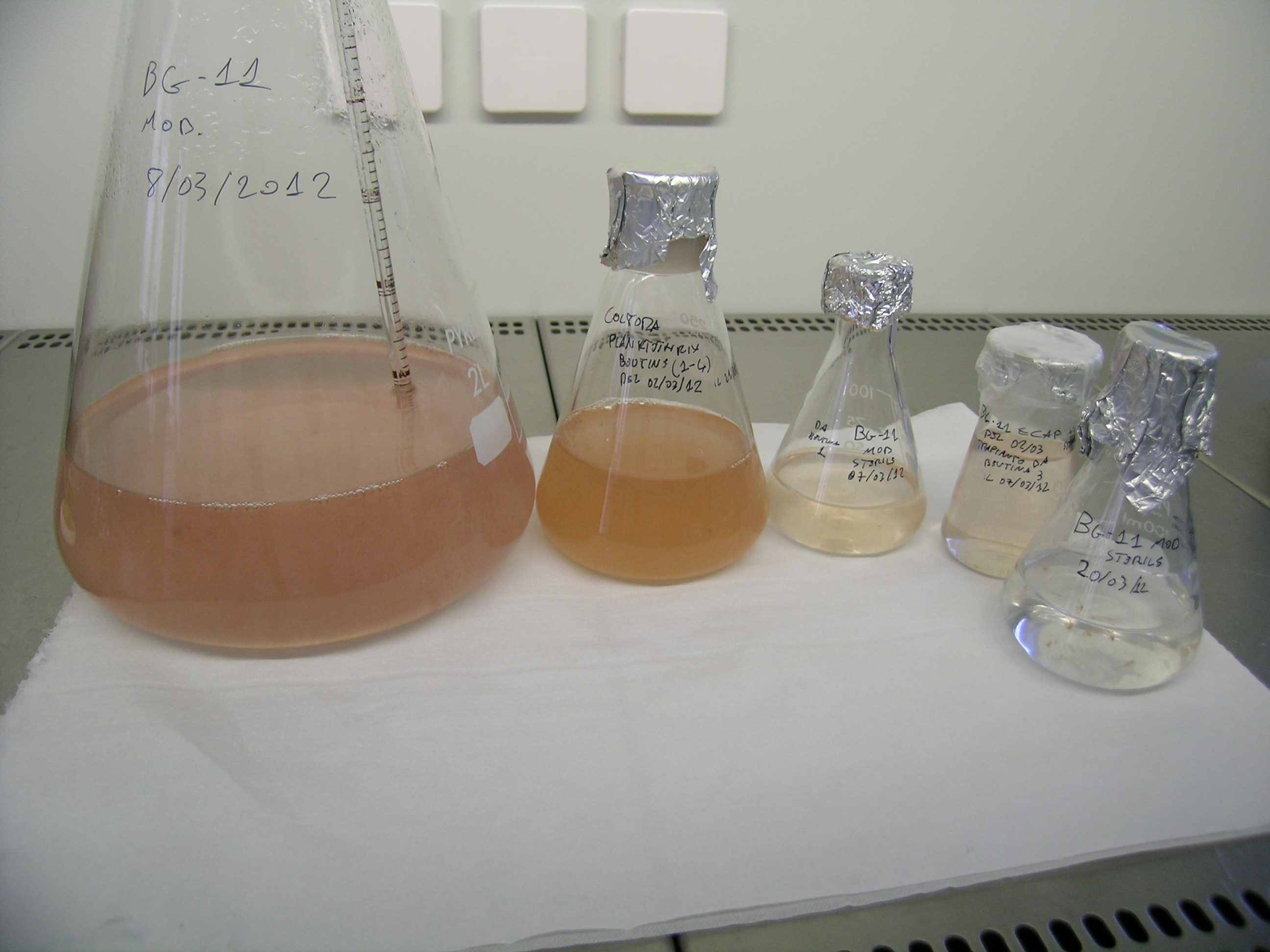
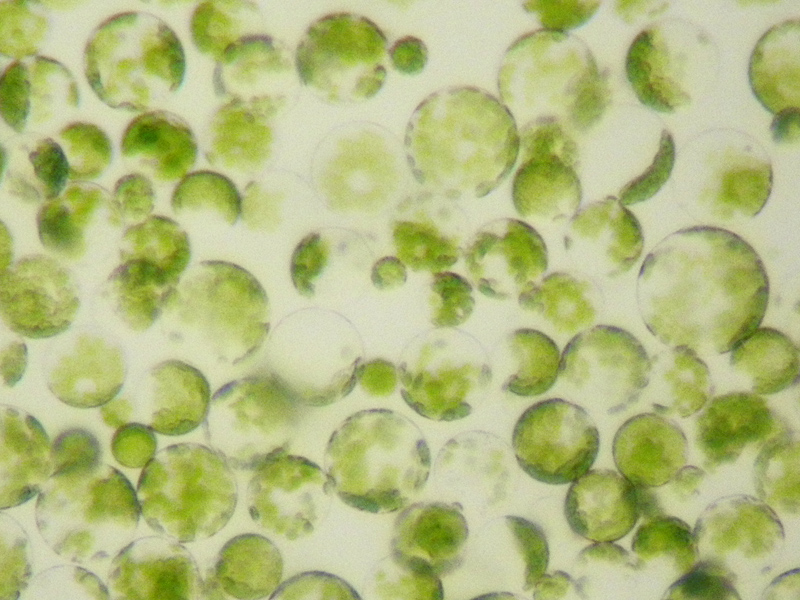
Planktothrix Rubescens
''Planktothrix'' is a diverse genus of filamentous cyanobacteria observed to amass in algal blooms in water ecosystems across the globe. Like all Oscillatoriales, ''Planktothrix'' species have no heterocysts and no akinetes. Planktothrix are unique because they have trichomes and contain gas vacuoles unlike typical planktonic organisms. Previously, some species of the taxon were grouped within the genus '' Oscillatoria,'' but recent work has defined Planktothrix as its own genus. A tremendous body of work on ''Planktothrix'' ecology and physiology has been done by Anthony E. Walsby, and the 55.6 kb microcystin synthetase gene which gives these organisms the ability to synthesize toxins has been sequenced. ''P. agardhii'' is an example of a type species of the genus. ''P. agardhii'' and ''P. rubescens'' are commonly observed in lakes of the Northern Hemisphere where they are known producers of potent hepatotoxins called microcystins. Habitats and niches Both ''P. agardhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filamentous Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacterial morphology refers to the form or shape of cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria are a large and diverse phylum of bacteria defined by their unique combination of pigments and their ability to perform oxygenic photosynthesis. Cyanobacteria often live in colonial aggregates that can take a multitude of forms. Of particular interest among the many species of cyanobacteria are those that live colonially in elongate hair-like structures, known as trichomes. These filamentous species can contain hundreds to thousands of cells. They often dominate the upper layers of microbial mats found in extreme environments such as hot springs, hypersaline water, deserts and polar regions, as well as being widely distributed in more mundane environments. Many filamentous species are also motile, gliding along their long axis, and displaying photomovement by which a trichome modulates its gliding according to the incident light. The latter has been found to play an important role in guidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperate Climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout the year and more distinct seasonal changes compared to tropical climates, where such variations are often small and usually only have precipitation changes. In temperate climates, not only do latitudinal positions influence temperature changes, but sea currents, prevailing wind direction, continentality (how large a landmass is) and altitude also shape temperate climates. The Köppen climate classification defines a climate as "temperate" C, when the mean temperature is above but below in the coldest month to account for the persistency of frost. However, other climate classifications set the minimum at . Zones and climates The north temperate zone extends from the Tropic of Cancer (approximately 23.5° north latitude) to the Arctic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcystis
''Microcystis'' is a genus of freshwater cyanobacteria that includes the harmful algal bloom-forming ''Microcystis aeruginosa''. Many members of a ''Microcystis'' community can produce neurotoxins and hepatotoxins, such as microcystin and cyanopeptolin. Communities are often a mix of toxin-producing and nonproducing isolates. Etymology The genus ''Microcystis'' derives from the Greek ''mikros'' (small) + ''kystis'' (bladder) Physical characteristics As the etymological derivation implies, ''Microcystis'' is characterized by small cells (a few micrometre, micrometers in diameter), possessing gas-filled vesicles (also lacking individual sheaths). The cells are usually organized into colonies (aggregations of which are visible with the naked eye) that begin in a spherical shape, losing coherence to become perforated or irregularly shaped over time. These colonies are bound by a thick mucilage composed of complex polysaccharide compounds, including xylose, mannose, glucose, fuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcystin
Microcystins—or cyanoginosins—are a class of toxins produced by certain freshwater cyanobacteria, commonly known as blue-green algae. Over 250 different microcystins have been discovered so far, of which microcystin-LR is the most common. Chemically they are cyclic heptapeptides produced through nonribosomal peptide synthases. Cyanobacteria can produce microcystins in large quantities during algal blooms which then pose a major threat to drinking and irrigation water supplies, and the environment at large. Characteristics Microcystins—or cyanoginosins—are a class of toxins produced by certain freshwater cyanobacteria; primarily ''Microcystis aeruginosa'' but also other ''Microcystis'', as well as members of the ''Planktothrix'', ''Anabaena'', ''Oscillatoria'' and ''Nostoc'' genera. Over 250 different microcystins have been discovered so far, of which microcystin-LR is the most common. Chemically they are cyclic heptapeptides produced through nonribosomal peptide synthase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anabaena
''Anabaena'' is a genus of filamentous cyanobacteria that exist as plankton. They are known for nitrogen-fixing abilities, and they form symbiotic relationships with certain plants, such as the mosquito fern. They are one of four genera of cyanobacteria that produce neurotoxins, which are harmful to local wildlife, as well as farm animals and pets. Production of these neurotoxins is assumed to be an input into its symbiotic relationships, protecting the plant from grazing pressure. A DNA sequencing project was undertaken in 1999, which mapped the complete genome of ''Anabaena'', which is 7.2 million base pairs long. The study focused on heterocysts, which convert nitrogen into ammonia. Certain species of ''Anabaena'' have been used on rice paddy fields, proving to be an effective natural fertilizer. Nitrogen fixation by ''Anabaena'' Under nitrogen-limiting conditions, vegetative cells differentiate into heterocysts at semiregular intervals along the filaments. Heterocyst c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
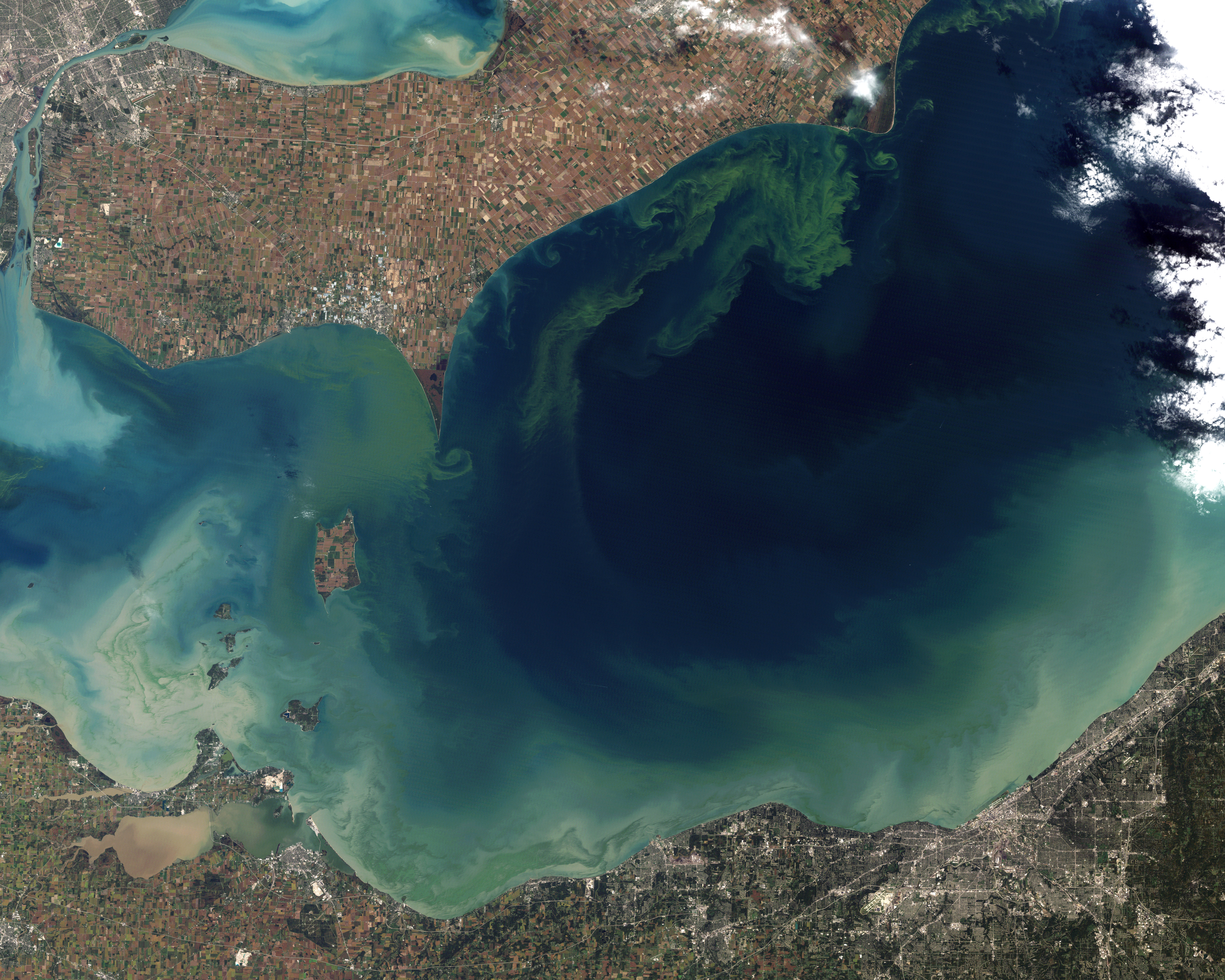
Algal Bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompasses many types of aquatic photosynthetic organisms, both macroscopic multicellular organisms like seaweed and microscopic unicellular organisms like cyanobacteria. ''Algal bloom'' commonly refers to the rapid growth of microscopic unicellular algae, not macroscopic algae. An example of a macroscopic algal bloom is a kelp forest. Algal blooms are the result of a nutrient, like nitrogen or phosphorus from various sources (for example fertilizer runoff or other forms of nutrient pollution), entering the aquatic system and causing excessive growth of algae. An algal bloom affects the whole ecosystem. Consequences range from the benign feeding of higher trophic levels to more harmful effects like blocking sunlight from reaching other organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxitoxin
Saxitoxin (STX) is a potent neurotoxin and the best-known paralytic shellfish toxin (PST). Ingestion of saxitoxin by humans, usually by consumption of shellfish contaminated by toxic algal blooms, is responsible for the illness known as paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP). The term saxitoxin originates from the genus name of the butter clam (''Saxidomus'') from which it was first isolated. But the term saxitoxin can also refer to the entire suite of more than 50 structurally related neurotoxins (known collectively as "saxitoxins") produced by protists, algae and cyanobacteria which includes saxitoxin itself (STX), neosaxitoxin (NSTX), gonyautoxins (GTX) and decarbamoylsaxitoxin (dcSTX). Saxitoxin has a large environmental and economic impact, as its presence in bivalve shellfish such as mussels, clams, oysters and scallops frequently leads to bans on commercial and recreational shellfish harvesting in many temperate coastal waters around the world including the Northeastern and W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatoxin-a
Anatoxin-a, also known as Very Fast Death Factor (VFDF), is a secondary, bicyclic amine alkaloid and cyanotoxin with acute neurotoxicity. It was first discovered in the early 1960s in Canada, and was isolated in 1972. The toxin is produced by multiple genera of cyanobacteria and has been reported in North America, South America, Central America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and Oceania. Symptoms of anatoxin-a toxicity include loss of coordination, muscular fasciculations, convulsions and death by respiratory paralysis. Its mode of action is through the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAchR) where it mimics the binding of the receptor's natural ligand, acetylcholine. As such, anatoxin-a has been used for medicinal purposes to investigate diseases characterized by low acetylcholine levels. Due to its high toxicity and potential presence in drinking water, anatoxin-a poses a threat to animals, including humans. While methods for detection and water treatment exist, scientists have called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanotoxin
Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they exponential growth, reproduce exponentially to form Algal bloom, blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning. Some of the most powerful natural poisons known are cyanotoxins. They include potent neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, cytotoxins, and endotoxins. Despite the similarity in name, they are unrelated to cyanides. Exposure to cyanobacteria can result in gastro-intestinal and hayfever symptoms or pruritic skin rashes. Exposure to the cyanobacteria neurotoxin BMAA may be an environmental cause of neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoplast
Protoplast (), is a biological term coined by Hanstein in 1880 to refer to the entire cell, excluding the cell wall. Protoplasts can be generated by stripping the cell wall from plant, bacterial, or fungal cells by mechanical, chemical or enzymatic means. Protoplasts differ from spheroplasts in that their cell wall has been completely removed. Spheroplasts retain part of their cell wall. In the case of Gram-negative bacterial spheroplasts, for example, the peptidoglycan component of the cell wall has been removed but the outer membrane component has not. Enzymes for the preparation of protoplasts Cell walls are made of a variety of polysaccharides. Protoplasts can be made by degrading cell walls with a mixture of the appropriate polysaccharide-degrading enzymes: During and subsequent to digestion of the cell wall, the protoplast becomes very sensitive to osmotic stress. This means cell wall digestion and protoplast storage must be done in an isotonic solution to prevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycoerythrin
Phycoerythrin (PE) is a red protein-pigment complex from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, present in cyanobacteria, red algae and cryptophytes, accessory to the main chlorophyll pigments responsible for photosynthesis.The red pigment is due to the prosthetic group, phycoerythrobilin, which gives phycoerythrin its red color. Like all phycobiliproteins, it is composed of a protein part covalently binding chromophores called phycobilins. In the phycoerythrin family, the most known phycobilins are: phycoerythrobilin, the typical phycoerythrin acceptor chromophore. Phycoerythrobilin is a linear tetrapyrrole molecule found in cyanobacteria, red algae, and cryptomonads. Together with other bilins such as phycocyanobilin it serves as a light-harvesting pigment in the photosynthetic light-harvesting structures of cyanobacteria called phycobilisomes. Phycoerythrins are composed of (αβ) monomers, usually organised in a disk-shaped trimer (αβ)3 or hexamer (αβ)6 (second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |