|
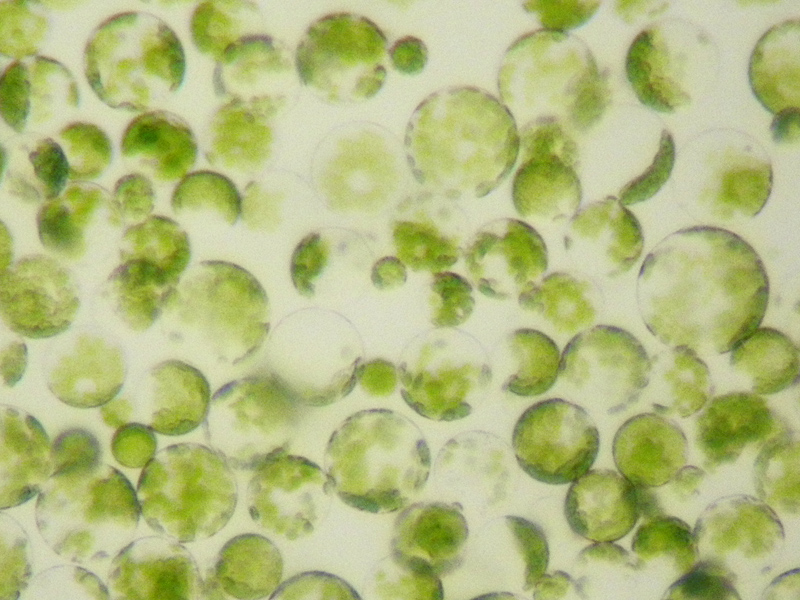
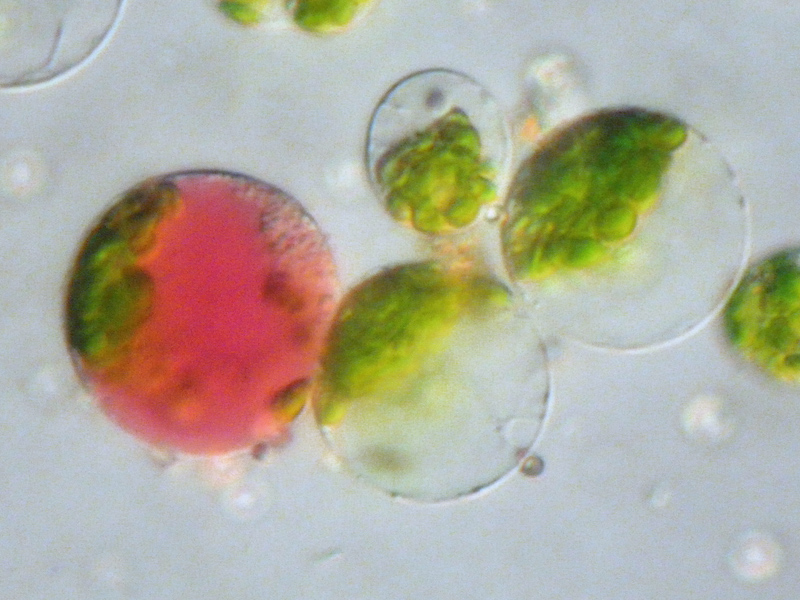
Protoplast
Protoplast (), is a biological term coined by Hanstein in 1880 to refer to the entire cell, excluding the cell wall. Protoplasts can be generated by stripping the cell wall from plant, bacterial, or fungal cells by mechanical, chemical or enzymatic means. Protoplasts differ from spheroplasts in that their cell wall has been completely removed. Spheroplasts retain part of their cell wall. In the case of Gram-negative bacterial spheroplasts, for example, the peptidoglycan component of the cell wall has been removed but the outer membrane component has not. Enzymes for the preparation of protoplasts Cell walls are made of a variety of polysaccharides. Protoplasts can be made by degrading cell walls with a mixture of the appropriate polysaccharide-degrading enzymes: During and subsequent to digestion of the cell wall, the protoplast becomes very sensitive to osmotic stress. This means cell wall digestion and protoplast storage must be done in an isotonic solution to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoplasts Petunia Sp
Protoplast (), is a biology, biological term coined by Johannes von Hanstein, Hanstein in 1880 to refer to the entire cell, excluding the cell wall. Protoplasts can be generated by stripping the cell wall from plant, bacterium, bacterial, or fungus, fungal cells by mechanical, chemical or enzymatic means. Protoplasts differ from spheroplasts in that their cell wall has been completely removed. Spheroplasts retain part of their cell wall. In the case of Gram-negative bacterial spheroplasts, for example, the peptidoglycan component of the cell wall has been removed but the bacterial outer membrane, outer membrane component has not. Enzymes for the preparation of protoplasts Cell walls are made of a variety of polysaccharides. Protoplasts can be made by degrading cell walls with a mixture of the appropriate polysaccharide-degrading enzymes: During and subsequent to digestion of the cell wall, the protoplast becomes very sensitive to osmosis, osmotic stress. This means cell wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoplast Fusion
Somatic fusion, also called protoplast fusion, is a type of genetic modification in plants by which two distinct species of plants are fused together to form a new hybrid plant with the characteristics of both, a somatic hybrid. Hybrids have been produced either between different varieties of the same species (e.g. between non-flowering potato plants and flowering potato plants) or between two different species (e.g. between wheat ''Triticum'' and rye '' Secale'' to produce Triticale). Uses of somatic fusion include making potato plants resistant to potato leaf roll disease. Through somatic fusion, the crop potato plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' – the yield of which is severely reduced by a viral disease transmitted on by the aphid vector – is fused with the wild, non-tuber-bearing potato ''Solanum brevidens'', which is resistant to the disease. The resulting hybrid has the chromosomes of both plants and is thus similar to polyploid plants. Somatic hybridization was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformation (genetics)
In molecular biology and genetics, transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material from its surroundings through the cell membrane(s). For transformation to take place, the recipient bacterium must be in a state of competence, which might occur in nature as a time-limited response to environmental conditions such as starvation and cell density, and may also be induced in a laboratory. Transformation is one of three processes that lead to horizontal gene transfer, in which exogenous genetic material passes from one bacterium to another, the other two being conjugation (transfer of genetic material between two bacterial cells in direct contact) and transduction (injection of foreign DNA by a bacteriophage virus into the host bacterium). In transformation, the genetic material passes through the intervening medium, and uptake is completely dependent on the recipient bacterium. As of 2014 abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. Cell walls are absent in many eukaryotes, including animals, but are present in some other ones like fungi, algae and plants, and in most prokaryotes (except mollicute bacteria). A major function is to act as pressure vessels, preventing over-expansion of the cell when water enters. The composition of cell walls varies between taxonomic group and species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin. Often, other polymers such as lignin, suberin or cutin are anchored to or embedded in plant cell walls. Algae possess cell walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides such as carrageenan and agar that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''tru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spheroplasts
A spheroplast (or sphaeroplast in British usage) is a microbial cell from which the cell wall has been almost completely removed, as by the action of penicillin or lysozyme. According to some definitions, the term is used to describe Gram-negative bacteria. According to other definitions, the term also encompasses yeasts. The name spheroplast stems from the fact that after the microbe's cell wall is digested, membrane tension causes the cell to acquire a characteristic spherical shape. Spheroplasts are osmotically fragile, and will lyse if transferred to a hypotonic solution. When used to describe Gram-negative bacteria, the term spheroplast refers to cells from which the peptidoglycan component but not the outer membrane component of the cell wall has been removed. Spheroplast formation Antibiotic-induced spheroplasts Various antibiotics convert Gram-negative bacteria into spheroplasts. These include peptidoglycan synthesis inhibitors such as fosfomycin, vancomycin, moenomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Cell
Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capability to perform photosynthesis and store starch, a large vacuole that regulates turgor pressure, the absence of flagella or centrioles, except in the gametes, and a unique method of cell division involving the formation of a cell plate or phragmoplast that separates the new daughter cells. Characteristics of plant cells * Plant cells have cell walls, constructed outside the cell membrane and composed of cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. Their composition contrasts with the cell walls of fungi, which are made of chitin, of bacteria, which are made of peptidoglycan and of archaea, which are made of pseudopeptidoglycan. In many cases lignin or suberin are secreted by the protoplast as secondary wall layers inside the primary ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''tru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Von Hanstein
Johannes Ludwig Emil Robert von Hanstein (15 May 1822 – 27 August 1880) was a German botanist who was a native of Potsdam. He attended classes at the ''Gärtnerlehranstalt'' (Institute of Horticulture) in Potsdam, and later studied sciences in Berlin, obtaining his doctorate in 1848. In 1855 he was a lecturer of botany at the University of Berlin, and six years later became curator of the royal herbarium. In 1865 he was appointed professor of botany at the University of Bonn and director of the botanical garden. Hanstein is remembered for studies in plant anatomy and morphology. In 1868 he introduced the " histogen theory" to explain shoot apex behaviour in plants. With his close friend, Nathanael Pringsheim (1823–1894), he conducted pioneer research on the fertilization process in ferns. The plant genus '' Hansteinia'' of the family Acanthaceae is named after him. Gallery File:Capsella bursa-pastoris, kiembol (Hanstein).jpg, ''Capsella bursa-pastoris'' drawing by Joha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysostaphin
Lysostaphin (, ''glycyl-glycine endopeptidase'') is a '' Staphylococcus simulans'' metalloendopeptidasecrystal structure of lysostaphin. It can function as a bacteriocin (antimicrobial) against '' Staphylococcus aureus''. Lysostaphin is a 27 KDa glycylglycine endopeptidase, an antibacterial enzyme which is capable of cleaving the crosslinking pentaglycine bridges found in the cell wall peptidoglycan of certain ''Staphylococci''. Lysostaphin was first isolated from a culture of ''Staphylococcus simulans'' by Schindler and Schuhardt in 1964. ''S. aureus'' cell walls contain high proportions of pentaglycine, making lysostaphin a highly effective agent against both actively growing and quiescent bacteria. ''Staphylococcal'' infections of both ''Staphylococcus aureus'' and '' Staphylococcus epidermidis'' continue to be a major issue in clinical settings, particularly those with implantable devices. ''Staphylococci'' cause a significant percentage of device infections, and like many oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somaclonal Variation
Somaclonal variation is the variation seen in plants that have been produced by plant tissue culture. Chromosomal rearrangements are an important source of this variation. The term somaclonal variation is a phenomenon of broad taxonomic occurrence, reported for species of different ploidy levels, and for outcrossing and inbreeding, vegetatively and seed propagated, and cultivated and non-cultivated plants. Characters affected include both qualitative and quantitative traits. Somaclonal variation is not restricted to, but is particularly common in, plants regenerated from callus. The variations can be genotypic or phenotypic, which in the latter case can be either genetic or epigenetic in origin. Typical genetic alterations are: changes in chromosome numbers (polyploidy and aneuploidy), chromosome structure ( translocations, deletions, insertions and duplications) and DNA sequence (base mutations). A typical epigenetics-related event would be gene methylation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |