|
Plan Worek
The Worek Plan (or ''Operation Worek'', pl, Plan Worek, literally ''Plan Sack'') was an operation of the Polish Navy in the first days of World War II, in which its five submarines formed a screen in order to prevent German naval forces from carrying out landings on the Polish coast, and to attack enemy ships bombarding Polish coastal fortifications, in particular the base on the Hel Peninsula. The operation came to naught, as the Germans did not have any plans for naval landings. It caused the submarines to operate in a confined area near the shore in shallow waters, making them vulnerable to strong enemy anti-submarine forces. As a result, despite making a number of attempts, the submarines were unable to directly sink any enemy ships during the operation, although a mine placed by the ''Żbik'' did sink a German minesweeper. No Polish submarines were lost to enemy action, but they suffered progressive wear and tear, and technical problems, forcing the submarine comman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Poland (1939)
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The invasion is also known in Poland as the September campaign ( pl, kampania wrześniowa) or 1939 defensive war ( pl, wojna obronna 1939 roku, links=no) and known in Germany as the Poland campaign (german: Überfall auf Polen, Polenfeldzug). German forces invaded Poland from the north, south, and west the morning after the Gleiwitz incident. Slovak military forces adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minesweeper (ship)
A minesweeper is a small warship designed to remove or detonate naval mines. Using various mechanisms intended to counter the threat posed by naval mines, minesweepers keep waterways clear for safe shipping. History The earliest known usage of the naval mine dates to the Ming dynasty.Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, 203–205. Dedicated minesweepers, however, only appeared many centuries later during the Crimean War, where they were deployed by the British. The Crimean War minesweepers were rowboats trailing grapnels to snag mines. Minesweeping technology picked up in the Russo-Japanese War, using aging torpedo boats as minesweepers. In Britain, naval leaders recognized before the outbreak of World War I that the development of sea mines was a threat to the nation's shipping and began efforts to counter the threat. Sir Arthur Wilson noted the real threat of the time was blockade aided by mines and not invasion. The function of the fishing fleet's trawlers with their trawl gear was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
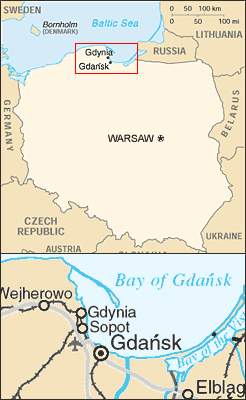
Hel Fortified Area
The Hel Fortified Area ( pl, Rejon Umocniony Hel) was a set of Polish fortifications, constructed on the Hel Peninsula in northern Poland, in close proximity to the interwar border of Poland and the Third Reich. It was created in 1936, upon a decree of President Ignacy Mościcki. It covered most part of the peninsula, and during Polish September Campaign, it was the last place of Poland to surrender to the invading Wehrmacht (for more information, see Battle of Hel). During World War II, the naval base in Hel was used as a major training facility for U-boat crews. History After Poland regained independence in autumn 1918, and the symbolic wedding ceremony with the Baltic Sea by units of the Polish Army under General Józef Haller de Hallenburg ( Puck, 10 February 1920), Polish military authorities began preparations of a fortified army garrison along the coast. As early as 22 July 1920 General Kazimierz Sosnkowski ordered construction of a strategic rail line which ran f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rozewie, Pomeranian Voivodeship
Rozewie is a village on the south coast of the Baltic Sea in the Kashubia, in the administrative district of Gmina Władysławowo, within Puck County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It lies approximately north-west of Władysławowo, north-west of Puck, and north-west of the regional capital Gdańsk. The nearby Cape Rozewie is named after the village. Prior to January 1, 2015, it was a part of the town Władysławowo. For details of the history of the region, see History of Pomerania The history of Pomerania starts shortly before 1000 AD with ongoing conquests by newly arrived Polans rulers. Before that, the area was recorded nearly 2000 years ago as Germania, and in modern-day times Pomerania is split between Germany and Po .... References Villages in Puck County {{Puck-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland. The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in the south of Poland, above sea level in the Silesian Beskids (western part of Carpathian Mountains), where it begins with the Little White Vistula (''Biała Wisełka'') and the Black Little Vistula (''Czarna Wisełka''). It flows through Poland's largest cities, including Kraków, Sandomierz, Warsaw, Płock, Włocławek, Toruń, Bydgoszcz, Świecie, Grudziądz, Tczew and Gdańsk. It empties into the Vistula Lagoon (''Zalew Wiślany'') or directly into the Gdańsk Bay of the Baltic Sea with a delta of six main branches (Leniwka, Przekop, Śmiała Wisła, Martwa Wisła, Nogat and Szkarpawa). The river is often associated with Polish culture, history and national identity. It is the country's most important waterway and natural symbol, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jastarnia
Jastarnia ( csb, Jastarniô, german: Heisternest) is a resort town in Puck County, Pomeranian Voivodship, northern Poland. It is located on the Hel Peninsula on the Baltic Sea. It is a popular Polish seaside resort and small fishing port. The municipal gmina, commune of Jastarnia consists of three districts: Jastarnia, Kuźnica, Pomeranian Voivodeship, Kuźnica, Jurata. International relations Jastarnia is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with: References Gallery File:WK15 Jastarnia (3) Travelarz.jpg, Jastarnia train station File:Jastarnia - port.jpg, Jastarnia Port File:Jastarnia plaza 2007.jpg File:Jastarnia, schron bojowy Sęp (WLZ14).jpg File:Jastarnia Stefańskiego-8.jpg, Jastarnia town File:Urząd miasta Jastarnia-4.jpg File:Jastarnia-2.jpg File:Urząd miasta Jastarnia-3.jpg, Jastarnia town Hall External links * *Official website of Jastarnia [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for states across a broad range of domains, including war, diplomacy, economic relations, and human rights. Scholars distinguish between international legal institutions on the basis of their obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply and make rules). The sources of international law include international custom (general state practice accepted as law), treaties, and general principles of law recognized by most national legal systems. Although international law may also be reflected in international comity—the practices adopted by states to maintain good relations and mutua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Danzig
A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodies of salt water that are enclosed by the coastline. Many gulfs are major shipping areas, such as the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Mexico, Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Aden The Gulf of Aden ( ar, خليج عدن, so, Gacanka Cadmeed 𐒅𐒖𐒐𐒕𐒌 𐒋𐒖𐒆𐒗𐒒) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channe .... See also * References External links * {{Authority control Bodies of water Coastal and oceanic landforms Coastal geography Oceanographical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label=Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's Free State of Prussia, until 1945. Its capital city was Königsberg (present-day Kaliningrad). East Prussia was the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast. The bulk of the ancestral lands of the Baltic Old Prussians were enclosed within East Prussia. During the 13th century, the native Prussians were conquered by the crusading Teutonic Knights. After the conquest the indigenous Balts were gradually converted to Christianity. Because of Germanization and colonisation over the following centuries, Germans became the dominant ethnic group, while Masurians and Lithuanians formed minorities. From the 13th century, East Prussia was part of the mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Gdańsk
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narrow entrance. A fjord is an elongated bay formed by glacial action. A bay can be the estuary of a river, such as the Chesapeake Bay, an estuary of the Susquehanna River. Bays may also be nested within each other; for example, James Bay is an arm of Hudson Bay in northeastern Canada. Some large bays, such as the Bay of Bengal and Hudson Bay, have varied marine geology. The land surrounding a bay often reduces the strength of winds and blocks waves. Bays may have as wide a variety of shoreline characteristics as other shorelines. In some cases, bays have beaches, which "are usually characterized by a steep upper foreshore with a broad, flat fronting terrace".Maurice Schwartz, ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science'' (2006), p. 129. Bays were sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish NavySmith, Charles Edgar: ''A short history of naval and marine engineering.'' Babcock & Wilcox, ltd. at the University Press, 1937, page 263 as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War. Before World War II, destroyers were light vessels with little endurance for unattended o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ORP Ryś
ORP ''Ryś'' was a which saw service in the Polish Navy from 1931 to 1955. Her name means Lynx in Polish. History ''Ryś'' was laid down in 1927 in Nantes, France; launched in 1929; and entered service in 1932. When World War II began on September 1, 1939, she took part in the Worek Plan for the defense of the Polish coast. After suffering battle damage, the submarine withdrew to neutral Swedish waters and was interned on September 17. After the war, she returned to Poland in October 1945 and served in the navy of the Polish People's Republic The Polish People's Republic ( pl, Polska Rzeczpospolita Ludowa, PRL) was a country in Central Europe that existed from 1947 to 1989 as the predecessor of the modern Republic of Poland. With a population of approximately 37.9 million ne ... until 1955. She was scrapped in 1956. External links Uboat.net on ORP ''Ryś'' Wilk-class submarines World War II submarines of Poland 1929 ships Ships built in France {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |