|
Plain Old Telephone Service
Plain old telephone service (POTS), or plain ordinary telephone system, is a retronym for voice-grade telephone service employing analog signal transmission over copper loops. POTS was the standard service offering from telephone companies from 1876 until 1988 in the United States when the Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) Basic Rate Interface (BRI) was introduced, followed by cellular telephone systems, and voice over IP (VoIP). POTS remains the basic form of residential and small business service connection to the telephone network in many parts of the world. The term reflects the technology that has been available since the introduction of the public telephone system in the late 19th century, in a form mostly unchanged despite the introduction of Touch-Tone dialing, electronic telephone exchanges and fiber-optic communication into the public switched telephone network (PSTN). Characteristics POTS is characterized by several aspects: *Bi-directional (full duplex) comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucent
Lucent Technologies, Inc. was an American Multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications equipment company headquartered in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey. It was established on September 30, 1996, through the divestiture of the former AT&T Technologies business unit of AT&T Corporation, which included Western Electric and Bell Labs. Lucent was merged with Alcatel SA of France on December 1, 2006, forming Alcatel-Lucent. Alcatel-Lucent was absorbed by Nokia in January 2016. Name Lucent means "light-bearing" in Latin (language), Latin. The name was applied for in 1996 at the time of the split from AT&T. The name was widely criticised, as the logo was to be, both internally and externally. Corporate communications and business cards included the strapline 'Bell Labs Innovations' in a bid to retain the prestige of the internationally famous research lab, within a new business under an as-yet unknown name. This same linguistic root also gives Lucife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
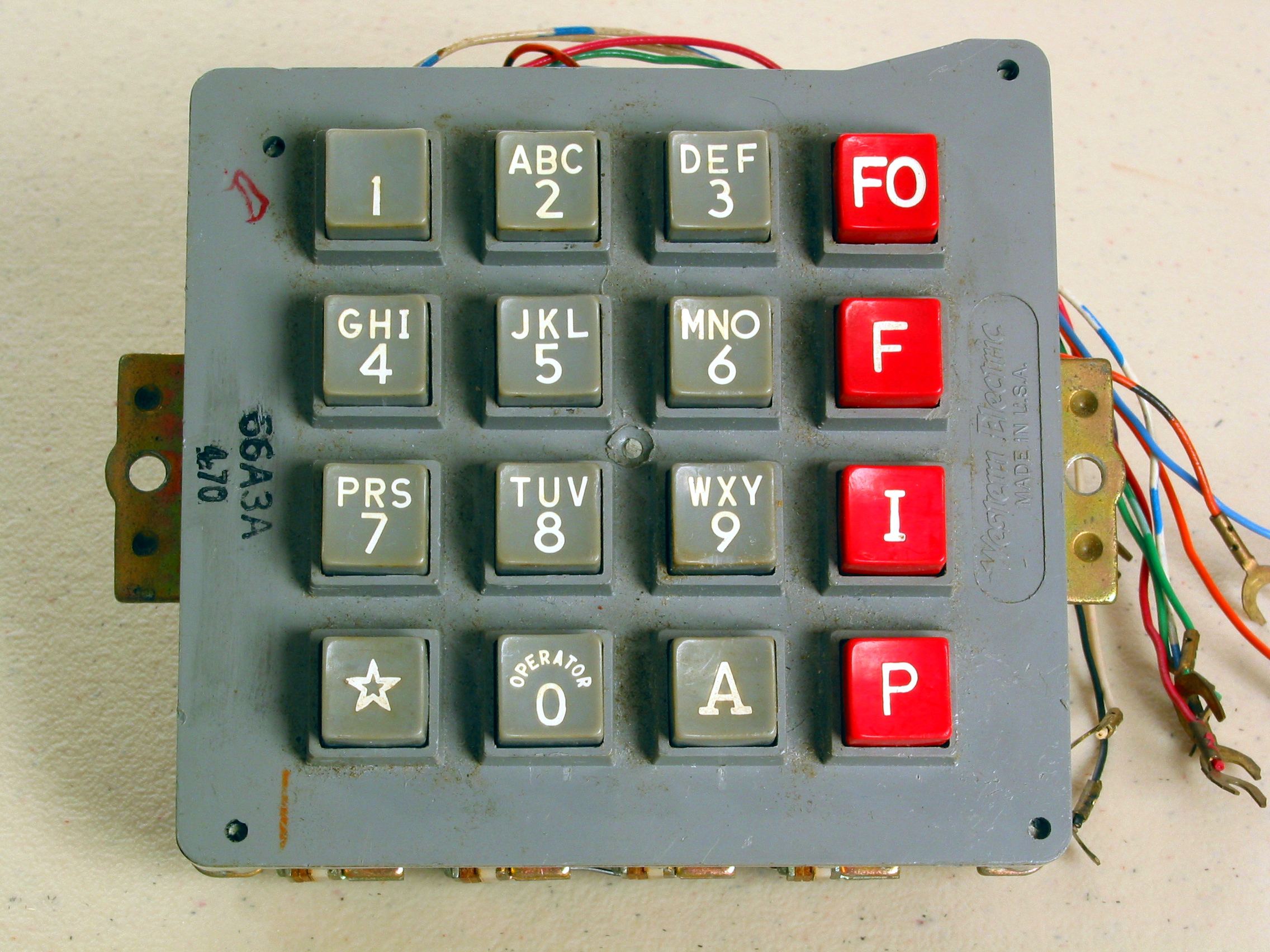
Dual-tone Multi-frequency Signaling
Dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF) is a telecommunication signaling system using the voice-frequency band over telephone lines between telephone equipment and other communications devices and switching centers. DTMF was first developed in the Bell System in the United States, and became known under the trademark Touch-Tone for use in push-button telephones supplied to telephone customers, starting in 1963. DTMF is standardized as ITU-T Recommendation Q.23. It is also known in the UK as ''MF4''. The Touch-Tone system using a telephone keypad gradually replaced the use of rotary dial and has become the industry standard for landline and mobile service. Other multi-frequency systems are used for internal signaling within the telephone network. Multifrequency signaling Before the development of DTMF, telephone numbers were dialed by users with a loop-disconnect (LD) signaling, more commonly known as pulse dialing (dial pulse, DP) in the United States. It functions by int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbreviated Dialing
Abbreviated dialing is the use of a very short digit sequence to reach specific telephone numbers, such as those of public services. The purpose of such numbers is to be universal, short, and easy to remember. Typically they are two or three digits. Carriers refer to the shortened number sequences as ''abbreviated dialing codes'' (ADCs). Unlike SMS shortcodes, they are generally not automatically synchronized across carriers. ADCs are provisioned separately for mobile networks versus landline networks. Examples The most commonly known examples are emergency telephone numbers such as 9-9-9, 1-1-2 and 9-1-1. Other services may also be available through abbreviated dialing numbers, such as the other of the eight N11 codes of the North American Numbering Plan (NANP) besides 9-1-1. State highway departments in recent years have used abbreviated dialing codes to allow drivers to obtain information about road conditions or to reach the state highway patrol. Examples are *55 in Misso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Call Waiting
Call waiting is a telephone service where a subscriber can accept a second incoming telephone call by placing an in-progress call on hold—and may also switch between calls. With some providers it can be combined with additional features such as conferencing, call forwarding, and caller ID. Call waiting is intended to alleviate the need to have more than one telephone line or number for voice communications. History Call waiting was introduced to North America in the early 1970s when the first generation of electronic switch machines built by Western Electric, Electronic Signaling System 1 started to replace older mechanical equipment in the old Bell System local telephone companies. At first, some smaller municipalities were able to offer customers call waiting only on a specific phone exchange (e.g., phone customers in Trenton, Michigan initially had to have a phone number starting with 671 to have call waiting, since 671 was at that time the only exchange in that area served ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caller ID
Caller identification (Caller ID) is a telephone service, available in analog and digital telephone systems, including voice over IP (VoIP), that transmits a caller's telephone number to the called party's telephone equipment when the call is being set up. The caller ID service may include the transmission of a name associated with the calling telephone number, in a service called Calling Name Presentation (CNAM). The service was first defined in 1993 in International Telecommunication Union—Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) Recommendation Q.731.3. The information received from the service is displayed on a telephone display screen, on a separately attached device, or on other displays, such as cable television sets when telephone and television service is provided by the same vendor. Value to society includes use by suicide-prevention hot lines and enabling businesses "like pizza restaurants and florists" to quickly have confidence in telephoned orders. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voicemail
A voicemail system (also known as voice message or voice bank) is a computer-based system that allows users and subscribers to exchange personal voice messages; to select and deliver voice information; and to process transactions relating to individuals, organizations, products, and services, using an ordinary phone. The term is also used more broadly to denote any system of conveying a stored telecommunications voice messages, including using an answering machine. Most cell phone services offer voicemail as a basic feature; many corporate private branch exchanges include versatile internal voice-messaging services, and *98 vertical service code subscription is available to most individual and small business landline subscribers (in the US). History The term ''Voicemail'' was coined by Televoice International (later Voicemail International, or VMI) for their introduction of the first US-wide Voicemail service in 1980. Although VMI trademarked the term, it eventually became a gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calling Feature
A vertical service code (VSC) is a sequence of digits and the signals star (*) and number sign (#) dialed on a telephone keypad or rotary dial to enable or disable certain telephone service features. Some vertical service codes require dialing of a telephone number after the code sequence. On a touch tone telephone, the codes are usually initiated with the star key, resulting in the commonly used name ''star codes''. On rotary dial telephones, the star is replaced by dialing ''11''. In North American telephony, VSCs were developed by AT&T Corp. as Custom Local Area Signaling Services (CLASS or LASS) codes in the 1960s and 70s. Their use became ubiquitous throughout the 1990s and eventually became a recognized standard. As ''CLASS'' was an AT&T trademark, the term ''vertical service code'' was adopted by the North American Numbering Plan Administration. The use of ''vertical'' is a somewhat dated reference to older switching methods and the fact that these services can only be ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827). Definition One volt is defined as the electric potential between two points of a conducting wire when an electric current of one ampere dissipates one watt of power between those points. Equivalently, it is the potential difference between two points that will impart one joule of energy per coulomb of charge that passes through it. It can be expressed in terms of SI base units ( m, kg, second, s, and ampere, A) as : \text = \frac = \frac = \frac. It can also be expressed as amperes times ohms (current times resistance, Ohm's law), webers per second (magnetic flux per time), watts per ampere (power per current), or joules per coulomb (energy per charge), which is also equivalent to electronvolts per elementary charge: : \text = \tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Loop
In telephony, the local loop (also referred to as the local tail, subscriber line, or in the aggregate as the last mile) is the physical link or circuit that connects from the demarcation point of the customer premises to the edge of the common carrier or telecommunications service provider's network. At the edge of the carrier access network in a traditional public telephone network, the local loop terminates in a circuit switch housed in an incumbent local exchange carrier or telephone exchange. Infrastructure Traditionally, the local loop was an electrical circuit in the form of a single pair of conductors from the telephone on the customer's premises to the local telephone exchange. Single-wire earth return lines had been used in some countries until the introduction of electric tramways from the 1900s made them unusable. Historically the first section was often an aerial open-wire line, with several conductors attached to porcelain insulators on cross-arms on "telegra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tip And Ring
Tip and ring are the two conductors or sides of a telephone line. Their names are derived from the telephone plugs used for connecting telephone calls in manual switchboards. One side of the line is connected to the metal ''tip'' of the plug, and the second is connected to a metal ''ring'' behind the tip, separated and insulated from the tip by a non-conducting material. When inserted into a jack, the plug's tip conductor connects first, followed by the ring conductor. In many European countries, tip and ring are referred to as the ''A'' and ''B'' wires. Neither of the tip and ring conductors is permanently connected to earth ground, but may be connected to ground during signaling operations. Typically, the ring conductor has a direct current (DC) potential of to with respect to the tip conductor when the line is in the on-hook (idle) state. Floating both conductors, not referencing either one to ground, minimizes the pickup of hum from any nearby alternating current (AC) power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E And M Signaling
E and M signaling is a type of supervisory line signaling that uses DC signals on separate leads, called the "E" lead and "M" lead, traditionally used in the telecommunications industry between telephone switches. Various mnemonic names have been used to memorize these letters, such as ''Ear'' and ''Mouth'', the most common variation. E&M was originally developed for signaling between PABXs in different geographic locations over an analog private circuit. The protocol was later extended for use on digital carrier system with Channel Associated Signaling (CAS). Signaling units and trunk circuits The E&M standards were initially developed by Bell Labs and extended by national PTT administrations. The standard defines two sides of the interface, the trunk circuit and the signaling unit. The trunk circuit is normally the side to which the PABX is connected. The signaling unit is the special modem that converts the DC signaling protocol into tones that could be transmitted over a fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |