|
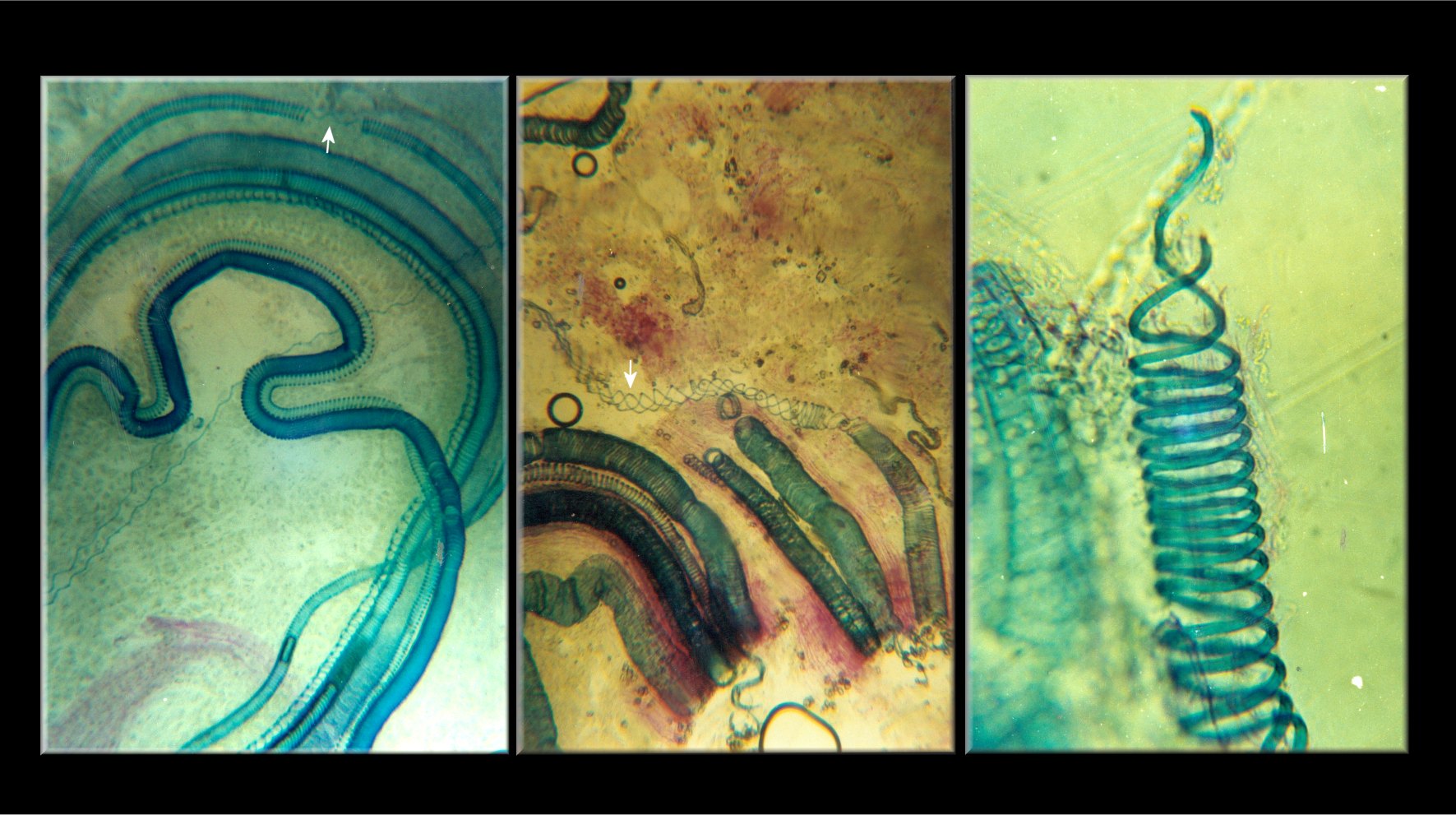
Placopsis Perrugosa
''Placopsis perrugosa'' is a saxicolous (rock-dwelling), placodioid lichen in the family Trapeliaceae. It was formally described as a new species in 1867 by Finnish lichenologist William Nylander, originally as a member of the genus ''Lecanora''. After the retreat of the Glaciar Frías in the Patagonian Andes, Argentina, ''Placopsis perrugosa'' dominated the pioneer stage on newly exposed rock outcrops. This was followed by a mid-successional stage, in which a lichen-moss mat was dominated by the moss ''Racomitrium lanuginosum'', providing the foundation for a larger diversity of vascular plants in the final successional stage. Like other members of genus ''Placopsis'', ''P. perrugosa'' is a fast-growing crustose lichen; this allows them to dominate as early colonisers on snow-free moraine A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racomitrium Lanuginosum
''Racomitrium lanuginosum'' is a widespread species of moss found in montane and arctic tundra, the genus Racomitrium is found across the Northern and Southern hemispheres., however Racomitrium lanuginosum is only found in the Northern hemisphere. It grows as large mats on exposed rock and in boulder scree, particularly on acidic rocks. Its leaves have a characteristically decurrent and toothed hair-point, which gives rise to its regional common names woolly fringemoss, hoary rock-moss and woolly moss. Description ''Racomitrium lanuginosum'' grows as "large cushiony mats". Its stems are up to long and irregularly branched. The leaves are long, wide, lanceolate, pointed and with a strong midrib. They end in a long, thin hair-point, with teeth along both sides pointing 40°–90° from the axis of the leaf. The hyaline (transparent) margins of the hair-point are decurrent along the sides of the leaf. Especially when dry, these hair-points give the plant a downy appearance, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichens Described In 1867
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches (); flat leaf-like structures ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By William Nylander (botanist)
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baeomycetales
The Baeomycetales are an order of mostly lichen-forming fungi in the subclass Ostropomycetidae, in the class Lecanoromycetes. It contains 8 families, 33 genera and about 170 species. As a result of molecular phylogenetics research published in the late 2010s, several orders were folded into the Baeomycetales, resulting in a substantial increase in the number of taxa. Taxonomy The family Baeomycetaceae was originally proposed by Barthélemy Charles Joseph Dumortier in 1829 (under the spelling ''Baeomyceae''); he included two genera, ''Baeomyces'' and ''Calicium''. Baeomycetaceae was initially classified in the Lecanorales, and Baeomycetaceae and Cladoniaceae were thought to be closely related, sharing a phylogenetic origin in Lecideaceae. It was transferred to the order Helotiales based on the structure of its ascus, which is similar to those in genus '' Leotia''. However, the Helotiales consists of mostly non-lichenised fungi. The first DNA studies conducted with ''Baeomyces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Fungorum
''Index Fungorum'' is an international project to index all formal names (scientific names) in the fungus kingdom. the project is based at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, one of three partners along with Landcare Research and the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. It is somewhat comparable to the International Plant Names Index (IPNI), in which the Royal Botanic Gardens is also involved. A difference is that where IPNI does not indicate correct names, the ''Index Fungorum'' does indicate the status of a name. In the returns from the search page a currently correct name is indicated in green, while others are in blue (a few, aberrant usages of names are indicated in red). All names are linked to pages giving the correct name, with lists of synonyms. ''Index Fungorum'' is one of three nomenclatural repositories recognized by the Nomenclature Committee for Fungi; the others are ''MycoBank'' and ''Fungal Names''. Current names in ''Index Fungorum'' (''Specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice sheet. It may consist of partly rounded particles ranging in size from boulders (in which case it is often referred to as boulder clay) down to gravel and sand, in a groundmass of finely-divided clayey material sometimes called glacial flour. Lateral moraines are those formed at the side of the ice flow, and terminal moraines were formed at the foot, marking the maximum advance of the glacier. Other types of moraine include ground moraines (till-covered areas forming sheets on flat or irregular topography) and medial moraines (moraines formed where two glaciers meet). Etymology The word ''moraine'' is borrowed from French , which in turn is derived from the Savoyard Italian ("mound of earth"). ''Morena'' in this case was derived from Proven� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placopsis
''Placopsis'' (bullseye lichen) is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Trapeliaceae. Species , Species Fungorum (via the Catalog of Life) accepts 29 species of ''Placopsis''. *'' Placopsis ampliata'' *'' Placopsis antarctica'' *'' Placopsis aspicilioides'' *'' Placopsis bicolor'' *'' Placopsis brachyloba'' *'' Placopsis campbelliana'' *'' Placopsis centrifuga'' *'' Placopsis clavifera'' *'' Placopsis cribellans'' *'' Placopsis dennanensis'' *'' Placopsis durietziorum'' *'' Placopsis elixii'' *'' Placopsis erosa'' *'' Placopsis fusciduloides'' *'' Placopsis gelida'' *''Placopsis hertelii ''Placopsis'' (bullseye lichen) is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Trapeliaceae. Species , Species Fungorum (via the Catalog of Life The Catalogue of Life is an online database that provides an index of known species of animals, ...'' *'' Placopsis illita'' *'' Placopsis imshaugii'' *'' Placopsis lambii'' *'' Placopsis macrospora'' *'' Placopsis mur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Succession
Ecological succession is the process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time. The time scale can be decades (for example, after a wildfire) or more or less. Bacteria allows for the cycling of nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen and sulphur. The community begins with relatively few pioneering plants and animals and develops through increasing complexity until it becomes stable or self-perpetuating as a climax community. The "engine" of succession, the cause of ecosystem change, is the impact of established organisms upon their own environments. A consequence of living is the sometimes subtle and sometimes overt alteration of one's own environment. Succession is a process by which an ecological community undergoes more or less orderly and predictable changes following a disturbance or the initial colonization of a new habitat. Succession may be initiated either by formation of new, unoccupied habitat, such as from a lava flow or a severe lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers), and angiosperms (flowering plants). Scientific names for the group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Some early land plants (the rhyniophytes) had less developed vascular tissue; the term eutracheophyte has been used for all other vascular plants, including all living ones. Historically, vascular plants were known as "higher plants", as it was believed that they were further evolved than other plants due to being more complex organisms. However, this is an antiquated remnant of the obsolete scala naturae, and the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing spores. They are typically tall, though some species are much larger. ''Dawsonia'', the tallest moss in the world, can grow to in height. There are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxicolous Lichen
A saxicolous lichen is a lichen that grows on rock. The prefix "sax" from the Latin means "rock" or "stone". Characteristics Saxicolous lichens exhibit very slow growth rates. They may develop on rock substrates for long periods of time, given the absence of external disturbances. The importance of the mineral composition of the rock substrate, as well as the elemental geochemistry Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the e ... is also important to the distribution of saxicolous lichens, but the relationship between the substrate influence on lichens, either chemical or textural, is still obscure. Communities of saxicolous lichens are often species-rich in terms of number. References Lichenology {{lichen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |