|
Pituitary Pars Intermedia Dysfunction
Pituitary pars intermedia dysfunction (PPID), or equine Cushing's disease, is an endocrine disease affecting the pituitary gland of horses. It is most commonly seen in older animals, and is classically associated with the formation of a long, wavy coat (hirsutism) and chronic laminitis. Pathophysiology Unlike the human and canine forms of Cushing's disease, which most commonly affect the ''pars distalis'' region of the pituitary gland, equine Cushing's disease is a result of hyperplasia or adenoma formation in the pars intermedia. This adenoma then secretes excessive amounts of normal products, leading to clinical signs. Dopaminergic control of the pars intermedia The pituitary gland consists of three parts: the ''pars nervosa'', the ''pars intermedia'', and the ''pars distalis''. The most critical structure to PPID, the ''pars intermedia'', is regulated by the hypothalamus. The neurons of the hypothalamus innervate cells known as melanotropes within the ''pars intermedia'', relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
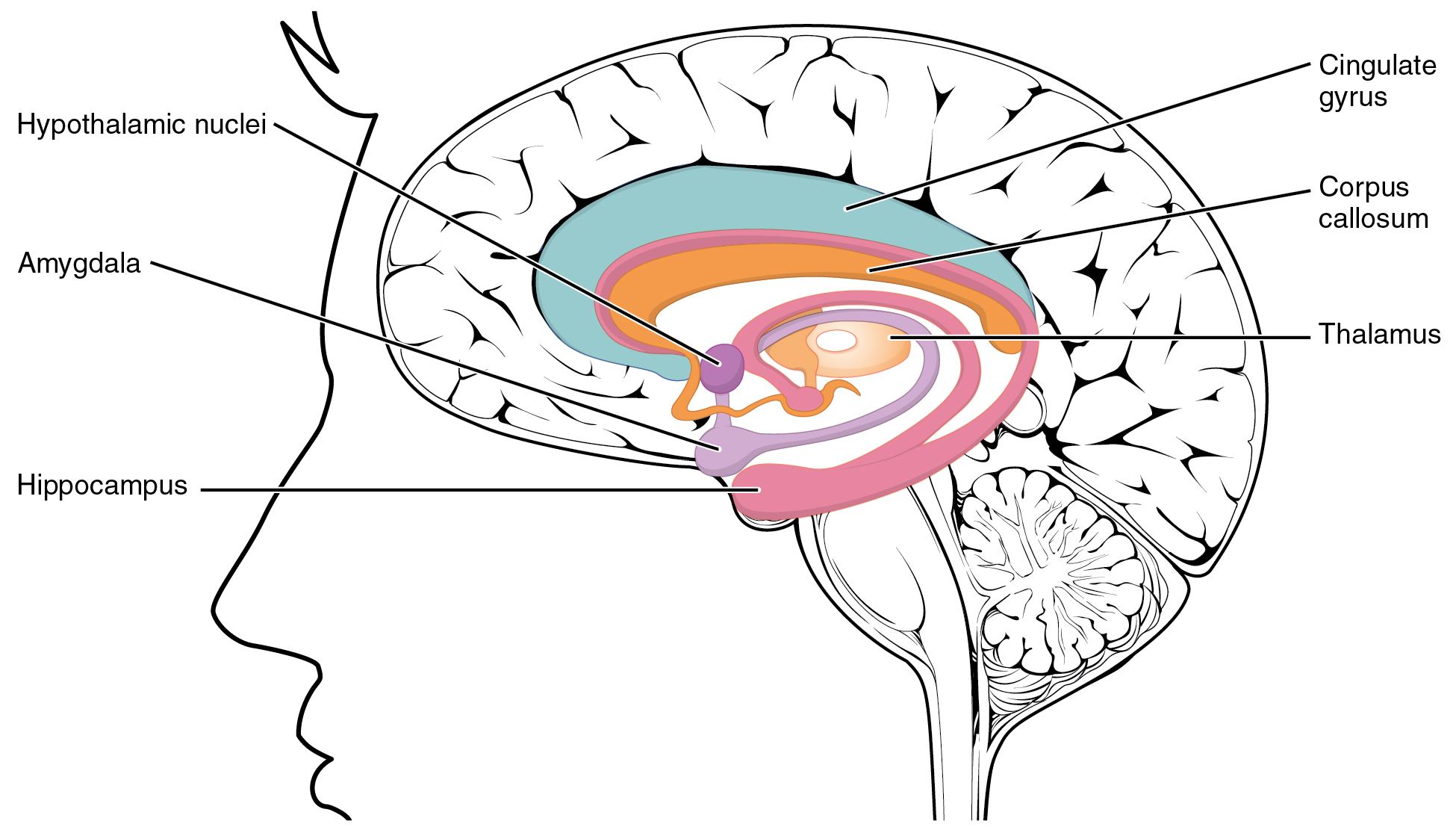
Pituitary Gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity ( sella turcica) covered by a dural fold ( diaphragma sellae). The anterior pituitary (or adenohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. The intermediate lobe synthesizes and secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone. The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the pituitary stalk (also called the infundibular stalk or the infundibulum). Hormones secreted from the pituitary glan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrichosis
Hypertrichosis is an abnormal amount of hair growth over the body. The two distinct types of hypertrichosis are generalized hypertrichosis, which occurs over the entire body, and localized hypertrichosis, which is restricted to a certain area. Hypertrichosis can be either congenital (present at birth) or acquired later in life. The excess growth of hair occurs in areas of the skin with the exception of androgen-dependent hair of the pubic area, face, and axillary regions. Several circus sideshow performers in the 19th and early 20th centuries, such as Julia Pastrana, had hypertrichosis. Many of them worked as freaks and were promoted as having distinct human and animal traits. Classification Two methods of classification are used for hypertrichosis. One divides them into either generalized versus localized hypertrichosis, while the other divides them into congenital versus acquired. Congenital Congenital forms of hypertrichosis are caused by genetic mutations, and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell. The name "glucocorticoid" is a portmanteau (glucose + cortex + steroid) and is composed from its role in regulation of glucose metabolism, synthesis in the adrenal cortex, and its steroidal structure (see structure below). Glucocorticoids are part of the feedback mechanism in the immune system, which reduces certain aspects of immune function, such as inflammation. They are therefore used in medicine to treat diseases caused by an overactive immune system, such as allergies, asthma, autoimmune diseases, and sepsis. Glucocorticoids have many diverse ( pleiotropic) effects, including potentially harmful side effects. They also interfere with some of the abnormal mechanisms in cancer cells, so they are used in high doses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, superior vena cava syndrome (a complication of some forms of cancer), and along with antibiotics in tuberculosis. In adrenocortical insufficiency, it may be used in combination with a mineralocorticoid medication such as fludrocortisone. In preterm labor, it may be used to improve outcomes in the baby. It may be given by mouth, as an injection into a muscle, as an injection into a vein, as a topical cream or ointment for the skin or as a topical ophthalmic solution to the eye. The effects of dexamethasone are frequently seen within a day and last for about three days. The long-term use of dexamethasone may result in thrush, bone loss, cataracts, easy bruising, or muscle weakness. It is in pregnancy category C in the United States, meaning that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexamethasone Suppression Test
The dexamethasone suppression test (DST) is used to assess adrenal gland function by measuring how cortisol levels change in response to oral doses or an injection of dexamethasone. It is typically used to diagnose Cushing's syndrome. The DST was historically used for diagnosing depression, but by 1988 it was considered to be "at best, severely limited in its clinical ability" for this purpose. Physiology Dexamethasone is an exogenous steroid that provides negative feedback to the pituitary gland to suppress the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Specifically, dexamethasone binds to glucocorticoid receptors in the anterior pituitary gland, which lie outside the blood–brain barrier, resulting in regulatory modulation. Test Procedures There are several types of DST procedures: # Overnight DST - An oral dose of dexamethasone is given between 11pm and midnight, and the cortisol level is measured at 8 - 9am the next morning # Two-day DST - This involves giving an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a hypophysiotropic hormone produced by neurons in the hypothalamus that stimulates the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and prolactin from the anterior pituitary. TRH has been used clinically for the treatment of spinocerebellar degeneration and disturbance of consciousness in humans. Its pharmaceutical form is called protirelin (INN) (). Synthesis and release TRH is synthesized within parvocellular neurons of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. It is translated as a 242-amino acid precursor polypeptide that contains 6 copies of the sequence -Gln-His-Pro-Gly-, flanked by Lys-Arg or Arg-Arg sequences. To produce the mature form, a series of enzymes are required. First, a protease cleaves to the C-terminal side of the flanking Lys-Arg or Arg-Arg. Second, a carboxypeptidase removes the Lys/Arg residues leaving Gly as the C-terminal residue. Then, this Gly is converted into an amide residue by a series of enzym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equine Metabolic Syndrome
Equine metabolic syndrome (EMS) is an endocrinopathy affecting horses and ponies. It is of primary concern due to its link to obesity, insulin dysregulation, and subsequent laminitis. There are some similarities in clinical signs between EMS and pituitary pars intermedia dysfunction, also known as PPID or Cushing's disease, and some equines may develop both, but they are not the same condition, having different causes and different treatment. Pathogenesis The cells of adipose (fat) tissue synthesizes hormones known as adipokines. In humans, dysfunction of adipose tissue, even in cases without obesity, has been associated with the development of insulin resistance, hypertension, systemic inflammation, and increased risk of blood clots (thrombosis). The inflammation produced by these hormones are thought to inflame adipose tissue, leading to the production of more adipokines and perpetuation of the cycle, and a constant low-level, pro-inflammatory state. Although it is suspected th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a long-term neurological disorder that involves a decreased ability to regulate sleep–wake cycles. Symptoms often include periods of excessive daytime sleepiness and brief involuntary sleep episodes. About 70% of those affected also experience episodes of sudden loss of muscle strength, known as cataplexy. Narcolepsy paired with cataplexy is evidenced to be an autoimmune disorder. These experiences of cataplexy can be brought on by strong emotions. Less commonly, there may be vivid hallucinations or an inability to move (sleep paralysis) while falling asleep or waking up. People with narcolepsy tend to sleep about the same number of hours per day as people without, but the quality of sleep tends to be lessened. Narcolepsy is a clinical syndrome of hypothalamic disorder, however, the exact cause of narcolepsy is unknown, with potentially several causes. In up to 10% of cases, there is a family history of the disorder. Often, those affected have low levels o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphagia
Polyphagia or hyperphagia is an abnormally strong, incessant sensation of hunger or desire to eat often leading to overeating. In contrast to an increase in appetite following exercise, polyphagia does not subside after eating and often leads to rapid intake of excessive quantities of food. Polyphagia is not a disorder by itself; rather, it is a symptom indicating an underlying medical condition. It is frequently a result of abnormal blood glucose levels (both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia), and, along with polydipsia and polyuria, it is one of the "3 Ps" commonly associated with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. Etymology and pronunciation The word ''polyphagia'' () uses combining forms of ''poly-'' + '' -phagia'', from the Greek words πολύς (polys), "very much" or "many", and φαγῶ (phago), "eating" or "devouring". Underlying conditions and possible causes Polyphagia is one of the most common symptoms of diabetes mellitus. It is associated with hyperthyroidism and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhydrosis
Hypohidrosis is a disorder in which a person exhibits diminished sweating in response to appropriate stimuli. In contrast with hyp''er''hidrosis, which is a socially troubling yet often benign condition, the consequences of untreated hypohidrosis include hyperthermia, heat stroke and death. An extreme case of hypohidrosis in which there is a complete absence of sweating and the skin is dry is termed anhidrosis. Causes Diagnosis Sweat is readily visualized by a topical indicator such as iodinated starch (Minor test) or sodium alizarin sulphonate, both of which undergo a dramatic colour change when moistened by sweat. A thermoregulatory sweat test can evaluate the body’s response to a thermal stimulus by inducing sweating through a hot box ⁄ room, thermal blanket or exercise. Failure of the topical indicator to undergo a colour change during thermoregulatory sweat testing indicates hypohidrosis, and further tests may be required to localize the lesion. Magnetic resonance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis is a condition characterized by abnormally increased sweating, in excess of that required for regulation of body temperature. Although primarily a benign physical burden, hyperhidrosis can deteriorate quality of life from a psychological, emotional, and social perspective. In fact, hyperhidrosis almost always leads to psychological as well as physical and social consequences. It is thus responsible for more than ¼ of the cases of social phobia. Patients suffering from it present difficulties in the professional field, more than 80% of patients experience a moderate to severe emotional impact from the disease and half are subject to depression. This excess of sweat happens even if the person is not engaging in tasks that require muscular effort, and it does not depend on the exposure to heat. Common places to sweat can include underarms, face, neck, back, groin, feet, and hands. It has been called by some researchers 'the silent handicap'. Both '' diaphoresis'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyuria
Polyuria () is excessive or an abnormally large production or passage of urine (greater than 2.5 L or 3 L over 24 hours in adults). Increased production and passage of urine may also be termed diuresis. Polyuria often appears in conjunction with polydipsia (increased thirst), though it is possible to have one without the other, and the latter may be a cause or an effect. Primary polydipsia may lead to polyuria. Polyuria is usually viewed as a symptom or sign of another disorder (not a disease by itself), but it can be classed as a disorder, at least when its underlying causes are not clear. Causes The most common cause of polyuria in both adults and children is uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, which causes osmotic diuresis, when glucose levels are so high that glucose is excreted in the urine. Water follows the glucose concentration passively, leading to abnormally high urine output. In the absence of diabetes mellitus, the most common causes are decreased secretion of aldo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |