|
Pistosaurs
Pistosauroidea is a group of marine reptiles within the superorder Sauropterygia that first appeared in the latter part of the Early Triassic and were the ancestors of plesiosaurs. Pistosauroids are rare in Triassic marine assemblages, and are represented by only a few fossils from central Europe, the United States, and China. Recent phylogenetic analyses consider the Triassic pistosauroids to be a paraphyletic grouping, meaning that they do not form a true clade. Plesiosauria is now placed within Pistosauroidea, while the traditional pistosauroids are successively more basal, or primitive, sauropterygians. Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... of pistosauroid relationships from Cheng ''et al.'' (2006): Below is a cladogram of pistosauroi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistosaurus BW
''Pistosaurus'' (''pistos'' in Greek meaning 'credible' and ''sauros'' 'lizard') is an extinct genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile closely related to plesiosaurs. Fossils have been found in France and Germany, and date to the Middle Triassic. It contains a single species, ''Pistosaurus longaevus. Pistosaurus'' is known as the oldest "subaquatic flying" reptile on earth. The skull of ''Pistosaurus'' generally resembles that of other Triassic sauropterygians. However, there are several synapomorphies that make ''Pistosaurus'' distinguished: the long, slender, snout; the possession of splint-like nasals that are excluded from the external naris; and the posterior extension of the premaxilla to the frontals. Based on synapomorphies such as the small nasals size and the presence of interpterygoid vacuity, ''Pistosaurus'' is more closely related to Plesiosauria than to ''Nothosaurus''. ''Pistosaurus'' is often mistaken with ''Nothosaurus'' and Plesiosauria. ''Nothosaurus'' belongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wangosaurus
''Wangosaurus'' is an extinct genus of basal pistosauroid known from the Middle Triassic (late Ladinian stage) Falang Formation of Xingyi in Guizhou Province, southwestern China. It contains a single species, ''Wangosaurus brevirostris'', first described and named by Le-Tian Ma, Da-Yong Jiang, Olivier Rieppel, Ryosuke Motani and Andrea Tintori in 2015. The specific name ''brevirostris'' comes from Greek for "short snout". It is known solely from its holotype, a nearly complete and articulated skeleton A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ... measuring long (without only the rear part of its tail). References Pistosaurs Triassic sauropterygians Ladinian genera Middle Triassic reptiles of Asia Triassic China Fossils of China Paleontology in Guizhou Xingyi, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
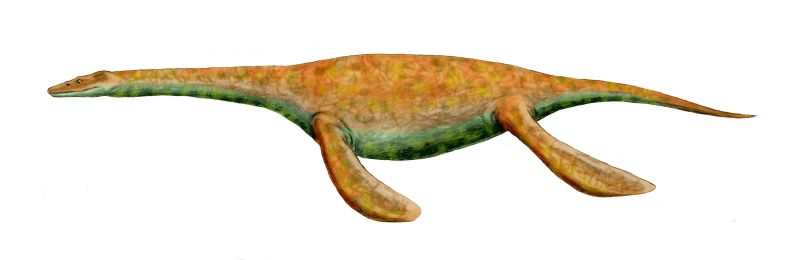
Corosaurus
''Corosaurus'' is an extinct genus of pistosauroid known from Wyoming of the United States. The holotype measured about long, while larger specimens would have belonged to individuals measuring more than long. History of discovery ''Corosaurus'' is known from the holotype UW 5485, a partial skeleton which includes the skull. Later, the referred specimens YPM 41030-41068, FMNH PR 135, FMNH PR 1368-1369, FMNH PR 242-246 and FMNH PR 1382-1383 were described by Glenn William Storrs in 1991. All specimens were collected in Jackson Canyon, Natrona County, from the Chugwater Group of the Alcova Limestone Formation, dating to the late Olenekian stage of the late Early Triassic, about 247.4-245 million years ago. Etymology ''Corosaurus'' was first named by Ermine Cowles Case in 1936 and the type species is ''Corosaurus alcovensis''. The specific name is derived from the name of the Alcova Limestone Formation, in which the holotyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunguisaurus
''Yunguisaurus'' is an extinct genus of pistosaur known from the Guizhou Province of China. Description ''Yunguisaurus'' is known from the holotype NMNS 004529/F003862, an articulated and almost complete skeleton missing only the distal tail. The preserved skeleton has a length of about with estimated total length about , while paratype specimen became much larger with length around . It was collected near Huangnihe River, Chajiang of Guizhou, from the Falang Formation. It is thought to belong to the ''Paragondolella naantangensis-P. polygnathiformis'' Assemblage Zone, dating to the Carnian stage of the early Late Triassic. It differs from other pistosauroids by a combination of characters. Nevertheless, its original description is a preliminary report while the postcranial skeleton still waits for further preparation and full description. Etymology ''Yunguisaurus'' was first named by Yen-Nien Cheng, Tamaki Sato, Xiao-Chun Wu and Chun Li in 2006 and the type species is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistosaurus
''Pistosaurus'' (''pistos'' in Greek meaning 'credible' and ''sauros'' 'lizard') is an extinct genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile closely related to plesiosaurs. Fossils have been found in France and Germany, and date to the Middle Triassic. It contains a single species, ''Pistosaurus longaevus. Pistosaurus'' is known as the oldest "subaquatic flying" reptile on earth. The skull of ''Pistosaurus'' generally resembles that of other Triassic sauropterygians. However, there are several synapomorphies that make ''Pistosaurus'' distinguished: the long, slender, snout; the possession of splint-like nasals that are excluded from the external naris; and the posterior extension of the premaxilla to the frontals. Based on synapomorphies such as the small nasals size and the presence of interpterygoid vacuity, ''Pistosaurus'' is more closely related to Plesiosauria than to ''Nothosaurus''. ''Pistosaurus'' is often mistaken with ''Nothosaurus'' and Plesiosauria. ''Nothosaurus'' belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cymatosaurus
''Cymatosaurus'' is an extinct genus of pistosauroid or nothosauriform sauropterygian. It is known to have been alive from the Early Triassic to the Middle Triassic period (latest Olenekian to Anisian stages) of Germany and they seem to originate from the Netherlands.Sander, P.M., Klein, N., Albers, P.C.H. et al. Paläontol Z (2014) 88: 55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12542-013-0181-5 See also * Timeline of plesiosaur research This timeline of plesiosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, taxonomic revisions, and cultural portrayals of plesiosaurs, an order of marine reptiles that flourished duri ... References Fossil taxa described in 1894 Early Triassic reptiles of Europe Pistosaurs Triassic sauropterygians Olenekian genus first appearances Anisian genus extinctions Middle Triassic reptiles of Europe Anisian life Sauropterygian genera {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kwangsisaurus
''Kwangsisaurus'' is an extinct genus of a basal pistosauroid known from the Early or Middle Triassic (Olenekian or Anisian age) of Guangxi, southern China. It contains a single species, ''Kwangsisaurus orientalis''. Discovery ''Kwangsisaurus'' is known solely from the holotype IVPP V2338, a fragmentary postcranial skeleton housed at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology. The skeleton consists of 20 back vertebrae, six front-most tail vertebrae, badly persevered shoulder girdle, and the right forelimb. Yang misoriented the specimen, mistaking the neck for a tail and the shoulder for a pelvis. IVPP V2338 was collected at Fupingtun, Dengilu of Wuming, Guangxi Province, from the Beisi Formation of the Loulou Group. Its dating is uncertain, but falls within the Olenekian or Anisian stage of the late Early Triassic or early Middle Triassic. A second species, ''K. lusiensis'', named by Young in 1978 based on IVPP RV 100 and collected at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cymatosauridae
''Cymatosaurus'' is an extinct genus of pistosauroid or nothosauriform sauropterygian. It is known to have been alive from the Early Triassic to the Middle Triassic period (latest Olenekian to Anisian stages) of Germany and they seem to originate from the Netherlands.Sander, P.M., Klein, N., Albers, P.C.H. et al. Paläontol Z (2014) 88: 55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12542-013-0181-5 See also * Timeline of plesiosaur research This timeline of plesiosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, taxonomic revisions, and cultural portrayals of plesiosaurs, an order of marine reptiles that flourished duri ... References Fossil taxa described in 1894 Early Triassic reptiles of Europe Pistosaurs Triassic sauropterygians Olenekian genus first appearances Anisian genus extinctions Middle Triassic reptiles of Europe Anisian life Sauropterygian genera {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corosauridae
''Corosaurus'' is an extinct genus of pistosauroid known from Wyoming of the United States. The holotype measured about long, while larger specimens would have belonged to individuals measuring more than long. History of discovery ''Corosaurus'' is known from the holotype UW 5485, a partial skeleton which includes the skull. Later, the referred specimens YPM 41030-41068, FMNH PR 135, FMNH PR 1368-1369, FMNH PR 242-246 and FMNH PR 1382-1383 were described by Glenn William Storrs in 1991. All specimens were collected in Jackson Canyon, Natrona County, from the Chugwater Group of the Alcova Limestone Formation, dating to the late Olenekian stage of the late Early Triassic, about 247.4-245 million years ago. Etymology ''Corosaurus'' was first named by Ermine Cowles Case in 1936 and the type species is ''Corosaurus alcovensis''. The specific name is derived from the name of the Alcova Limestone Formation, in which the holotype was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinchenia
''Chinchenia'' is an extinct genus of a basal pistosauroid known from the Middle Triassic (possibly Ladinian age) of Guizhou Province, southwestern China. It contains a single species, ''Chinchenia sungi''. Discovery ''Chinchenia'' is known from at least 4 extremely fragmentary individuals all preserved and collected together. The lectotype of ''Chinchenia'' was chosen to be IVPP V3227, the front end of the left mandible, since that at the time of its original description, its type material was not specified. Other elements from its original description are considered to be paratypes and include the front part of a left lower jaw with 5 broken teeth, 11 neck, six lower back and one sacral vertebrae in various degrees of completeness, 8 unidentified neural arch fragments, many fragments of dorsal and sacral ribs including one proximal part of a left dorsal rib, two right scapulae one of which is very incomplete, two complete humeri, 5 incomplete humeri of which four are d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustasaurus
''Augustasaurus'' is a genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile belonging to the Pistosauria, a clade containing plesiosaurs and their close relatives. ''Pistosaurus'' and ''Augustasaurus'' were thought to be the only known members of the family Pistosauridae.Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. Article: pp. 577–592. THE SKULL OF THE PISTOSAUR AUGUSTASAURUS FROM THE MIDDLE TRIASSIC OF NORTHWESTERN NEVADA. OLIVIER RIEPPEL, P. MARTIN SANDER, and GLENN W. STORRS. 1997 However, some recent cladistic analyses found ''Augustasaurus'' to be a more advanced pistosaur, as a sister group of the order Plesiosauria. The only known species of ''Augustasaurus'' is ''Augustasaurus hagdorni'', which was first described in 1997. Etymology The first part of ''Augustasaurus name comes from the Augusta Mountains of northwestern Nevada, USA, where its fossil bones were first discovered. The second part of the name is the Greek word ' (), which means "lizard" or "reptile." The type species, ''Augustas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a phylogenetic tree#Rooted tree, rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, Phylogenetic diversity, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and cladogenesis, diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |