|
Piscivorin
Piscivorin is a component of snake venom secreted by the Eastern Cottonmouth (''Agkistrodon piscivorus piscivorus''). It is a member of the cysteine-rich secretory protein (CRISP) family, which blocks voltage-dependent calcium channels. Etymology The name of piscivorin comes from the snake species name piscivorus, which is derived from the Latin words ''pisces'' and ''vorare'', meaning 'fish' and 'to devour' respectively. Sources Piscivorin is produced in the venom glands of the Eastern Cottonmouth snake (''Agkistrodon piscivorus piscivorus''), which populates the Eastern United States. Typically, crude venom from the Eastern Cottonmouth contains approximately 1.25% of piscivorin. Biochemistry Piscivorin belongs to the cysteine-rich secretory protein (CRISP) family, which are secreted as single-chain proteins with molecular masses between 20 and 30 kDa. They display significant amino acid sequence homology. Sixteen cysteine residues, forming 8 disulfide bonds, are strictly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triflin
Triflin is a cysteine-rich secretory protein (CRISP), which is excreted by the venom gland of the Habu snake (''Trimeresurus flavoviridis''). Triflin reduces high potassium-induced smooth muscle contraction, suggesting a blocking effect on L-type calcium channels. Sources Triflin is a toxin derived from snake venom. The toxin is produced in the gland of the Habu snake, ''Trimeresurus flavoviridis''. Chemistry Triflin is a cysteine-rich secretory protein, which means it belongs to the CRISP family. This is a group of single chain polypeptides found in various organisms. Triflin weighs 25 kDa and consists of 221 amino-acid residues. The first 163 residues of the N-terminal domain forms an α-β-α sandwich core. This domain is comparable with group 1 plant pathogenesis-related protein (PR-1). The C-terminal domain, has five disulfide bridges. This domain is responsible for the selectivity of the protein and consists of two subdomains: N-terminal subdomain (Cys 167 to Cys 179) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ablomin
Ablomin is a toxin present in the venom of the Japanese Mamushi snake, which blocks L-type voltage-gated calcium channels. Etymology The protein ablomin is a component of the venom of the Japanese Mamushi snake, ''Gloydius blomhoffii''. The term ‘ablomin’ is an acronym derived from ''Agkistrodon blomhoffi'', an old name for this snake. Sources The protein can be found in the venom of the Japanese Mamushi snake, a member of the Viperidae family. Chemistry Ablomin is part of the Cystein-Rich Secretory Protein (CRISP) family. CRISPs comprise a particular group of snake venom proteins distributed among the venom of several families of snakes, such as elapids, colubrids and vipers. The protein exists of 240 amino acids, coded by an mRNA of 1336 base pairs. Structurally, it is composed of three distinct regions: an N-terminal protein domain, a hinge region and a C-terminal cystein-rich domain. It has a molecular mass of 25 kDa The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latisemin
Latisemin is a cysteine-rich secretory protein that can be isolated from the venom of the Black-banded sea krait, a sea snake indigenous to the warmer waters of the western Pacific Ocean. It is a toxin that inhibits cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels and blocks L-type calcium channels, thereby reducing smooth muscle contraction. Sources Latisemin is a component of the venom produced by the Erabu sea snake (''Laticauda semifasciata'') of the family Elapidae and the Laticauda genus. These sea snakes inhabit coral reef areas in the seas of Southern Japan, Southeast Asia, and Australia. Though highly venomous, this snake is comparatively unaggressive, and is in fact caught and eaten in Erabu soup in Japan. Biochemistry Latisemin has a molecular weight of 24 kDa and consists of 217 amino acids. It belongs to the CRISP (cysteine-rich secretory protein) glycoprotein subfamily, which are single chain polypeptides containing strictly conserved cysteines (cysteines not oxidised to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake Venom
Snake venom is a highly toxic saliva containing zootoxins that facilitates in the immobilization and digestion of prey. This also provides defense against threats. Snake venom is injected by unique fangs during a bite, whereas some species are also able to spit venom. The glands that secrete zootoxins are a modification of the parotid salivary glands found in other vertebrates and are usually located on each side of the head, below and behind the eye, and enclosed in a muscular sheath. The venom is stored in large glands called alveoli in which it's stored before being conveyed by a duct to the base of channeled or tubular fangs through which it's ejected. Venom contains more than 20 different compounds, which are mostly proteins and polypeptides. The complex mixture of proteins, enzymes, and various other substances has toxic and lethal properties. Venom serves to immobilize prey. Enzymes in venom play an important role in the digestion of prey, and various other substances ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agkistrodon Piscivorus
''Agkistrodon piscivorus'' is a species of pit viper in the subfamily Crotalinae of the family Viperidae. It is one of the world's few semiaquatic vipers (along with the Florida cottonmouth), and is native to the southeastern United States. As an adult, it is large and capable of delivering a painful and potentially fatal bite. When threatened, it may respond by coiling its body and displaying its fangs. Individuals may bite when feeling threatened or being handled in any way. It tends to be found in or near water, particularly in slow-moving and shallow lakes, streams, and marshes. It is a capable swimmer and, like several species of snakes, is known to occasionally enter bays and estuaries and swim between barrier islands and the mainland. Gloyd HK, Conant R (1990). ''Snakes of the ''Agkistrodon'' Complex: A Monographic Review''. Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles. 614 pp. 52 plates. LCCN 89-50342. . The generic name is derived from the Greek words ''ankistro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine-rich Secretory Protein
Cysteine-rich secretory proteins, often abbreviated as CRISPs, are a group of glycoproteins. They are a subgroup of the CRISP, antigen 5 and Pr-1 (CAP) protein superfamily and also contain a domain related to the ShK toxins. They are substantially implicated in the functioning of the mammalian reproductive system. CRISPs are also found in a variety of snake venoms where they inhibit both smooth muscle contraction and cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels. Structure CRISPs contain two domains joined by a hinge region. The larger domain is a CAP-like 'Pathogenesis-related 1' domain (PR-1), followed by the smaller ShK-like 'Cysteine-Rich Domain' (CRD). CRISPs are glycoproteins, with a number of carbohydrate glycans covalently attached to amino acid side-chains on their surface via glycosylation. The primary structure is also rich in cysteine that form disulfide bonds, particularly in the hinge region and CRD. Mammalian reproduction CRISPs are found in the testes and epidid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Channels
A calcium channel is an ion channel which shows selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, although there are also ligand-gated calcium channels. Comparison tables The following tables explain gating, gene, location and function of different types of calcium channels, both voltage and ligand-gated. Voltage-gated Ligand-gated *the ''receptor-operated calcium channels'' (in vasoconstriction) **P2X receptors Page 479 Pharmacology L-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body, depolarization is mediated by sodium influx into a cell; changing the calcium permeability has little effect on action potentials. However, in many smooth muscle tissues, depolarization is mediated primarily by calcium influx into the cell. L-type calcium channel blockers selectively inhibit these action potentials in smooth muscle which leads to dilation of blood vessels; this in turn corrects hypertens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Reading Frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames will be "open" (the "reading", however, refers to the RNA produced by transcription of the DNA and its subsequent interaction with the ribosome in translation). Such an ORF may contain a start codon (usually AUG in terms of RNA) and by definition cannot extend beyond a stop codon (usually UAA, UAG or UGA in RNA). That start codon (not necessarily the first) indicates where translation may start. The transcription termination site is located after the ORF, beyond the translation stop codon. If transcription were to cease before the stop codon, an incomplete protein would be made during translation. In eukaryotic genes with multiple exons, introns are removed and exons are then joined together after transcription to yield the final ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine class. It is mainly used recreationally as a cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional performance. Caffeine acts by blocking binding of adenosine to the adenosine A1 receptor, which enhances release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Caffeine has a three-dimensional structure similar to that of adenosine, which allows it to bind and block its receptors. Caffeine also increases cyclic AMP levels through nonselective inhibition of phosphodiesterase. Caffeine is a bitter, white crystalline purine, a methylxanthine alkaloid, and is chemically related to the adenine and guanine bases of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). It is found in the seeds, fruits, nuts, or leaves of a number of plants native to Africa, East Asia and South America, and helps to protect them against herbivores and from competition by preventing the germination of nearby seeds, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
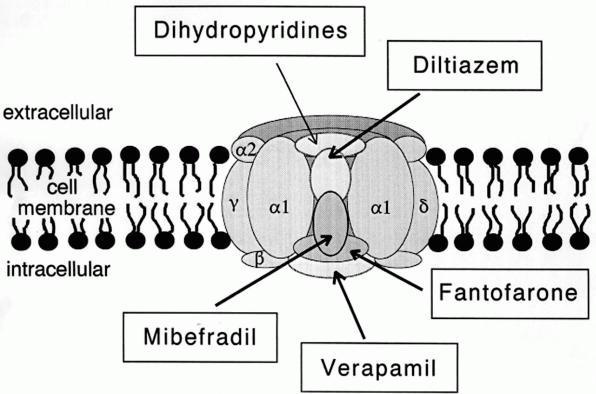
L-type Calcium Channel
The L-type calcium channel (also known as the dihydropyridine channel, or DHP channel) is part of the high-voltage activated family of voltage-dependent calcium channel. "L" stands for long-lasting referring to the length of activation. This channel has four isoforms: Cav1.1, Cav1.2, Cav1.3, and Cav1.4. L-type calcium channels are responsible for the excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal, smooth, cardiac muscle, and for aldosterone secretion in endocrine cells of the adrenal cortex. They are also found in neurons, and with the help of L-type calcium channels in endocrine cells, they regulate neurohormones and neurotransmitters. They have also been seen to play a role in gene expression, mRNA stability, neuronal survival, ischemic-induced axonal injury, synaptic efficacy, and both activation and deactivation of other ion channels. In cardiac myocytes, the L-type calcium channel passes inward Ca2+ current (ICaL) and triggers calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Nucleotide-gated Channels
Cycle, cycles, or cyclic may refer to: Anthropology and social sciences * Cyclic history, a theory of history * Cyclical theory, a theory of American political history associated with Arthur Schlesinger, Sr. * Social cycle, various cycles in social sciences ** Business cycle, the downward and upward movement of gross domestic product (GDP) around its ostensible, long-term growth trend Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Cycle'' (2008 film), a Malayalam film * ''Cycle'' (2017 film), a Marathi film Literature * ''Cycle'' (magazine), an American motorcycling enthusiast magazine * Literary cycle, a group of stories focused on common figures Music Musical terminology * Cycle (music), a set of musical pieces that belong together ** Cyclic form, a technique of construction involving multiple sections or movements **Interval cycle, a collection of pitch classes generated from a sequence of the same interval class **Song cycle, individually complete songs designed to be perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate Toxins
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * jawed vertebrates, which include: ** cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays, and ratfish) ** bony vertebrates, which include: *** ray-fins (the majority of living bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described animal species; the rest are invertebrates, which lack vertebral columns. The vertebrates traditionally include the hagfish, which do not have pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)