|
Pieniny Mountains
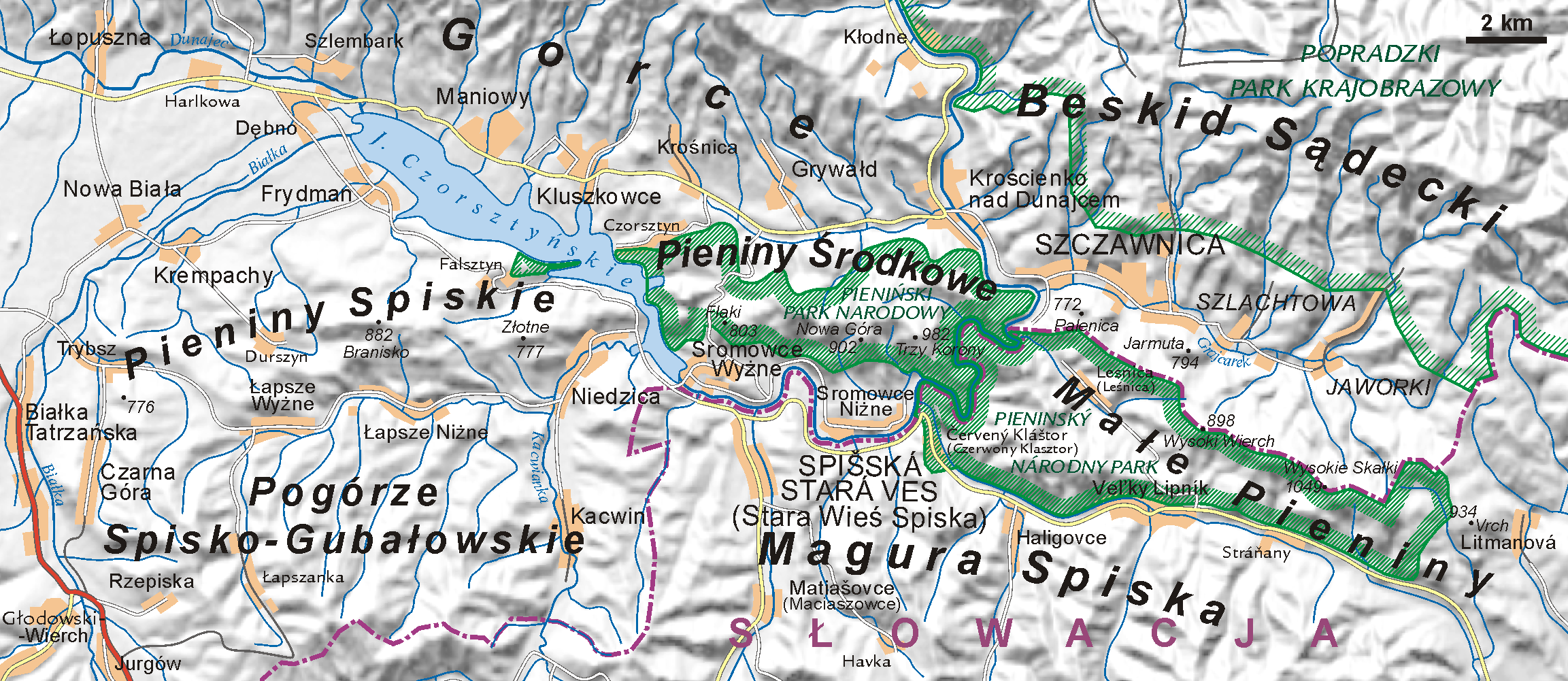
The Pieniny (sometimes also the PieninsSzafer, Władysław. 2013. ''The Vegetation of Poland: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology''. Warsaw: Pergamon Press, pp. 156, 388. or the Pienin Mountains,Griffiths, Graham C. D. 1976. Studies on Boreal Agromyzidae (Diptera). XII. ''Phytomyza'' and ''Chromatomyia'' miners on Astereae (Compositae).''Quaestiones Entomologicae'' 12: 239–275, p. 255. hu, Pieninek) is a mountain range in the south of Poland and the north of Slovakia. It is classified within the eastern section of the Western Beskids. The Pieniny mountain range is divided into three parts – ''Pieniny Spiskie'' ( sk, Spišské Pieniny) and ''Pieniny Właściwe'' (Slovak: ''Centrálne Pieniny'') in Poland; and, ''Małe Pieniny'' ( en, Lesser or Little Pieniny; sk, Malé Pieniny) in Poland and Slovakia. The Pieniny mountains consist mainly of beds of limestone and dolomite. The most famous peak, ''Trzy Korony'' (Three Crowns), is 982 metres high. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin. Poland has a temperate transitional climate and its territory traverses the Central European Plain, extending from Baltic Sea in the north to Sudeten and Carpathian Mountains in the south. The longest Polish river is the Vistula, and Poland's highest point is Mount Rysy, situated in the Tatra mountain range of the Carpathians. The country is bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. It also shares maritime boundaries with Denmark and Sweden. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Above Sea Level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''. The combination of unit of measurement and the physical quantity (height) is called "metres above mean sea level" in the metric system, while in United States customary and imperial units it would be called "feet above mean sea level". Mean sea levels are affected by climate change and other factors and change over time. For this and other reasons, recorded measurements of elevation above sea level at a reference time in history might differ from the actual elevation of a given location over sea level at a given moment. Uses Metres above sea level is the standard measurement of the elevation or altitude of: * Geographic locations such as towns, mountains and other landmarks. * The top of buildings and other structures. * Flying objects such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikołaj Zyblikiewicz
Mikołaj Zyblikiewicz (; uk, Миколай Зиблікевич; 28 November 1823 – 16 May 1887) was a Polish politician and lawyer of Ruthenian origin. He was the Mayor of Kraków – in the then Austrian sector of Partitioned Poland. A street in Kraków's Old Town is named in his memory, while his monument stands in front of the City Hall. Some of his achievements included the restoration of Sukiennice, the creation of a "national Panthéon" at Skałka, and his campaign towards the renovation of Wawel Castle. Career Mikołaj Zyblikiewicz was the son of Szymon Zyblikiewicz, a furrier of Ruthenian (Ukrainian) background in the town of Stare Miasto near Sambor (now Stary Sambir in western Ukraine); he would later self-identify as " gente Ruthenus, natione Polonus". After graduating from high-school in Lviv, he enrolled at the Lviv University while working as a home tutor for local nobility. His political activism began during the Spring of Nations when he join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pieniny National Park (Slovakia)
Pieniny National Park ( sk, Pieninský národný park; abbr. PIENAP) is a national park in northern Slovakia. The park is located in the eastern Pieniny Mountains on the border with Poland. It is the smallest national park in Slovakia with an area of 37.49 km2 (14.48 mi2) and a buffer zone of 224.44 km2 (86.66 mi2). The park is located in the Slovak districts of Kežmarok and Stará Ľubovňa in the Prešov Region. History The Zamagurie region was already declared as a protected territory in 1932, making it the first protected international nature park in Europe. On the Polish side it was called Pieniński Park Narodowy, while the Slovak part of the Pieniny Mountains was a national nature reserve. The National Park itself was founded on 16 January 1967, which makes it the second oldest national park in Slovakia after the Tatra National Park. By the 1994 act of the Slovak parliament regarding nature and landscape protection, the name of the park was changed to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czorsztyn
Czorsztyn (German: ''Schorstin'') is a village in Poland, in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Nowy Targ County. The village lies in Pieniny, the mountain range on the current Polish- Slovak border. It is famous for the ruins of a 14th-17th-century castle, which was the scene of the Kostka-Napierski Uprising in 1651. Highlights Czorsztyn gave its name to the man-made reservoir also known as Lake Czorsztyn, completed in 1994. The village along with its mountainous surroundings is a recreational destination with well developed tourist infrastructure: accommodations, pleasure-boats dock, and numerous marked hiking trails. from The Department of Hotel & Tourist Services ''Niedzica.com''. Gallery [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niedzica Castle
Niedzica Castle also known as Dunajec Castle ( lat, Castrum de Dunajecz, hu, Nedec Váralja / Nedec-Vár, german: Sub-Arx Unterschloss, sk, Nedecký hrad), is located in the southernmost part of Poland in Niedzica ( Nowy Targ County in Lesser Poland). It was erected between the years 1320 and 1326 by Kokos of Brezovica on the site of an ancient stronghold surrounded by earthen walls in the Pieniny mountains. The Niedzica Castle stands at an altitude of 566 m, on a hill upstream from the Dunajec River mouth, measured from the center of the dam on Lake Czorsztyn. The outline of Niedzica Castle can best be viewed from the ruins of Czorsztyn Castle on the other side of the lake. It is known as one of the most picturesque castles in the country and adorns the covers of many books. History The castle was an important centre of Polish-Hungarian relations since the 14th century. It was a place where the money lent by the Polish king to the Hungarian king Sigismund had to be ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunajec
The Dunajec (); Goral dialects: ''Dónajec'') is a river running through northeastern Slovakia and southern Poland. It is also regarded as the main river of the Goral Lands. It is a right tributary of the Vistula River. It begins in Nowy Targ at the junction of two short mountain rivers, Czarny Dunajec and Biały Dunajec (Black and White Dunajec). Dunajec forms the border between Poland and Slovakia for in the Pieniny Środkowe (Slovak: Centrálne Pieniny) range, east of the Czorsztyn reservoir. Geography The Dunajec is long, including its source river Czarny Dunajec,Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Poland 2017 |
Volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pieniny National Park (Poland)
'' , iucn_category = II , photo = Pieniny Trzy Korony.jpg , photo_caption = View of Trzy Korony Massif from Dunajec River Park logo with stylized Trzy Korony Massif , map = Poland , relief = 1 , map_caption = Location in Poland Map of Pieniny with two National Parks outlined , location = Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland , nearest_city = Szczawnica , coords = , area_km2 = 23.46 , established = 1932 , visitation_num = , visitation_year = , governing_body = Ministry of the Environment , url = Pieniny National Park ( pl, Pieniński Park Narodowy) is a protected area located in the heart of the Pieniny mountains in the southernmost part of Poland. Administratively, the Park lies in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship on the border with Slovakia. Its head office is in Krościenko nad Dunajcem. The Pieniny mountain chain is divided into three ranges: ''Pieniny Spiskie'', ''Małe Pieniny'', and the ''Pieniny Właściwe'' range where the Park is located. The Park's area is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunajec River Gorge
The Dunajec River Gorge ( pl, Przełom Dunajca; sk, Prielom Dunajca; german: Dohnst-Schlucht) runs through the Pieniny Mountains in the south of Poland and the north of Slovakia (as Dunajec is the border river between the two countries in the area). The gorge is characterized by some of the most interesting geological and geomorphological structures and area-specific natural ecosystems with little anthropogenic influence. It is featured on UNESCO's Tentative List of World Heritage Sites in Poland.UNESCO World Heritage List, Poland. Accessed 7 September 2011. Dunajec Gorge is also one of the best-known attractions in the Pieniny Mountains. Wooden [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar, Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion procee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |