|
Physogastric
Physogastrism or physogastry is a characteristic of certain arthropods (mostly insects and mites), where the abdomen is greatly enlarged and membranous. The most common examples are the "queens" of certain species of eusocial insects such as termites, bees and ants, in which the abdomen swells in order to hold enlarged ovaries, thus increasing fecundity. This means that the queen has the ability to hold more and produce more eggs at one time. Physogastric queens produce an enormous number of eggs which can account for a significant amount of their body weight. In the termite species '' Macrotermes subhyalinus'', eggs can make up a third of their body weight, and a 15-gram queen can produce up to 30 eggs per minute. The physogastric queens' egg production is supported by oocyte proteins supplied by the "queen body fat." In termites Physogastrism in termites presents itself in quite an unusual manner. Unlike most physogastric insects, the queen termite is able to increase its size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwarziana Quadripunctata
''Schwarziana quadripunctata'' is a small, stingless bee found in a stretch of the South American Amazon from Goiás, Brazil, through Paraguay, to Misiones, Argentina.Michener, C.D. (2007). ''The Bees of the World''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. This highly eusocial insect constructs earthen nests in the subterranean level of the subtropical environment, an unusual feature among other stingless bees. The species ranges in sizes from and feeds on a diverse diet of flowering plants found abundantly on the forest floor, including guacatonga (''Casearia sylvestris'') and the mistletoe species '' Struthanthus concinnus''. Taxonomy and phylogeny ''Schwarziana quadripunctata'' was first described by the French entomologist and former president of the French Entomologist Society Amédéé Louis Michel le Peletier in 1836. Although originally placed in the genus ''Trigona'', more recent taxonomic evaluations have since placed it under its current genus, following the 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paratrigona Subnuda
''Paratrigona subnuda'', commonly known as the jataí-da-terra ("ground jataí"), is a species of eusocial stingless bee in the family Apidae and tribe Meliponini. These social bees are prevalent in Neotropical moist forests, including Brazilian Atlantic and other South American forests. They inhabit spherical nests in moist underground environments with their forest habitats. Within their Neotropical habitats the ''P. subnuda'' is considered to be a very successful and common species of bee. ''P. subnuda''’s main source of food is pollen and nectar from a large variety of native Mesoamerican tropical plants. They have been extensively studied due to social conflicts arising from single mate behaviors and particular virgin behaviors. ''P. subnuda'' also exhibits the particular daily behavior in which they open the nest entrance at dawn and close the entrance at dusk when all their activities are done. Taxonomy and phylogeny ''P. subnuda'' belongs to the family Apidae, but far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
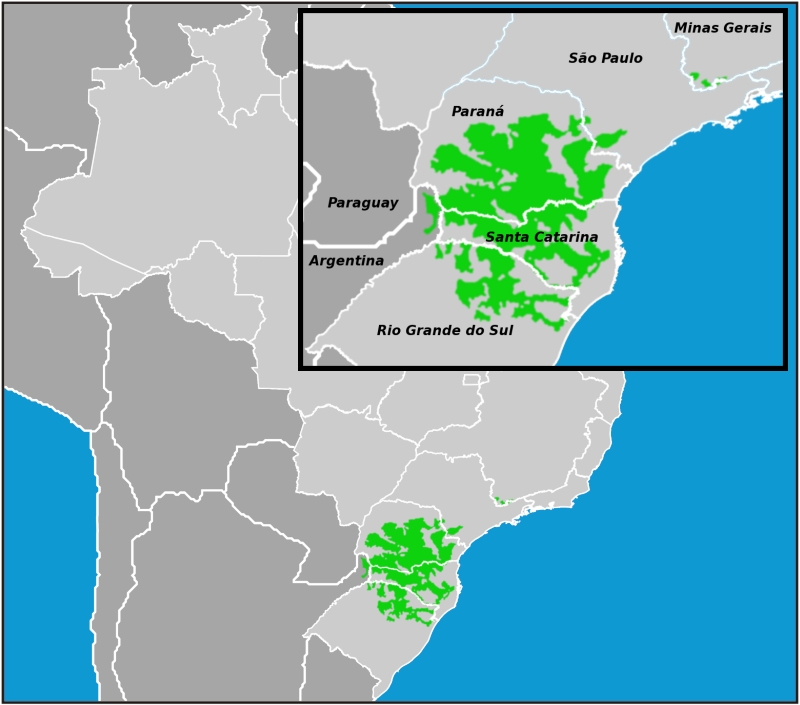
Melipona Bicolor
''Melipona bicolor'' , commonly known as Guaraipo or Guarupu, is a eusocial bee found primarily in South America. It is an inhabitant of the Araucaria Forest and the Atlantic Rainforest, and is most commonly found from South to East Brazil, Bolivia, Argentina, and Paraguay. It prefers to nest close to the soil, in hollowed trunks or roots of trees. ''M. bicolor'' is a member of the tribe Meliponini, and is therefore a stingless bee. This species is unique among the stingless bees species because it is polygynous, which is rare for eusocial bees. Taxonomy and phylogeny ''M. bicolor'' belongs to the genus ''Melipona'' and the tribe Meliponini, which comprises about 500 species of stingless bees. Although they are called stingless, these bees do have a stinger, but it is extremely small and cannot be used for defense.Michener, C D. The bees of the World. Johns Hopkins University Press, 972 pp. ''M. bicolor'' is closely related to the other 40 known species in the genus ''Melipona' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Termite
Termites are small insects that live in colonies and have distinct castes (eusocial) and feed on wood or other dead plant matter. Termites comprise the infraorder Isoptera, or alternatively the epifamily Termitoidae, within the order Blattodea (along with cockroaches). Termites were once classified in a separate order from cockroaches, but recent phylogenetic studies indicate that they evolved from cockroaches, as they are deeply nested within the group, and the sister group to wood eating cockroaches of the genus ''Cryptocercus''. Previous estimates suggested the divergence took place during the Jurassic or Triassic. More recent estimates suggest that they have an origin during the Late Jurassic, with the first fossil records in the Early Cretaceous. About 3,106 species are currently described, with a few hundred more left to be described. Although these insects are often called "white ants", they are not ants, and are not closely related to ants. Like ants and some bees a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusociality
Eusociality (from Greek εὖ ''eu'' "good" and social), the highest level of organization of sociality, is defined by the following characteristics: cooperative brood care (including care of offspring from other individuals), overlapping generations within a colony of adults, and a division of labor into reproductive and non-reproductive groups. The division of labor creates specialized behavioral groups within an animal society which are sometimes referred to as 'castes'. Eusociality is distinguished from all other social systems because individuals of at least one caste usually lose the ability to perform at least one behavior characteristic of individuals in another caste. Eusocial colonies can be viewed as superorganisms. Eusociality exists in certain insects, crustaceans, and mammals. It is mostly observed and studied in the Hymenoptera (ants, bees, and wasps) and in Blattodea (termites). A colony has caste differences: queens and reproductive males take the roles of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beetle
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described insects and 25% of all known animal life-forms; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae (ladybirds or ladybugs) eat aphids, scale insects, thrips, and other plant-sucking insects that damage crops. Beetles typically have a particularly hard e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunga Penetrans
''Tunga penetrans'' is a species of flea also known as the jigger, jigger flea, chigoe, chigo, chigoe flea, chigo flea, nigua, sand flea, or burrowing flea. It is a parasitic insect found in most tropical and sub-tropical climates. In its parasitic phase it has significant impact on its hosts, which include humans and certain other mammalian species. A parasitical infestation of ''T. penetrans'' is called tungiasis. Jiggers are often confused with chiggers, a type of mite. Jiggers are native to Central and South America, and have been introduced by colonialists to sub-Saharan Africa.Cestari TF, Pessato S, Ramos-e-Silva M Tungiasis and myiasis.' Clin Dermatol. 2007 Mar-Apr;25(2):158-64. Synonyms for ''Tunga penetrans'' include ''Sarcopsylla penetrans'', ''Pulex penetrates'', and many others. Identification ''T. penetrans'' is the smallest known flea, at only 1 mm. It is most recognizable in its parasite phase. While embedded under the stratum corneum layer of the skin, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitism
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted paras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megetra
''Megetra'' is a genus of blister beetles in the family Meloidae. There are at least three described species in ''Megetra''. Species These three species belong to the genus ''Megetra'': * ''Megetra cancellata'' (Brandt & Erichson, 1832) * ''Megetra punctata'' Selander, 1965 * ''Megetra vittata ''Megetra vittata'' is a species of blister beetle in the family Meloidae Blister beetles are beetles of the family Meloidae, so called for their defensive secretion of a blistering agent, cantharidin. About 7,500 species are known worldwide. ...'' (LeConte, 1853) References Further reading * * * Meloidae Articles created by Qbugbot Tenebrionoidea genera {{meloidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meloidae
Blister beetles are beetles of the family Meloidae, so called for their defensive secretion of a blistering agent, cantharidin. About 7,500 species are known worldwide. Many are conspicuous and some are aposematically colored, announcing their toxicity to would-be predators. Description Blister beetles are hypermetamorphic, going through several larval stages, the first of which is typically a mobile triungulin. The larvae are insectivorous, mainly attacking bees, though a few feed on grasshopper eggs. While sometimes considered parasitoids, in general, the meloid larva apparently consumes the immature host along with its provisions, and can often survive on the provisions alone; thus it is not an obligatory parasitoid, but rather a facultative parasitoid, or simply a kleptoparasite. The adults sometimes feed on flowers and leaves of plants of such diverse families as the Amaranthaceae, Asteraceae, Fabaceae, and Solanaceae. Cantharidin, a poisonous chemical that causes blist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrophysa
''Gastrophysa'' is a genus of beetles in the family Chrysomelidae, in which the females typically exhibit swollen, membranous abdomens, a condition known as physogastrism. Species These nine species belong to the genus ''Gastrophysa'': * ''Gastrophysa analis'' (Reitter, 1890) * ''Gastrophysa atrocyanea'' Motschulsky * '' Gastrophysa cyanea'' F. E. Melsheimer, 1847 (green dock beetle) * ''Gastrophysa dissimilis'' (Say, 1824) * ''Gastrophysa formosa'' (Say, 1824) * ''Gastrophysa janthina'' Suffrian, 1851 * ''Gastrophysa polygoni'' (Linnaeus, 1758) (knotweed leaf beetle) * ''Gastrophysa unicolor'' (Marsham, 1802) * ''Gastrophysa viridula'' (De Geer, 1775) g Data sources: i = ITIS, c = Catalogue of Life, g = GBIF, b = Bugguide.net References External links * * * Chrysomelinae Chrysomelidae genera Taxa named by Louis Alexandre Auguste Chevrolat {{Chrysomelinae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysomelidae
The insects of the beetle family Chrysomelidae are commonly known as leaf beetles, and include over 37,000 (and probably at least 50,000) species in more than 2,500 genera, making up one of the largest and most commonly encountered of all beetle families. Numerous subfamilies are recognized, but the precise taxonomy and systematics are likely to change with ongoing research. Leaf beetles are partially recognizable by their tarsal formula, which appears to be 4-4-4, but is actually 5-5-5 as the fourth tarsal segment is very small and hidden by the third. As with many taxa, no single character defines the Chrysomelidae; instead, the family is delineated by a set of characters. Some lineages are only distinguished with difficulty from longhorn beetles (family Cerambycidae), namely by the antennae not arising from frontal tubercles. Adult and larval leaf beetles feed on all sorts of plant tissue, and all species are fully herbivorous. Many are serious pests of cultivated plants, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |