|
Physical Oncology
Physical oncology (PO) is defined as the study of the role of mechanical signals in a cancerous tumor. The mechanical signals can be forces, pressures ("pull", "push" and "shear" designating the forces / pressures that push, pull or are tangential). If we generalize we will speak of "stress field" and " stress tensor". A cancerous tumor (or "solid tumor" in the jargon of oncologists to differentiate them from hematological malignancies) is an organ consisting of two tissues: in the center the cancerous tumor proper and around the ExtraCellular Matrix (ECM), sometimes called stroma, chorion or connective tissue. The concept of connective tissue is interesting because it defines a tissue that travels the entire organism (except the brain) and is a preferred transmitter of mechanical signals. But for the cancer organ - isolated from this connective system - we prefer the term ECM. The cancerous tissue is derived from a normal tissue of the body: breast cancer arises from a cancerous tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancerous Tumor
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of a cell. Ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catenin
Catenins are a family of proteins found in complexes with cadherin cell adhesion molecules of animal cells. The first two catenins that were identified became known as α-catenin and β-catenin. α-Catenin can bind to β-catenin and can also bind filamentous actin (F-actin). β-Catenin binds directly to the cytoplasmic tail of classical cadherins. Additional catenins such as γ-catenin and δ-catenin have been identified. The name "catenin" was originally selected ('catena' means 'chain' in Latin) because it was suspected that catenins might link cadherins to the cytoskeleton. Types * α-catenin * β-catenin *γ-catenin * δ-catenin All but α-catenin contain armadillo repeats. They exhibit a high degree of protein dynamics, alone or in complex. Function Several types of catenins work with N-cadherins to play an important role in learning and memory. Cell-cell adhesion complexes are required for simple epithelia in higher organisms to maintain structure, function and pola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanobiology
Mechanobiology is an emerging field of science at the interface of biology, engineering, chemistry and physics. It focuses on how physical forces and changes in the mechanical properties of cells and tissues contribute to development, cell differentiation, physiology, and disease. Mechanical forces are experienced and may be interpreted to give biological responses in cells. The movement of joints, compressive loads on the cartilage and bone during exercise, and shear pressure on the blood vessel during blood circulation are all examples of mechanical forces in human tissues. A major challenge in the field is understanding mechanotransduction—the molecular mechanisms by which cells sense and respond to mechanical signals. While medicine has typically looked for the genetic and biochemical basis of disease, advances in mechanobiology suggest that changes in cell mechanics, extracellular matrix structure, or mechanotransduction may contribute to the development of many diseases, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
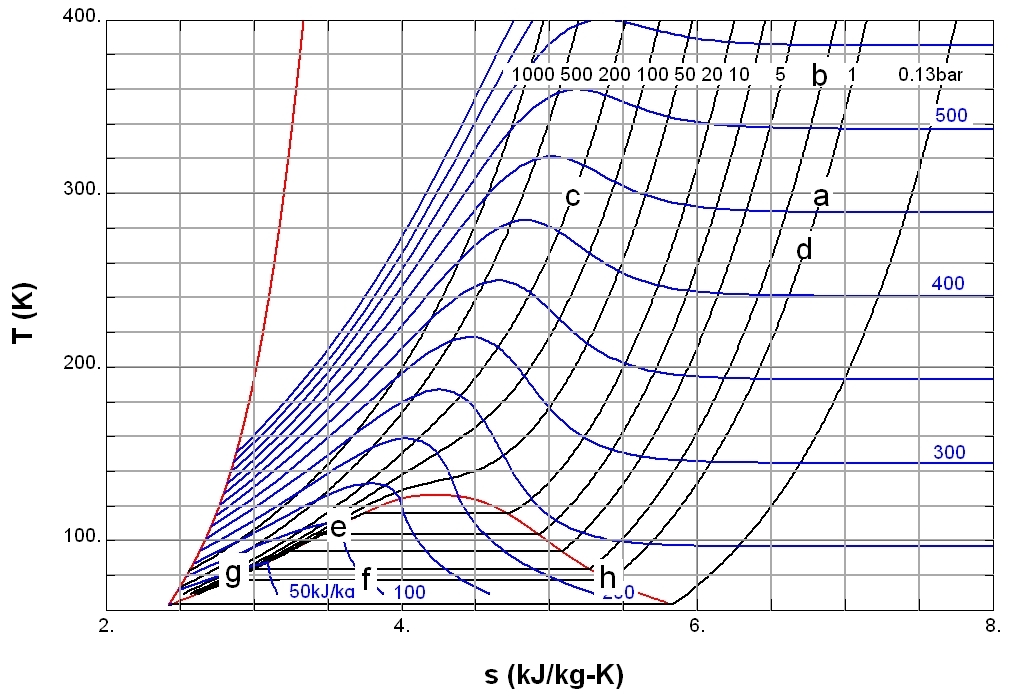
Enthalpy
Enthalpy , a property of a thermodynamic system, is the sum of the system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant pressure, which is conveniently provided by the large ambient atmosphere. The pressure–volume term expresses the work required to establish the system's physical dimensions, i.e. to make room for it by displacing its surroundings. The pressure-volume term is very small for solids and liquids at common conditions, and fairly small for gases. Therefore, enthalpy is a stand-in for energy in chemical systems; bond, lattice, solvation and other "energies" in chemistry are actually enthalpy differences. As a state function, enthalpy depends only on the final configuration of internal energy, pressure, and volume, not on the path taken to achieve it. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement for enthalpy is the joule. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change, and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication. The thermodynamic concept was referred to by Scottish scientist and engineer William Rankine in 1850 with the names ''thermodynamic function'' and ''heat-potential''. In 1865, German physicist Rudolf Clausius, one of the leading founders of the field of thermodynamics, defined it as the quotient of an infinitesimal amount of hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Changement D'architecture Histologique
''Perdu d'avance'' is the debut studio album by French rapper Orelsan. It was released on 16 February 2009 by 3e Bureau and 7th Magnitude. It peaked at number 10 on the French Albums Chart, and sold more than 10,000 copies. It was also nominated for a Prix Constantin award. Track listing All songs written by Aurélien Cotentin and produced by Skread. ;Notes * "Pour le pire" features vocals by Nadia. * "Gros poissons dans une petite mare" features vocals by Keina. Personnel Credits for ''Perdu d'avance'' adapted from Discogs. * 123 Klan – Artwork * Benjamin Brard – Artwork * Jean-Pierre Chalbos – Mastering * Véronica Ferraro – Mixing * Gringe – Featured artist * Keina – Vocals * Manuel Lagos Cid – Photography * Nadia – Vocals * Orelsan – Primary artist * Skread – Producer, recording A record, recording or records may refer to: An item or collection of data Computing * Record (computer science), a data structure ** Record, or row (database), a set of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Stress
Radial stress is stress towards or away from the central axis of a component. Pressure vessels The walls of pressure vessels generally undergo triaxial loading. For cylindrical pressure vessels, the normal loads on a wall element are: * the longitudinal stress * the circumferential (hoop) stress * the radial stress. The radial stress for a thick-walled cylinder is equal and opposite to the gauge pressure Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressur ... on the inside surface, and zero on the outside surface. The circumferential stress and longitudinal stresses are usually much larger for pressure vessels, and so for thin-walled instances, radial stress is usually neglected. Formula The radial stress for a thick walled pipe at a point r from the central axis is given by : \sigma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. It is composed of three main components, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules, and these are all capable of rapid growth or disassembly dependent on the cell's requirements. A multitude of functions can be performed by the cytoskeleton. Its primary function is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation, and through association with extracellular connective tissue and other cells it stabilizes entire tissues. The cytoskeleton can also contract, thereby deforming the cell and the cell's environment and allowing cells to migrate. Moreover, it is involved in many cell signaling pathways and in the uptake of extracellular material ( endocytosis), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voxel
In 3D computer graphics, a voxel represents a value on a regular grid in three-dimensional space. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (i.e. coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. Instead, rendering systems infer the position of a voxel based upon its position relative to other voxels (i.e., its position in the data structure that makes up a single volumetric image). In contrast to pixels and voxels, polygons are often explicitly represented by the coordinates of their vertices (as points). A direct consequence of this difference is that polygons can efficiently represent simple 3D structures with much empty or homogeneously filled space, while voxels excel at representing regularly sampled spaces that are non-homogeneously filled. Voxels are frequently used in the visualization and analysis of medical and scientific data (e.g. geographic information systems (GIS)). Some volumetric displays use voxels to describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Force Microscopy
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit. Overview Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit. The information is gathered by "feeling" or "touching" the surface with a mechanical probe. Piezoelectric elements that facilitate tiny but accurate and precise movements on (electronic) command enable precise scanning. Despite the name, the Atomic Force Microscope does not use the Nuclear force. Abilities The AFM has three major abilities: force measurement, topographic imaging, and manipulation. In force measurement, AFMs can be used to measure the forces between the probe and the sample as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ex Vivo
''Ex vivo'' (Latin: "out of the living") literally means that which takes place outside an organism. In science, ''ex vivo'' refers to experimentation or measurements done in or on tissue from an organism in an external environment with minimal alteration of natural conditions. Testing the effect of compounds on skin biopsies is an example of ''ex vivo'' research, while isolating the primary cells from that biopsy and creating a 3D cell culture model is an example of ''in vitro'' research. Both use human tissues, but the former is a more complex and translational environment for drug testing. A primary advantage of using ''ex vivo'' tissues is the ability to perform tests or measurements that would otherwise not be possible or ethical in living subjects. Tissues may be experimented on in many ways, including in part (e.g. cardiac contractility models using atrial pectinate muscles) or as whole organs (e.g. isolated perfused heart model). Examples of ''ex vivo'' models include: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal à Euclidien
In mathematics, a fractal is a geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illustrated in successive magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. This exhibition of similar patterns at increasingly smaller scales is called self-similarity, also known as expanding symmetry or unfolding symmetry; if this replication is exactly the same at every scale, as in the Menger sponge, the shape is called affine self-similar. Fractal geometry lies within the mathematical branch of measure theory. One way that fractals are different from finite geometric figures is how they scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a filled polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the conventional dimension of the filled polygon). Likewise, if the radius of a filled sphere i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |