|
Phycobilisome Structure
Phycobilisomes are light harvesting antennae of photosystem II in cyanobacteria, red algae and glaucophytes. It was lost in the plastids of green algae / plants (chloroplasts). General structure Phycobilisomes are protein complexes (up to 600 polypeptides) anchored to thylakoid membranes. They are made of stacks of chromophorylated proteins, the phycobiliproteins, and their associated linker polypeptides. Each phycobilisome consists of a core made of allophycocyanin, from which several outwardly oriented rods made of stacked disks of phycocyanin and (if present) phycoerythrin(s) or phycoerythrocyanin. The spectral property of phycobiliproteins are mainly dictated by their prosthetic groups, which are linear tetrapyrroles known as phycobilins including phycocyanobilin, phycoerythrobilin, phycourobilin and phycobiliviolin. The spectral properties of a given phycobilin is influenced by its protein environment. Function Each phycobiliprotein has a specific absorption and fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Harvesting Complex
A light-harvesting complex consists of a number of chromophores which are complex subunit proteins that may be part of a larger super complex of a photosystem, the functional unit in photosynthesis. It is used by plants and photosynthetic bacteria to collect more of the incoming light than would be captured by the photosynthetic reaction center alone. The light which is captured by the chromophores is capable of exciting molecules from their ground state to a higher energy state, known as the excited state. This excited state does not last very long and is known to be short-lived. Light-harvesting complexes are found in a wide variety among the different photosynthetic species, with no homology among the major groups. The complexes consist of proteins and photosynthetic pigments and surround a photosynthetic reaction center to focus energy, attained from photons absorbed by the pigment, toward the reaction center using Förster resonance energy transfer. Function Photosyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosthetic Group
A prosthetic group is the non-amino acid component that is part of the structure of the heteroproteins or conjugated proteins, being tightly linked to the apoprotein. Not to be confused with the cofactor that binds to the enzyme apoenzyme (either a holoprotein or heteroprotein) by non-covalent binding a non-protein (non-amino acid) This is a component of a conjugated protein that is required for the protein's biological activity. The prosthetic group may be organic (such as a vitamin, sugar, RNA, phosphate or lipid) or inorganic (such as a metal ion). Prosthetic groups are bound tightly to proteins and may even be attached through a covalent bond. They often play an important role in enzyme catalysis. A protein without its prosthetic group is called an apoprotein, while a protein combined with its prosthetic group is called a holoprotein. A non-covalently bound prosthetic group cannot generally be removed from the holoprotein without denaturating the protein. Thus, the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stokes Shift
__NOTOC__ Stokes shift is the difference (in energy, wavenumber or frequency units) between positions of the band maxima of the absorption and emission spectra ( fluorescence and Raman being two examples) of the same electronic transition. It is named after Irish physicist George Gabriel Stokes. Sometimes Stokes shifts are given in wavelength units, but this is less meaningful than energy, wavenumber or frequency units because it depends on the absorption wavelength. For instance, a 50 nm Stokes shift from absorption at 300 nm is larger in terms of energy than a 50 nm Stokes shift from absorption at 600 nm. When a system (be it a molecule or atom) absorbs a photon, it gains energy and enters an excited state. One way for the system to relax is to emit a photon, thus losing its energy (another method would be the loss of energy as translational mode energy (via vibrational-translational or electronic-translational collisional processes with other atoms or molecules)). When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microarrays
A microarray is a multiplex lab-on-a-chip. Its purpose is to simultaneously detect the expression of thousands of genes from a sample (e.g. from a tissue). It is a two-dimensional array on a solid substrate—usually a glass slide or silicon thin-film cell—that assays (tests) large amounts of biological material using high-throughput screening miniaturized, multiplexed and parallel processing and detection methods. The concept and methodology of microarrays was first introduced and illustrated in antibody microarrays (also referred to as antibody matrix) by Tse Wen Chang in 1983 in a scientific publication and a series of patents. The " gene chip" industry started to grow significantly after the 1995 ''Science Magazine'' article by the Ron Davis and Pat Brown labs at Stanford University. With the establishment of companies, such as Affymetrix, Agilent, Applied Microarrays, Arrayjet, Illumina, and others, the technology of DNA microarrays has become the most sophisticat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
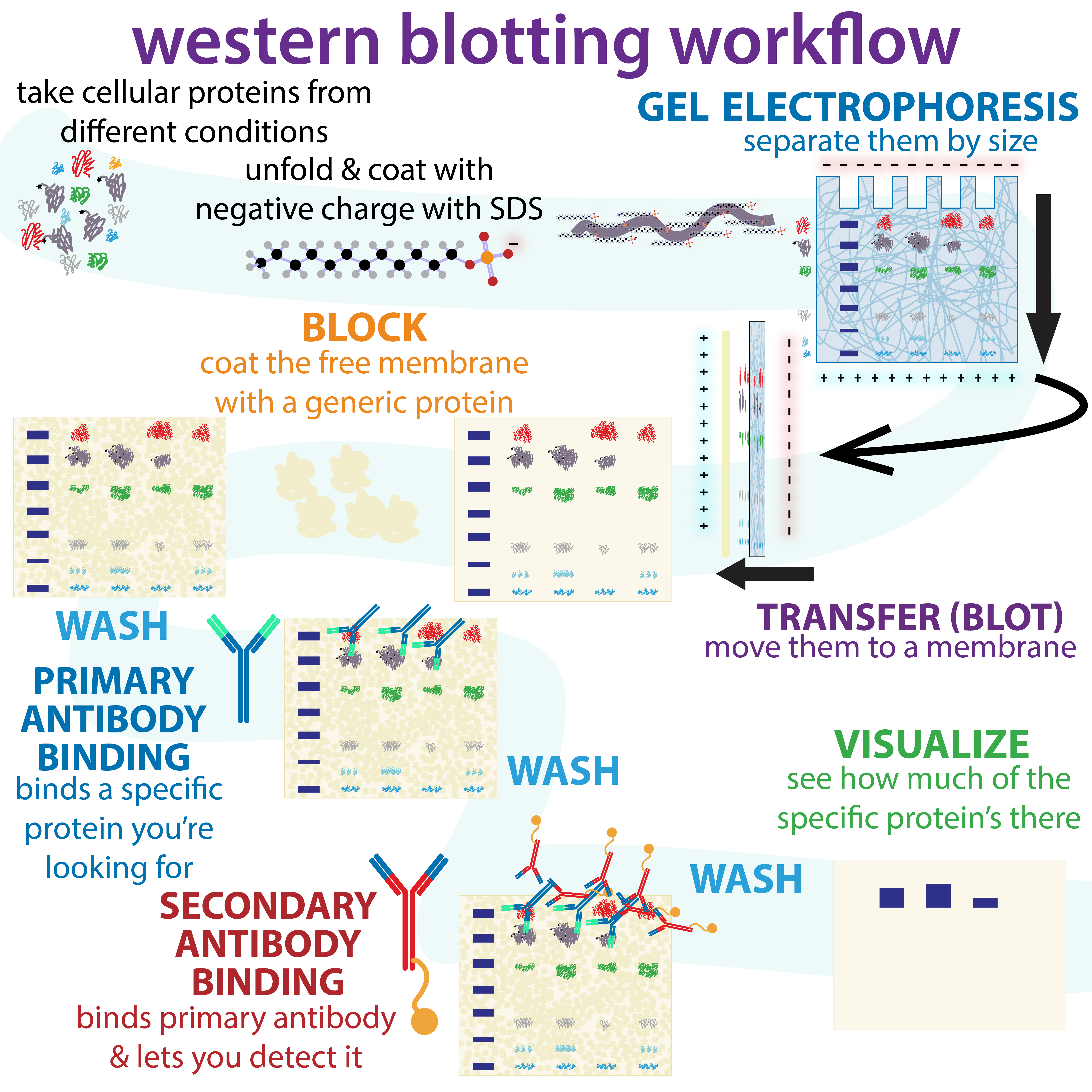
Western Blotting
The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot), or western blotting, is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. Besides detecting the proteins, this technique is also utilized to visualize, distinguish, and quantify the different proteins in a complicated protein combination. Western blot technique uses three elements to achieve its task of separating a specific protein from a complex: separation by size, transfer of protein to a solid support, and marking target protein using a primary and secondary antibody to visualize. A synthetic or animal-derived antibody (known as the primary antibody) is created that recognizes and binds to a specific target protein. The electrophoresis membrane is washed in a solution containing the primary antibody, before excess antibody is washed off. A secondary antibody is added which recognizes and binds to the primary antibody. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles. In this process, a sample containing cells or particles is suspended in a fluid and injected into the flow cytometer instrument. The sample is focused to ideally flow one cell at a time through a laser beam, where the light scattered is characteristic to the cells and their components. Cells are often labeled with fluorescent markers so light is absorbed and then emitted in a band of wavelengths. Tens of thousands of cells can be quickly examined and the data gathered are processed by a computer. Flow cytometry is routinely used in basic research, clinical practice, and clinical trials. Uses for flow cytometry include: * Cell counting * Cell sorting * Determining cell characteristics and function * Detecting microorganisms * Biomarker detection * Protein engineering detection * Diagnosis of health disorders such as blood cancers * Measur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stopping Power (particle Radiation)
In nuclear and materials physics, stopping power is the retarding force acting on charged particles, typically alpha and beta particles, due to interaction with matter, resulting in loss of particle kinetic energy. Its application is important in areas such as radiation protection, ion implantation and nuclear medicine.ICRU Report 73: Stopping of Ions heavier than Helium, Journal of the ICRU, 5 No. 1 (2005), Oxford Univ. Press Definition and Bragg curve Both charged and uncharged particles lose energy while passing through matter. Positive ions are considered in most cases below. The stopping power depends on the type and energy of the radiation and on the properties of the material it passes. Since the production of an ion pair (usually a positive ion and a (negative) electron) requires a fixed amount of energy (for example, 33.97 eV in dry air), the number of ionizations per path length is proportional to the stopping power. The ''stopping power'' of the material is num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Column
A water column is a conceptual column of water from the surface of a sea, river or lake to the bottom sediment.Munson, B.H., Axler, R., Hagley C., Host G., Merrick G., Richards C. (2004).Glossary. ''Water on the Web''. University of Minnesota-Duluth. Retrieved 27 May 2014. Descriptively, the deep sea water column is divided into five parts—''pelagic zones'' (from Greek πέλαγος (pélagos), 'open sea')—from the surface to below the floor, as follows: '' epipelagic'', from the surface to 200 meters below the surface; '' mesopelagic'', from 200 to 1000 meters below the surface; ''bathypelagic'', from 1000 to 4000 meters below the surface; '' abyssopelagic'', from 4000 meters below the surface to the level sea floor; '' hadopelagic'', depressions and crevices below the level sea floor. The concept of water column is useful since many aquatic phenomena are explained by the incomplete vertical mixing of waters with discrete chemical, physical or biological characteristics. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to absorb energy from light. Chlorophylls absorb light most strongly in the blue portion of the electromagnetic spectrum as well as the red portion. Conversely, it is a poor absorber of green and near-green portions of the spectrum. Hence chlorophyll-containing tissues appear green because green light, diffusively reflected by structures like cell walls, is less absorbed. Two types of chlorophyll exist in the photosystems of green plants: chlorophyll ''a'' and ''b''. History Chlorophyll was first isolated and named by Joseph Bienaimé Caventou and Pierre Joseph Pelletier in 1817. The presence of magnesium in chlorophyll was discovered in 1906, and was that element's first detection in living tissue. After initial work done by German c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycourobilin
Phycourobilin is an orange tetrapyrrole involved in photosynthesis in cyanobacteria and red algae. This chromophore is bound to the phycobiliprotein phycoerythrin, the distal component of the light-harvesting system of cyanobacteria and red algae (phycobilisome). When bound to phycoerythrin, phycourobilin shows an absorption maximum around 495 nm. This chromophore is always a donor chromophore of phycoerythrins, since their acceptor chromophore is always phycoerythrobilin. It can also be linked to the linker polypeptides of the phycobilisome, in which its precise role remains unclear. Phycourobilin is found in marine phycobilisome containing organisms, allowing them to efficiently absorb blue-green light. In the ubiquitous marine cyanobacteria ''Synechococcus ''Synechococcus'' (from the Greek ''synechos'', in succession, and the Greek ''kokkos'', granule) is a unicellular cyanobacterium that is very widespread in the marine environment. Its size varies from 0.8 to 1.5 µ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycoerythrobilin
Phycoerythrobilin is a red phycobilin, i.e. an open tetrapyrrole chromophore found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae, glaucophytes and some cryptomonads. Phycoerythrobilin is present in the phycobiliprotein phycoerythrin, of which it is the terminal acceptor of energy. The amount of phycoerythrobilin in phycoerythrins varies a lot, depending on the considered organism. In some Rhodophytes and oceanic cyanobacteria, phycoerythrobilin is also present in the phycocyanin Phycocyanin is a pigment-protein complex from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, along with allophycocyanin and phycoerythrin. It is an accessory pigment to chlorophyll. All phycobiliproteins are water-soluble, so they cannot exist ..., then termed R-Phycocyanin. Like all phycobilins, phycoerythrobilin is covalently linked to these phycobiliproteins by a thioether bond. References * External links Chemical Structure of phycoerythrobilin {{Tetrapyrroles Tetrapyrroles Pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |