|
Photographic Lenses
Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed in many fields of science, manufacturing (e.g., photolithography), and business, as well as its more direct uses for art, film and video production, recreational purposes, hobby, and mass communication. Typically, a lens is used to focus the light reflected or emitted from objects into a real image on the light-sensitive surface inside a camera during a timed exposure. With an electronic image sensor, this produces an electrical charge at each pixel, which is electronically processed and stored in a digital image file for subsequent display or processing. The result with photographic emulsion is an invisible latent image, which is later chemically "developed" into a visible image, either negative or positive, depending on the purpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Art
The visual arts are art forms such as painting, drawing, printmaking, sculpture, ceramics, photography, video, filmmaking, design, crafts and architecture. Many artistic disciplines such as performing arts, conceptual art, and textile arts also involve aspects of visual arts as well as arts of other types. Also included within the visual arts are the applied arts such as industrial design, graphic design, fashion design, interior design and decorative art. Current usage of the term "visual arts" includes fine art as well as the applied or decorative arts and crafts, but this was not always the case. Before the Arts and Crafts Movement in Britain and elsewhere at the turn of the 20th century, the term 'artist' had for some centuries often been restricted to a person working in the fine arts (such as painting, sculpture, or printmaking) and not the decorative arts, craft, or applied Visual arts media. The distinction was emphasized by artists of the Arts and Craf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
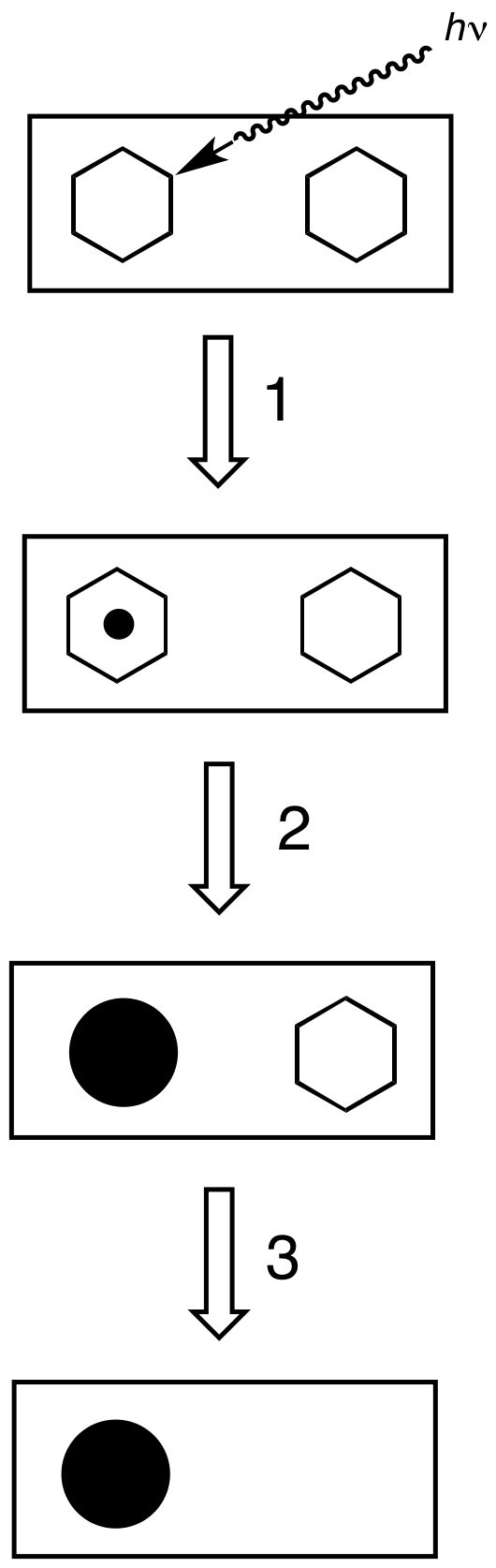
Photographic Emulsion
Photographic emulsion is a light-sensitive colloid used in film-based photography. Most commonly, in silver-gelatin photography, it consists of silver halide crystals dispersed in gelatin. The emulsion is usually coated onto a substrate of glass, films (of cellulose nitrate, cellulose acetate or polyester), paper, or fabric. Photographic emulsion is not a true emulsion, but a suspension of solid particles (silver halide) in a fluid (gelatin in solution). However, the word ''emulsion'' is customarily used in a photographic context. Gelatin or gum arabic layers sensitized with dichromate used in the dichromated colloid processes carbon and gum bichromate are sometimes called ''emulsions''. Some processes do not have emulsions, such as platinum, cyanotype, salted paper, or kallitype. Components Photographic emulsion is a fine suspension of insoluble light-sensitive crystals in a colloid sol, usually consisting of gelatin. The light-sensitive component is one or a mixt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Herschel
Sir John Frederick William Herschel, 1st Baronet (; 7 March 1792 – 11 May 1871) was an English polymath active as a mathematician, astronomer, chemist, inventor, experimental photographer who invented the blueprint and did botanical work. Herschel originated the use of the Julian day system in astronomy. He named seven moons of Saturn and four moons of Uranus – the seventh planet, discovered by his father Sir William Herschel. He made many contributions to the science of photography, and investigated colour blindness and the chemical power of ultraviolet rays. His ''Preliminary Discourse'' (1831), which advocated an inductive approach to scientific experiment and theory-building, was an important contribution to the philosophy of science. Early life and work on astronomy Herschel was born in Slough, Buckinghamshire, the son of Mary Baldwin and astronomer William Herschel. He was the nephew of astronomer Caroline Herschel. He studied shortly at Eton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Von Maedler
Johann, typically a male given name, is the German form of ''Iohannes'', which is the Latin form of the Greek name ''Iōánnēs'' (), itself derived from Hebrew name '' Yochanan'' () in turn from its extended form (), meaning "Yahweh is Gracious" or "Yahweh is Merciful". Its English language equivalent is John. It is uncommon as a surname. People People with the name Johann include: Mononym * Johann, Count of Cleves (died 1368), nobleman of the Holy Roman Empire * Johann, Count of Leiningen-Dagsburg-Falkenburg (1662–1698), German nobleman * Johann, Prince of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen (1578–1638), German nobleman A–K * Johann Adam Hiller (1728–1804), German composer * Johann Adam Reincken (1643–1722), Dutch/German organist * Johann Adam Remele (died 1740), German court painter * Johann Adolf I, Duke of Saxe-Weissenfels (1649–1697) * Johann Adolph Hasse (1699-1783), German Composer * Johann Altfuldisch (1911—1947), German Nazi SS concentration camp officer execut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Fox Talbot
William Henry Fox Talbot Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE Royal Astronomical Society, FRAS (; 11 February 180017 September 1877) was an English scientist, inventor, and photography pioneer who invented the Salt print, salted paper and calotype processes, precursors to photographic processes of the later 19th and 20th centuries. His work in the 1840s on photomechanical reproduction led to the creation of the photoglyphic engraving process, the precursor to photogravure. He was the holder of a controversial patent that affected the early development of commercial photography in Britain. He was also a noted photographer who contributed to the development of photography as an artistic medium. He published ''The Pencil of Nature'' (1844–46), which was illustrated with original salted paper prints from his calotype Negative (photography), negatives and made some important early photographers of York, early photographs of Oxford, Paris, Reading, Berkshire, Reading, and York. A p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area and the seventh most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and its most populous city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 states and the Federal District. It is the largest country to have Portuguese as an official language and the only one in the Americas; one of the most multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass immigration from around the world; and the most populous Roman Catholic-majority country. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a coastline of . It borders all other countries and territories in South America except Ecuador and Chile and covers roughly half of the continent's land area. Its Amazon basin includes a vast tropical forest, ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hercules Florence
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures. The Romans adapted the Greek hero's iconography and myths for their literature and art under the name ''Hercules''. In later Western art and literature and in popular culture, ''Hercules'' is more commonly used than ''Heracles'' as the name of the hero. Hercules is a multifaceted figure with contradictory characteristics, which enabled later artists and writers to pick and choose how to represent him. This article provides an introduction to representations of Hercules in the later tradition. Mythology Birth and early life In Roman mythology, although Hercules was seen as the champion of the weak and a great protector, his personal problems started at birth. Juno sent two witches to prevent the birth, but they were tricked by one of Alcmene's servants and sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Print
A contact print is a photographic image produced from film; sometimes from a film negative, and sometimes from a film positive or paper negative. In a darkroom an exposed and developed piece of film or photographic paper is placed emulsion side down, in contact with a piece of photographic paper, light is briefly shone through the negative or paper and then the paper is developed to reveal the final print. The defining characteristic of a contact print is that the resulting print is the same size as the original, rather than having been projected through an enlarger. Basic tools Contact printing is a simple and inexpensive process. Its simplicity avails itself to those who may want to try darkroom processing without buying an enlarger. One or more negatives are placed on a sheet of photographic paper which is briefly exposed to a light source. The light may come from a low wattage frosted bulb hanging above an easel which holds them together, or contained in an exposur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enlarger
An enlarger is a specialized transparency projector used to produce photographic prints from film or glass negatives, or from transparencies. Construction All enlargers consist of a light source, normally an incandescent light bulb shining though a condenser or translucent screen to provide even illumination, a holder for the negative or transparency, and a specialized lens for projection. The light passes through a film holder, which holds the exposed and developed photographic negative or transparency. Prints made with an enlarger are called ''enlargements''. Typically, enlargers are used in a darkroom, an enclosed space from which extraneous light may be excluded; some commercial enlargers have an integral dark box so that they can be used in a light-filled room. History Josef Maria Eder, in his ''History of Photography'' attributes the invention of photographic enlargement to Humphry Davy who realised the idea of using a solar microscope to project images onto sens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Print
Photographic printing is the process of producing a final image on paper for viewing, using chemically sensitized paper. The paper is exposed to a photographic negative, a positive transparency (or ''slide''), or a digital image file projected using an enlarger or digital exposure unit such as a LightJet or Minilab printer. Alternatively, the negative or transparency may be placed atop the paper and directly exposed, creating a contact print. Digital photographs are commonly printed on plain paper, for example by a color printer, but this is not considered "photographic printing". Following exposure, the paper is processed to reveal and make permanent the latent image. Printing on black-and-white paper The process consists of four major steps, performed in a photographic darkroom or within an automated photo printing machine. These steps are: *Exposure of the image onto the sensitized paper using a contact printer or enlarger; * Processing of the latent image using the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Processing
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image into a visible image, makes this permanent and renders it insensitive to light.Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. All processes based upon the gelatin silver process are similar, regardless of the film or paper's manufacturer. Exceptional variations include instant films such as those made by Polaroid and thermally developed films. Kodachrome required Kodak's proprietary K-14 process. Kodachrome film production ceased in 2009, and K-14 processing is no longer available as of December 30, 2010. Ilfochrome materials use the dye destruction process. Deliberately using the wrong process for a film is known as cross processing. Common processes All p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive (photography)
Positive has multiple meanings in the world of photography. The two main definitions of positive photography include positive space and positive film. Positive space Positive space is the idea that any part of a photo that includes the subject, stands out from the rest of the photo. It is key component in most photographs that helps convey emotions towards an audience. The technique can illustrate emotions ranging from crowdedness, to power, to chaos, or even to movement in a photo. Positive photos often busy and active so that most of the focus is drawn towards the subject. It is important to note that positive space in photography is usually balanced with negative space to make an appealing composition. For example, if a photo is over-crowded and it is hard to distinguish what is and is not the subject of the photo (meaning there is a lack of definition or negative space, or there's too much negative space), then the photo may not be compositionally well thought out or perhaps fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)