|
Phinnoi
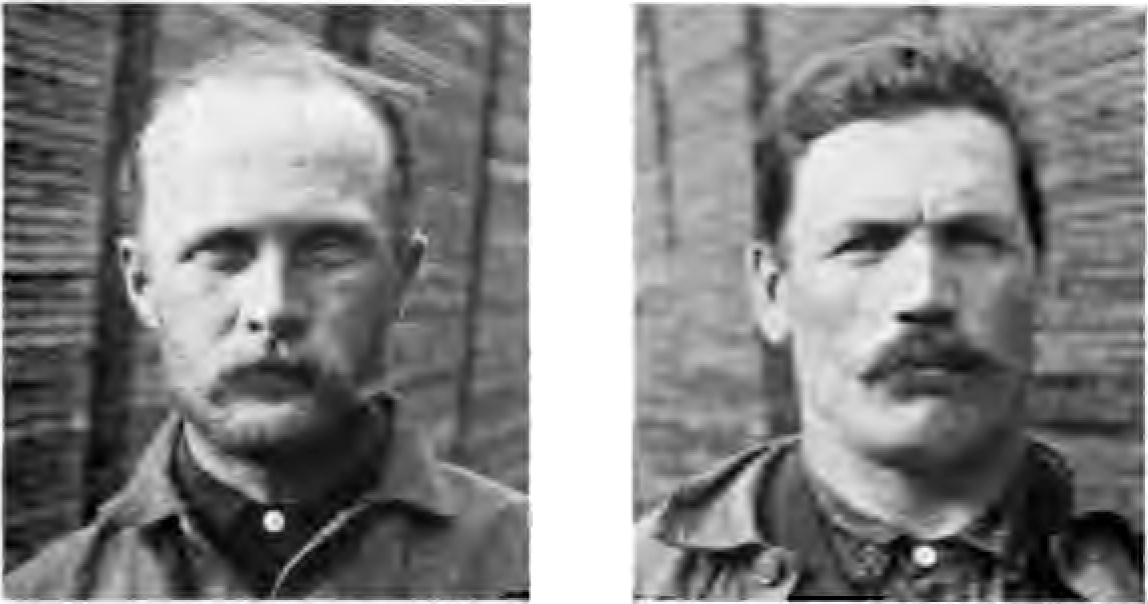
The Fenni were an ancient people of northeastern Europe, first described by Cornelius Tacitus in ''Germania'' in AD 98. Ancient accounts The Fenni are first mentioned by Cornelius Tacitus in ''Germania'' in 98 A.D. Their location is uncertain, due to the vagueness of Tacitus' account: ''"they (Venedi) overrun in their predatory excursions all the woody and mountainous tracts between the Peucini and the Fenni"''.Tacitus G.46 The Greco-Roman geographer Ptolemy, who produced his ''Geographia'' in ca. 150 AD, mentions a people called the ''Phinnoi'' (Φιννοι), generally believed to be synonymous with the Fenni. He locates them in two different areas: a northern group in northern ''Scandia'' (Scandinavia), then believed to be an island; and a southern group, apparently dwelling to the East of the upper Vistula river (SE Poland). It remains unclear what was the relationship between the two groups. The next ancient mention of the Fenni/Finni is in the ''Getica'' of 6th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnic People
The Finnic or Fennic peoples, sometimes simply called Finns, are the nations who speak languages traditionally classified in the Finnic (now commonly '' Finno-Permic'') language family, and which are thought to have originated in the region of the Volga River. The largest Finnic peoples by population are the Finns (or more precisely the Suomi, 6 million), the Estonians (1 million), the Mordvins (800,000), the Mari (570,000), the Udmurts (550,000), the Komis (330,000) and the Sami (100,000). The scope of the name "Finn" and "Finnic" varies by country. Today, Finnish and Estonian scholars restrict the term "Finnic" to the Baltic Finns, who include the Western Finns of Finland and their closest relatives but not the Sami. In Russia, however, where the Eastern Finns live, the word continues to be used in the broad sense, and sometimes implies the Volga Finns who have their own national republics. Three groups of people are covered by the names "Finn" and "Finnic" in the broad sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish People
Finns or Finnish people ( fi, suomalaiset, ) are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland. Finns are traditionally divided into smaller regional groups that span several countries adjacent to Finland, both those who are native to these countries as well as those who have resettled. Some of these may be classified as separate ethnic groups, rather than subgroups of Finns. These include the Kvens and Forest Finns in Norway, the Tornedalians in Sweden, and the Ingrian Finns in Russia. Finnish, the language spoken by Finns, is closely related to other Balto-Finnic languages, e.g. Estonian and Karelian. The Finnic languages are a subgroup of the larger Uralic family of languages, which also includes Hungarian. These languages are markedly different from most other languages spoken in Europe, which belong to the Indo-European family of languages. Native Finns can also be divided according to dialect into subgroups sometimes called ''heimo'' (lit. ''tribe''), although suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire 125
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter in the New Testament of the Christian Bible Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television * Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), including a list of people named Roman or Romans *Ῥωμα ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finningia
Finningia is an old Latin name for Finland, along with ''Fennia'', ''Finnia'' and most often used ''Finlandia''. The name first appears in the work of Olaus Magnus from 1539, who placed ''Finningia olim regnum'' on the Scandinavian map to indicate the unhistorical past kingdom of Finland. The name presumably is a misconception of Pliny the Elder's ''Aeningia'' that probably did not mean Finland but the area of the present-day Baltic States. Aeningia seems to have first been confused with Finland by Jacob Ziegler The humanist and theologian Jacob Ziegler (c. 1470/71 — August 1549) of Landau in Bavaria, was an itinerant scholar of geography and cartographer, who lived a wandering life in Europe. He studied at the University of Ingolstadt, then spent some ... in 1532. Both Finlandia and Einingia are placed next to each other in the present-day southwestern Finland. References {{Finland-hist-stub Baltic Sea Geographic history of Finland Latin words and phrases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitones
The Sitones were a Germanic people living somewhere in Northern Europe in the first century CE. They are mentioned only by Cornelius Tacitus in 97 CE in Germania. Tacitus considered them similar to Suiones (ancestors of modern Swedes) apart from one descriptor, namely that women were the ruling sex. Upon the Suiones, border the people Sitones; and, agreeing with them in all other things, differ from them in one, that here the sovereignty is exercised by a woman. So notoriously do they degenerate not only from a state of liberty, but even below a state of bondage. Speculations on the Sitones' background are numerous. According to one theory, the name is a partial misunderstanding of Sigtuna, one of the central locations in the Swedish kingdom, which much later had a Latin spelling ''Situne''. Another view is that the "queen" of the Sitones derives by linguistic confusion with an Old Norse word for "woman" from the name of the Kvens or Quains. According to medievalist Kemp Malo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
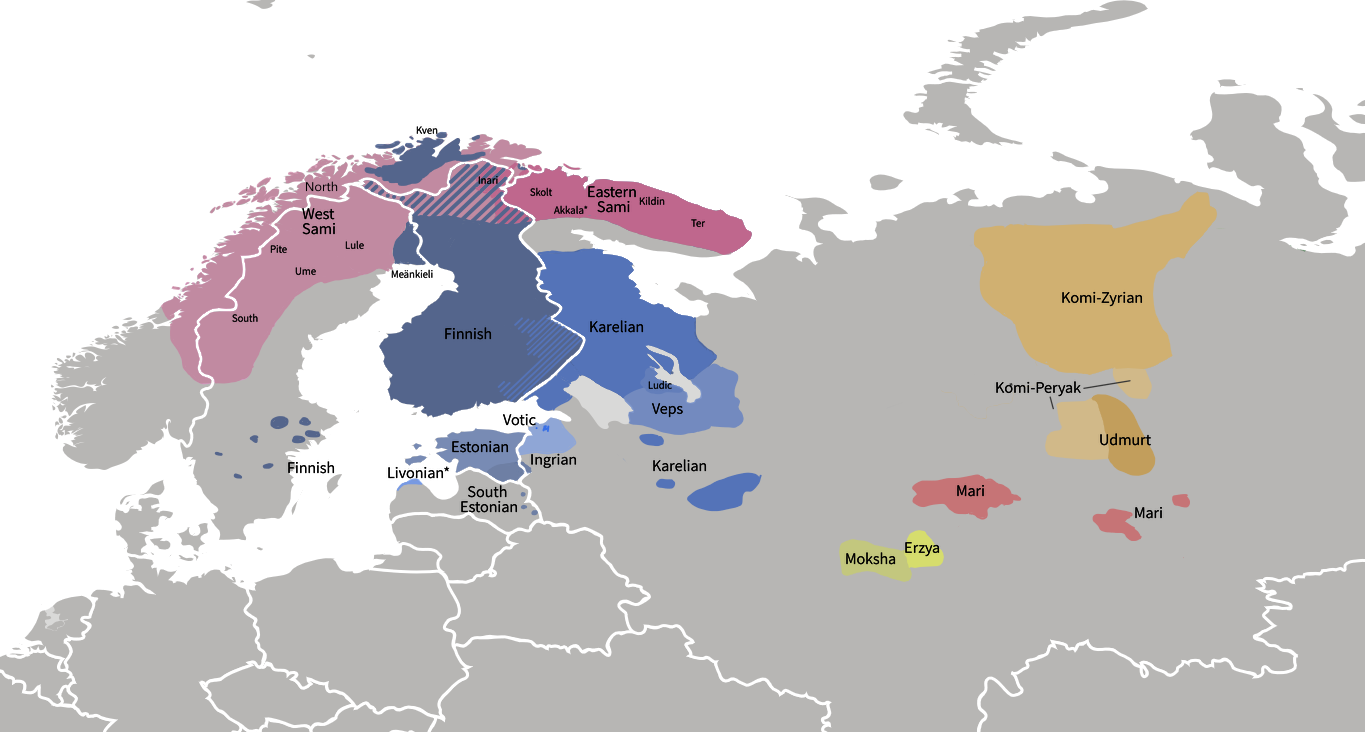
Baltic Finnic Peoples
The Baltic Finnic or Balto-Finnic peoples, also referred to as the Baltic Sea Finns, Baltic Finns, sometimes Western Finnic and often simply as the Finnic peoples, are the peoples inhabiting the Baltic Sea region in Northern and Eastern Europe who speak Finnic languages. They include the Finns, Estonians (including Võros and Setos), Karelians (including Ludes and Livvi), Veps, Izhorians, Votes, and Livonians. In some cases the Kvens, Ingrians, Tornedalians and speakers of Meänkieli are considered separate from the Finns. The bulk of the Finnic peoples (more than 98%) are ethnic Finns and Estonians, who reside in the only two independent Finnic nation states—Finland and Estonia. Finnic peoples are also significant minority groups in neighbouring countries of Sweden, Norway and especially Russia. Theories of origin According to the "Migration Theory" that was based primarily on comparative linguistics, the proto-Finns migrated from an ancient homeland somewhere in north- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Orel
Vladimir Emmanuilovich Orël (russian: Владимир Эммануилович Орëл; 9 February 1952 – 5 August 2007) was a Russian linguist and etymologist. Biography At the Moscow State University he studied theoretical linguistics (1971) and structural linguistics (1973). He defended his Ph.D. in 1981 (''Sostav i xarakteristika balkanoslavjanskix jazykov''), on the comparative analysis of Slavic languages in the Balkans. Until 1990 he worked at the Institute of Slavic and Balkan Studies in Moscow, where he completed his second doctoral thesis in 1989 (''Sravniteľno-istoričeskaja grammatika albanskogo jazyka: fonetika i morfologija''), on the historical grammar of Albanian. In the period 1989–1990 he also taught historical linguistics at Moscow State University. After his emigration to Israel he continued to teach at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (1991–92). Later he relocated to the Tel Aviv University, where he taught in the Department of Classical Studi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venedi
The Vistula Veneti (also called Baltic Veneti) were an Indo-European people that inhabited the region of central Europe east of the Vistula River and the areas around the Bay of Gdańsk. The name first appeared in the 1st century AD in the writings of ancient Romans who differentiated a group of peoples whose manner and language differed from that of the Germanic and Sarmatian tribes. In the 6th century AD, Byzantine sources described the Veneti as the ancestors of the Slavs,Alexander M. Schenker, ''The Dawn of Slavic: An Introduction to Slavic Philology'' (1995), 1.4., including a reference to J. Ochmański, Ochmański, ''Historia Litwy'', 2nd ed. (Wrocław, 1982) who during the second phase of the Migration Period moved south across the northern frontier of the Byzantine Empire. Roman historical sources Pliny the Elder places the Veneti along the Baltic coast. He calls them the Sarmatian Venedi (Latin: ''Sarmatae Venedi''). Thereafter, the 2nd century Greco-Roman geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peucini
The Bastarnae (Latin variants: ''Bastarni'', or ''Basternae''; grc, Βαστάρναι or Βαστέρναι) and Peucini ( grc, Πευκῖνοι) were two ancient peoples who between 200 BC and 300 AD inhabited areas north of the Roman frontier on the Lower Danube. The Bastarnae lived in the region between the Carpathian Mountains and the river Dnieper, to the north and east of ancient Dacia. The Peucini occupied the region north of the Danube Delta. The earliest Graeco-Roman historians to refer to the Bastarnae imply that they spoke Celtic languages. In contrast, later historical sources imply that they spoke Germanic languages, and could be considered Germanic peoples. Like other peoples who lived in the same geographical region, Graeco-Roman writers also referred to the Bastarnae as a "Scythian" people, but this was probably a reference to their general way of life, rather than a linguistic category. Although largely sedentary, some elements may have adopted a semi-nomad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fennoscandia
__NOTOC__ Fennoscandia (Finnish language, Finnish, Swedish language, Swedish and no, Fennoskandia, nocat=1; russian: Фенноскандия, Fennoskandiya) or the Fennoscandian Peninsula is the geographical peninsula in Europe, which includes the Scandinavian Peninsula, Scandinavian and Kola Peninsula, Kola peninsulas, mainland Finland, and Karelia. Administratively this roughly encompasses the mainlands of Finland, Norway and Sweden, as well as Murmansk Oblast, much of the Republic of Karelia, and parts of northern Leningrad Oblast in Russia. Its name comes from the Latin words ''Fennia'' (Finland) and ''Scandia'' (Scandinavian). The term was first used by the Finnish geologist Wilhelm Ramsay in 1898. Geologically, the area is distinct because its bedrock is Archean granite and gneiss with very little limestone, in contrast to adjacent areas in Europe. The similar term Fenno-Scandinavia is sometimes used as a synonym for Fennoscandia. Both terms are sometimes used in Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ante Aikio
Ante Aikio (Sámi: Luobbal Sámmol Sámmol Ánte; born 1977) is a Finnish linguist of Sámi origin who has been a professor of Sámi languages at the Sámi University of Applied Sciences in Kautokeino, Norway since 2015. Prior to this he has been a professor of Sámi language at the Giellagas Institute at the University of Oulu in Finland. In 2009, Aikio published his dissertation on Sámi loanwords in Finnish. In addition, Aikio has widely studied the history and etymology of the Uralic languages and the Sámi ethnolinguistic Ethnolinguistics (sometimes called cultural linguistics) is an area of anthropological linguistics that studies the relationship between a language and the nonlinguistic cultural behavior of the people who speak that language. __NOTOC__ Example ... past. Important publications *Ante Aikio. ''An essay on substrate studies and the origin of Saami'', in ''Etymologie, Entlehnungen und Entwicklungen: Festschrift für Jorma Koivulehto zum 70. Geburtstag'', Soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleo-European Languages
The Paleo-European languages, or Old European languages, are the mostly unknown languages that were spoken in Europe prior to the spread of the Indo-European and Uralic families caused by the Bronze Age invasion from the Eurasian steppe of pastoralists whose descendant languages dominate the continent today. Today, the vast majority of European populations speak Indo-European languages, but until the Bronze Age, it was the opposite, with Paleo-European languages of non-Indo-European affiliation dominating the linguistic landscape of Europe. The term Old European languages is also often used more narrowly to refer only to the unknown languages of the first Neolithic European farmers in Southeast (the Balkan Peninsula), Southern, Central and Western Europe, who emigrated from Anatolia around 8000–6000 BC, excluding unknown languages of various European hunter gatherers who were eventually absorbed by farming populations by the late Neolithic Age. A similar term, Pre-Indo-Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |