|
Phenazine Methosulfate
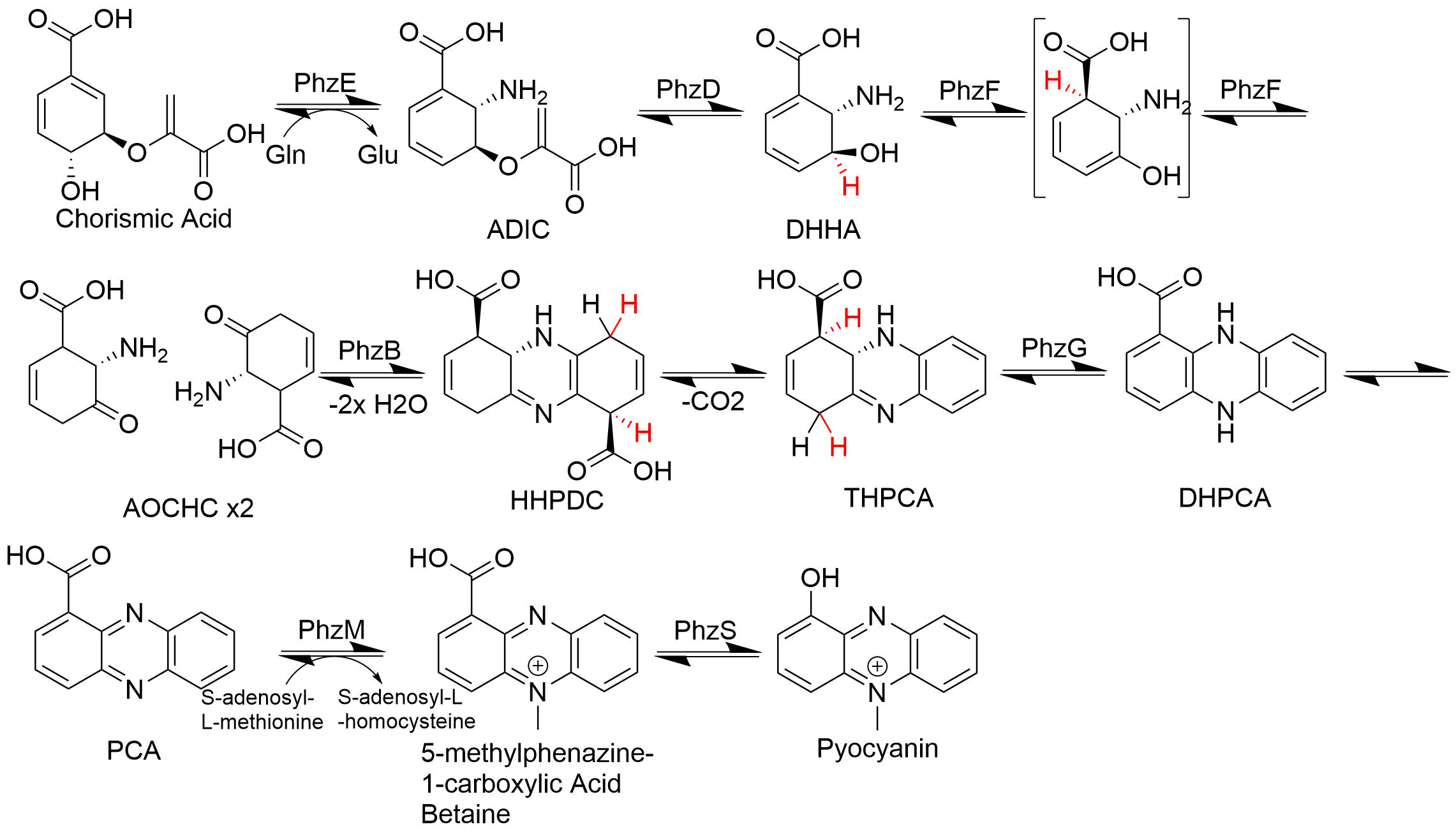
Phenazine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2N2. It is a dibenzo annulated pyrazine, and the parent substance of many dyestuffs, such as the toluylene red, indulines, and safranines (and the closely related eurhodines). Phenazine crystallizes in yellow needles, which are only sparingly soluble in alcohol. Sulfuric acid dissolves it, forming a deep-red solution. Synthesis Classically phenazine are prepared by the reaction of nitrobenzene and aniline in the Wohl-Aue reaction. Other methods include: * pyrolysis of the barium salt of azobenzoate * oxidation of aniline with lead oxide * oxidation of dihydrophenazine, which is prepared by heating pyrocatechin with o-phenylenediamine. * oxidation of ortho-aminodiphenylamine with lead peroxide. Derivatives * The more complex phenazines, such as the naphthophenazines, naphthazines, and naphthotolazines, may be prepared by condensing ortho-diamines with ortho-quinones or by the oxidation of an ortho-diamine in the pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society (professional association) in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 34,000 in the UK and a further 8,000 abroad. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Peroxide
Lead(IV) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula PbO2. It is an oxide where lead is in an oxidation state of +4. It is a dark-brown solid which is insoluble in water. It exists in two crystalline forms. It has several important applications in electrochemistry, in particular as the positive plate of lead acid batteries. Properties Physical Lead dioxide has two major polymorphs, alpha and beta, which occur naturally as rare minerals scrutinyite and plattnerite, respectively. Whereas the beta form had been identified in 1845, α-PbO2 was first identified in 1946 and found as a naturally occurring mineral 1988. The alpha form has orthorhombic symmetry, space group Pbcn (No. 60), Pearson symbol ''oP''12, lattice constants ''a'' = 0.497 nm, ''b'' = 0.596 nm, ''c'' = 0.544 nm, ''Z'' = 4 (four formula units per unit cell). The lead atoms are six-coordinate. The symmetry of the beta form is tetragonal, space group P42/mnm (No. 136), Pearson symbol ''tP''6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyl Iodide
Organoiodine compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more carbon–iodine bonds. They occur widely in organic chemistry, but are relatively rare in nature. The thyroxine hormones are organoiodine compounds that are required for health and the reason for government-mandated iodization of salt. Structure, bonding, general properties Almost all organoiodine compounds feature iodide connected to one carbon center. These are usually classified as derivatives of I−. Some organoiodine compounds feature iodine in higher oxidation states. The C–I bond is the weakest of the carbon–halogen bonds. These bond strengths correlate with the electronegativity of the halogen, decreasing in the order F > Cl > Br > I. This periodic order also follows the atomic radius of halogens and the length of the carbon-halogen bond. For example, in the molecules represented by CH3X, where X is a halide, the carbon-X bonds have strengths, or bond dissociation energies, of 115, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidant
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and the halogens. In one sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that undergoes a chemical reaction in which it gains one or more electrons. In that sense, it is one component in an oxidation–reduction (redox) reaction. In the second sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that transfers electronegative atoms, usually oxygen, to a substrate. Combust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form Hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction An acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH via titration. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms and their applica .... A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as Sodium hydroxide, NaOH or Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by certain characteristic properties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azo Compound
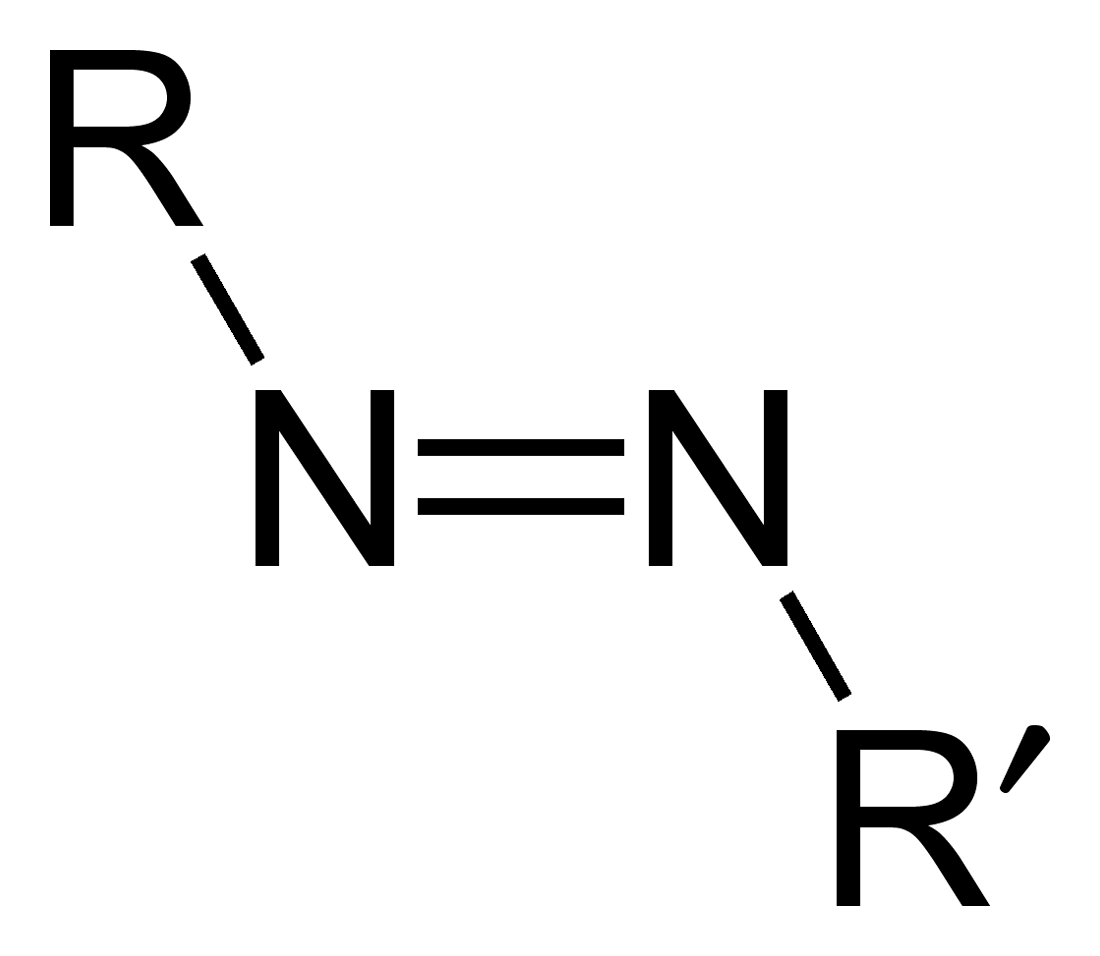
Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl (, in which R and R′ can be either aryl or alkyl groups). IUPAC defines azo compounds as: "Derivatives of diazene (diimide), , wherein both hydrogens are substituted by hydrocarbyl groups, e.g. azobenzene or diphenyldiazene." The more stable derivatives contain two aryl groups. The group is called an ''azo group'' (, ). Many textile and leather articles are dyed with azo dyes and pigments. Aryl azo compounds Aryl azo compounds are usually stable, crystalline species. Azobenzene is the prototypical aromatic azo compound. It exists mainly as the ''trans'' isomer, but upon illumination, converts to the ''cis'' isomer. Aromatic azo compounds can be synthesized by azo coupling, which entails an electrophilic substitution reaction where an aryl diazonium cation is attacked by another aryl ring, especially those substituted with electron-donating groups: :ArN2+ + Ar'H -> ArN=NAr' + H+ Since diazoniu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthol
Naphthol may refer to: * 1-Naphthol * 2-Naphthol {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bonds ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinone
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds, resulting in "a fully Conjugated system, conjugated cyclic diketone, dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone" (thus the name of the class). Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (''ortho''-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and anthraquinone, 9,10-anthraquinone. The name is derived from that of quinic acid (with the suffix "-one" indicating a ketone), since it is one of the compounds obtained upon oxidation of quinic acid. Quinic acid, like quinine is obtained from cinchona bark, called wikt:quinaquina, quinaquina in the indigenous languages of Peruvian tribes. Properties Quinones are oxidized derivatives of aromatic compounds and are often re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toluidine
There are three isomers of toluidine, which are organic compounds. These isomers are ''o''-toluidine, ''m''-toluidine, and ''p''-toluidine, with the prefixed letter abbreviating, respectively, ''ortho''; ''meta''; and ''para''. All three are aryl amines whose chemical structures are similar to aniline except that a methyl group is substituted onto the benzene ring. The difference between these three isomers is the position where the methyl group (–CH3) is bonded to the ring relative to the amino functional group (–NH2); see illustration of the chemical structures below. The chemical properties of the toluidines are quite similar to those of aniline, and toluidines have properties in common with other aromatic amines. Due to the amino group bonded to the aromatic ring, the toluidines are weakly basic. The toluidines are poorly soluble in pure water but dissolve well in acidic water due to formation of ammonium salts, as usual for organic amines. ''ortho''- and ''meta''-tolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |