Azo Compound on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Azo compounds are
Azo compounds are
 For instance a mixture of styrene and maleic anhydride in
For instance a mixture of styrene and maleic anhydride in
, Dr. A. Püntener and Dr. C. Page, Quality and Environment, TFL
 Azo compounds are
Azo compounds are organic compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
s bearing the functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions r ...
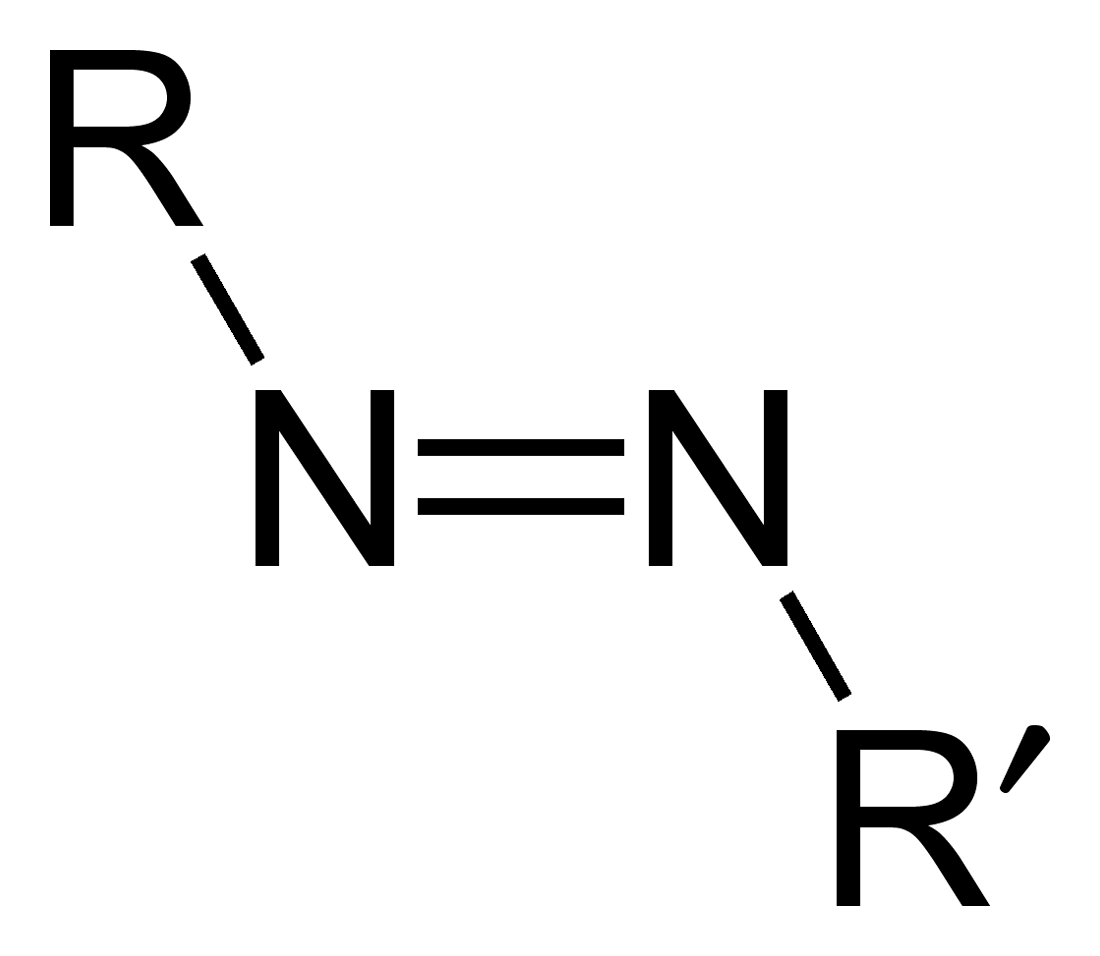
diazenyl (, in which R and R′ can be either aryl or alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl group is derived from a cy ...
groups).
IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...
defines azo compounds as: "Derivatives of diazene (diimide), , wherein both hydrogens are substituted by hydrocarbyl groups, e.g. azobenzene
Azobenzene is a photoswitchable chemical compound composed of two phenyl rings linked by a azo compound, N=N double bond. It is the simplest example of an aryl azo compound. The term 'azobenzene' or simply 'azo' is often used to refer to a wide c ...
or diphenyldiazene.", where Ph stands for phenyl group. The more stable derivatives contain two aryl groups. The group is called an ''azo group'' (, ).
Many textile
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ...
and leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning (leather), tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffal ...
articles are dyed with azo dyes and pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
s.
Aryl azo compounds
Phenazopyridine, an aryl azo compound, is used to treat urinary tract infections">150px Aryl">urinary tract infections">Phenazopyridine, an aryl azo compound, is used to treat urinary tract infections">150px Aryl azo compounds are usually stable, crystalline species. Azobenzene is the prototypical aromatic azo compound. It exists mainly as the Cis-trans isomerism, ''trans'' isomer, but upon illumination, converts to the Cis-trans isomerism, ''cis'' isomer. Aromatic azo compounds can be synthesized by azo coupling, which entails an electrophilic substitution reaction where an aryl diazonium cation is attacked by another aryl ring, especially those substituted with electron-donating groups: : Sincediazonium salt
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide. The parent, comp ...
s are often unstable near room temperature, the azo coupling reactions are typically conducted near 0 °C. The oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
of hydrazines
Hydrazines (R2N−NR2) are a class of chemical compounds with two nitrogen atoms linked via a covalent bond and which carry from one up to four alkyl or aryl substituents. Hydrazines can be considered as derivatives of the inorganic hydrazine ( ...
() also gives azo compounds. Azo dyes are also prepared by the condensation of nitroaromatics with anilines followed by reduction of the resulting azoxy
In chemistry, azoxy compounds are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group with the general structure . They are considered Amine oxide, N-oxides of azo compounds. Azoxy compounds are 1,3-dipoles and 1,3-dipolar cycloadditio ...
intermediate:
:
:
For textile dying, a typical nitro coupling partner would be disodium 4,4′-dinitrostilbene-2,2′-disulfonate. Typical aniline partners are shown below.Klaus Hunger, Peter Mischke, Wolfgang Rieper, Roderich Raue, Klaus Kunde, Aloys Engel: "Azo Dyes" in ''Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim..
As a consequence of ''π''- delocalization, aryl azo compounds have vivid colors, especially reds, oranges, and yellows. Therefore, they are used as dyes, and are commonly known as azo dyes, an example of which is Disperse Orange 1. Some azo compounds, e.g., methyl orange, are used as acid-base indicators due to the different colors of their acid and salt forms. Most DVD-R/ +R and some CD-R
CD-R (Compact disc-recordable) is a digital media, digital optical disc data storage device, storage format. A CD-R disc is a compact disc that can only be Write once read many, written once and read arbitrarily many times.
CD-R discs (CD-Rs) ...
discs use blue azo dye as the recording layer. The commercial success of azo dyes motivated the development of azo compounds in general.
Alkyl azo compounds
Aliphatic azo compounds (R and/or R′ = aliphatic) are less commonly encountered than the aryl azo compounds. A commercially important alkyl azo compound is azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN), which is widely used as an initiator in free-radical polymerizations and other radical-induced reactions. It achieves this initiation by decomposition, eliminating a molecule ofnitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
gas to form two 2-cyanoprop-2-yl radicals:
: For instance a mixture of styrene and maleic anhydride in
For instance a mixture of styrene and maleic anhydride in toluene
Toluene (), also known as toluol (), is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula , often abbreviated as , where Ph stands for the phenyl group. It is a colorless, water
Water is an inorganic compound with the c ...
will react if heated, forming the copolymer upon addition of AIBN.
A simple dialkyl diazo compound is diethyldiazene, , which can be synthesized through a variant of the Ramberg–Bäcklund reaction. Because of their instability, aliphatic azo compounds pose the risk of explosion
An explosion is a rapid expansion in volume of a given amount of matter associated with an extreme outward release of energy, usually with the generation of high temperatures and release of high-pressure gases. Explosions may also be generated ...
.
AIBN is produced by converting acetone cyanohydrin to the hydrazine derivative followed by oxidation:Jean-Pierre Schirmann, Paul Bourdauducq: "Hydrazine" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002. .
:
:
Safety and regulation
Many azo pigments are non-toxic, although some, such as dinitroaniline orange, ortho-nitroaniline orange, or pigment orange 1, 2, and 5 have been found to be mutagenic. Likewise, several case studies have linked azo pigments with basal cell carcinoma.European regulation
Certain azo dyes can break down under reductive conditions to release any of a group of defined aromatic amines. Consumer goods which contain listed aromatic amines originating from azo dyes were prohibited from manufacture and sale inEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
countries in September 2003. As only a small number of dyes contained an equally small number of amines, relatively few products were affected.European Ban on Certain Azo Dyes, Dr. A. Püntener and Dr. C. Page, Quality and Environment, TFL
See also
* Azo couplingReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Azo Compound Functional groups