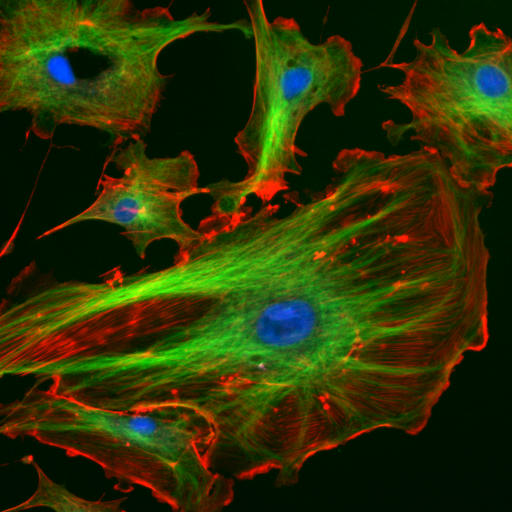
|
Phalloidin Staining Of Actin Filaments
Phalloidin belongs to a class of toxins called phallotoxins, which are found in the death cap mushroom ''(Amanita phalloides)''. It is a rigid bicyclic heptapeptide that is lethal after a few days when injected into the bloodstream. The major symptom of phalloidin poisoning is acute hunger due to the destruction of liver cells. It functions by binding and stabilizing filamentous actin (F-actin) and effectively prevents the depolymerization of actin fibers. Due to its tight and selective binding to F-actin, derivatives of phalloidin containing fluorescent tags are used widely in microscopy to visualize F-actin in biomedical research. Discovery and background Phalloidin was one of the first cyclic peptides to be discovered. It was isolated from the death cap mushroom and crystallized by Feodor Lynen and Ulrich WielandG. Semenza, E.C. Slater, R. JaenickeSelected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections- Google books in 1937. Its structure is unusual in that it co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phallotoxins
The phallotoxins consist of at least seven compounds, all of which are bicyclic heptapeptides (seven amino acids), isolated from the death cap mushroom ''(Amanita phalloides)''. They differ from the closely related amatoxins by being one residue smaller, both in the final product and the precursor protein. Phalloidin had been isolated in 1937 by Feodor Lynen, Heinrich Wieland's student and son-in-law, and Ulrich Wieland of the University of Munich. The remaining six are prophalloin, phalloin, phallisin, phallacidin, phallacin and phallisacin. Though highly toxic to liver cells, phallotoxins have since been found to have little contribution to the death cap's toxicity because they are not absorbed through the gut. Reports of phalloidin in the edible (and sought after) Blusher The blusher is the common name for several closely related species of the genus ''Amanita''. ''A. rubescens'' or the blushing amanita, is found in Europe and eastern North America, and ''A. novinupta'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalloidin Synthetic Scheme
Phalloidin belongs to a class of toxins called phallotoxins, which are found in the death cap mushroom ''(Amanita phalloides)''. It is a rigid bicyclic heptapeptide that is lethal after a few days when injected into the bloodstream. The major symptom of phalloidin poisoning is acute hunger due to the destruction of liver cells. It functions by binding and stabilizing filamentous actin (F-actin) and effectively prevents the depolymerization of actin fibers. Due to its tight and selective binding to F-actin, derivatives of phalloidin containing fluorescent tags are used widely in microscopy to visualize F-actin in biomedical research. Discovery and background Phalloidin was one of the first cyclic peptides to be discovered. It was isolated from the death cap mushroom and crystallized by Feodor Lynen and Ulrich WielandG. Semenza, E.C. Slater, R. JaenickeSelected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections- Google books in 1937. Its structure is unusual in that it co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin Inhibitors
Cytoskeletal drugs are small molecules that interact with actin or tubulin. These drugs can act on the cytoskeletal components within a cell in three main ways. Some cytoskeletal drugs stabilize a component of the cytoskeleton, such as taxol, which stabilizes microtubules, or Phalloidin, which stabilizes actin filaments. Others, such as Cytochalasin D, bind to actin monomers and prevent them from polymerizing into filaments. Drugs such as demecolcine act by enhancing the depolymerisation of already formed microtubules. Some of these drugs have multiple effects on the cytoskeleton: for example, Latrunculin both prevents actin polymerization as well as enhancing its rate of depolymerization. Typically the microtubule targeting drugs can be found in the clinic where they are used therapeutically in the treatment of some forms of cancer. As a result of the lack of specificity for specific type of actin (i.e. cannot distinguish between cardiac, smooth muscle, muscle and cytoskeletal for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycotoxins Found In Basidiomycota
A mycotoxin (from the Greek μύκης , "fungus" and τοξίνη , "toxin") is a toxic secondary metabolite produced by organisms of kingdom Fungi and is capable of causing disease and death in both humans and other animals. The term 'mycotoxin' is usually reserved for the toxic chemical products produced by fungi that readily colonize crops. Examples of mycotoxins causing human and animal illness include aflatoxin, citrinin, fumonisins, ochratoxin A, patulin, trichothecenes, zearalenone, and ergot alkaloids such as ergotamine. One mold species may produce many different mycotoxins, and several species may produce the same mycotoxin. Production Most fungi are aerobic (use oxygen) and are found almost everywhere in extremely small quantities due to the diminute size of their spores. They consume organic matter wherever humidity and temperature are sufficient. Where conditions are right, fungi proliferate into colonies and mycotoxin levels become high. The reason for the producti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. It is composed of three main components, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules, and these are all capable of rapid growth or disassembly dependent on the cell's requirements. A multitude of functions can be performed by the cytoskeleton. Its primary function is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation, and through association with extracellular connective tissue and other cells it stabilizes entire tissues. The cytoskeleton can also contract, thereby deforming the cell and the cell's environment and allowing cells to migrate. Moreover, it is involved in many cell signaling pathways and in the uptake of extracellular material ( endocytosis), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalloidin Staining Of Actin Filaments
Phalloidin belongs to a class of toxins called phallotoxins, which are found in the death cap mushroom ''(Amanita phalloides)''. It is a rigid bicyclic heptapeptide that is lethal after a few days when injected into the bloodstream. The major symptom of phalloidin poisoning is acute hunger due to the destruction of liver cells. It functions by binding and stabilizing filamentous actin (F-actin) and effectively prevents the depolymerization of actin fibers. Due to its tight and selective binding to F-actin, derivatives of phalloidin containing fluorescent tags are used widely in microscopy to visualize F-actin in biomedical research. Discovery and background Phalloidin was one of the first cyclic peptides to be discovered. It was isolated from the death cap mushroom and crystallized by Feodor Lynen and Ulrich WielandG. Semenza, E.C. Slater, R. JaenickeSelected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections- Google books in 1937. Its structure is unusual in that it co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosin
Eosin is the name of several fluorescent acidic compounds which bind to and form salts with basic, or eosinophilic, compounds like proteins containing amino acid residues such as arginine and lysine, and stains them dark red or pink as a result of the actions of bromine on eosin. In addition to staining proteins in the cytoplasm, it can be used to stain collagen and muscle fibers for examination under the microscope. Structures, that stain readily with eosin, are termed eosinophilic. In the field of histology, Eosin Y is the form of eosin used most often as a histologic stain. Etymology Eosin was named by its inventor Heinrich Caro after the nickname (Eos) of a childhood friend, Anna Peters. Variants There are actually two very closely related compounds commonly referred to as eosin. Most often used is in histology is Eosin Y (also known as eosin Y ws, eosin yellowish, Acid Red 87, C.I. 45380, bromoeosine, bromofluoresceic acid, D&C Red No. 22); it has a very slightly yellowi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraperitoneal Injection
Intraperitoneal injection or IP injection is the injection of a substance into the peritoneum (body cavity). It is more often applied to animals than to humans. In general, it is preferred when large amounts of blood replacement fluids are needed or when low blood pressure or other problems prevent the use of a suitable blood vessel for intravenous injection. In humans, the method is widely used to administer chemotherapy drugs to treat some cancers, particularly ovarian cancer. Although controversial, intraperitoneal use in ovarian cancer has been recommended as a standard of care. Fluids are injected intraperitoneally in infants, also used for peritoneal dialysis. Background Intraperitoneal injections are a way to administer therapeutics and drugs through a peritoneal route (body cavity). They are one of the few ways drugs can be administered through injection, and have uses in research involving animals, drug administration to treat ovarian cancers, and much more. Understanding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Lethal Dose
In toxicology, the median lethal dose, LD50 (abbreviation for "lethal dose, 50%"), LC50 (lethal concentration, 50%) or LCt50 is a toxic unit that measures the lethal dose of a toxin, radiation, or pathogen. The value of LD50 for a substance is the dose required to kill half the members of a tested population after a specified test duration. LD50 figures are frequently used as a general indicator of a substance's acute toxicity. A lower LD50 is indicative of increased toxicity. The test was created by J.W. Trevan in 1927. The term semilethal dose is occasionally used in the same sense, in particular with translations of foreign language text, but can also refer to a sublethal dose. LD50 is usually determined by tests on animals such as laboratory mice. In 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved alternative methods to LD50 for testing the cosmetic drug Botox without animal tests. Conventions The LD50 is usually expressed as the mass of substance administered per unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the protonated form (NH2+) under biological conditions, while the carboxyl group is in the deprotonated −COO− form. The "side chain" from the α carbon connects to the nitrogen forming a pyrrolidine loop, classifying it as a aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from the non-essential amino acid L-glutamate. It is encoded by all the codons starting with CC (CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG). Proline is the only proteinogenic secondary amino acid which is a secondary amine, as the nitrogen atom is attached both to the α-carbon and to a chain of three carbons that together form a five-membered ring. History and etymology Proline was first isolated in 1900 by Richard Willstätter who obtained the amino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |