|
Phajo Drugom Zhigpo
Phajo Drugom Shigpo () 184−1251 / 1208−1275was a Tibetan Buddhist particularly important in the early spread of the Drukpa school to Bhutan where he is revered as an emanation of Avalokiteśvara. His descendants played a significant role in the history of Bhutan. The ''Sacred Sites associated with Phajo Drugom Zhigpo and his descendants'' is listed as a tentative site in Bhutan's Tentative List for UNESCO inclusion. Biography Early life Just before he died, the founder of the Drukpa school, Tsangpa Gyare Yeshe Dorje told his nephew and heir, Onre Darma Senge (1177–1237), "A Khampa son from Kham is coming. But he won't meet me. You look after him. Send him to the southern valley that has been visited and blessed by Orgyen Padma Jungne. He will be of great service to the Buddha Dharma." Phajo Drugom Zhigpo was born, probably in 1184, at Yangtse Babchu ''(ryang tse 'bab chu)'', Tashigang in the Do-Kham region of East Tibet the youngest of three sons of the merchant Dabzan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majority regions surrounding the Himalayan areas of India (such as Ladakh, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and a minority in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand), in much of Central Asia, in the southern Siberian regions such as Tuva, and in Mongolia. Tibetan Buddhism evolved as a form of Mahāyāna Buddhism stemming from the latest stages of Indian Buddhism (which also included many Vajrayāna elements). It thus preserves many Indian Buddhist tantric practices of the post-Gupta early medieval period (500 to 1200 CE), along with numerous native Tibetan developments. In the pre-modern era, Tibetan Buddhism spread outside of Tibet primarily due to the influence of the Mongol Yuan dynasty (1271–1368), founded by Kublai Khan, which had ruled China, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rechungpa
Rechung Dorje Drakpa (, 1083/4-1161), known as Rechungpa, was one of the two most important students of the 11th century yogi and poet Milarepa and founder of the Rechung Kagyu subtradition of the Kagyu school of Tibetan Buddhism. (The other student was Gampopa, founder of the Dagpo Kagyu). Rechungpa was particularly important in the transmission of the cycle of esoteric teachings of the ''Cakrasaṃvara Tantra'' known as the Demchok Nyéngyü (), Réchung Nyéngyü (). Tibetan Buddhists believe Rechungpa compiled ''The Six Equal Tastes'' from Indian sources. The text was hidden by Rechungpa, later recovered as a terma by Tsangpa Gyare, who founded the Drukpa Lineage. Rechungpa's student Gyalwa Kyang Tsangpa transmitted the Rechung Kagyu lineage to the 12th century yogini Machik Ongyo. This lineage has been similarly transmitted without interruption until the present time. For example, Changling Rinpoche XV is one of the few holders of this lineage today, though in western teach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drukpa Kagyu Lamas
Druk ( dz, འབྲུག་) is the legendary Thunder Dragon of Bhutan. Druk may also refer to: Bhutan * Druk, of or pertaining to Bhutan :*of or pertaining to the Ngalop people, the majority ethnicity in Bhutan * Druk Gyalpo "Thunder Dragon King", the formal title of the King of Bhutan * Drukyul, the Dzongkha name for Bhutan, translates to ''Land of the Thunder Dragon'' * Druk tsendhen, the national anthem of Bhutan * Druk Air, the national airline of Bhutan * Druk Phuensum Tshogpa, the Bhutan Peace and Prosperity Party * Drukpa Kagyu, an independent branch of the Kagyu school of Tibetan Buddhism and the state religion of Bhutan ** Gyalwang Drukpa, the honorific title of the head of the Drukpa Lineage Other uses * Druk, a kind of small round Bohemian glass Bohemian glass, also referred to as Bohemia crystal, is glass produced in the regions of Bohemia and Silesia, now parts of the Czech Republic. It has a centuries long history of being internationally recognised for its hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Lamas
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo resisted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhutanese Lamas
Bhutanese may refer to: * Something of, or related to Bhutan * Dzongkha, the official national language of Bhutan (sometimes called "Bhutanese") * A person from Bhutan, or of Bhutanese descent, see Demographics of Bhutan * Bhutanese culture * Bhutanese cuisine * ''The Bhutanese'', a weekly newspaper in Bhutan See also *Bhutani (other) Bhutani may refer to: * Bhutani tribe, a tribe of the Baloch people of Pakistan * Bhutani language, a misnomer for several languages: **Bhotia language or Sherpa language **Bhutia language or Sikkimese language **Dzongkha, the official language of ... * * :Bhutanese people {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism In Bhutan
Buddhism is the most widely practiced religion in Bhutan. Vajrayana Buddhism is the spiritual heritage of Bhutan, and Buddhists comprise 84.3% and Hinduism 11.3% of its population. Although the Buddhism practiced in Bhutan originated in Tibetan Buddhism, it differs significantly in its rituals, liturgy, and monastic organization. The state religion has long been supported financially by the government through annual subsidies to Buddhist monasteries, shrines, monks, and nuns. In the modern era, support of the state religion during the reign of Jigme Dorji Wangchuck includes the manufacture of 10,000 gilded bronze images of the Buddha, publication of elegant calligraphic editions of the 108-volume Kangyur (Collection of the Words of the Buddha) and the 225-volume Tengyur (Collection of Commentaries), and the construction of numerous ''chorten'' (stupas) throughout the country. Guaranteed representation in the National Assembly and the Royal Advisory Council, Buddhists constitute th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kagyu Buddhists
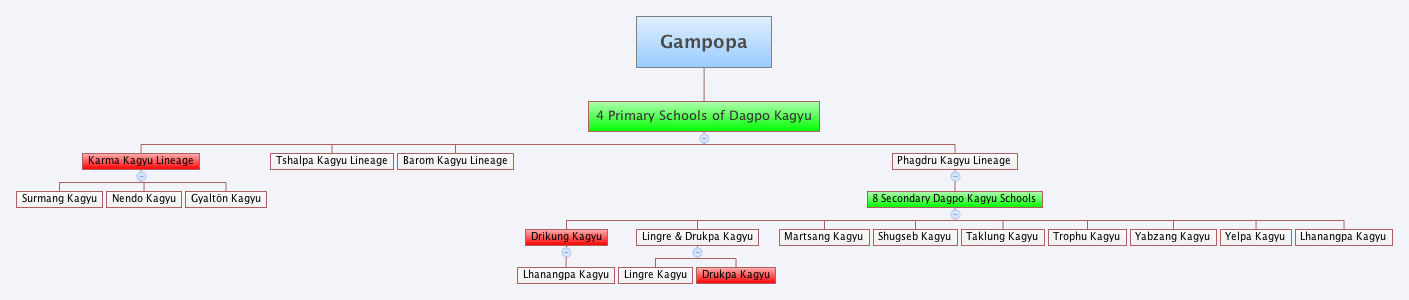
The ''Kagyu'' school, also transliterated as ''Kagyü'', or ''Kagyud'' (), which translates to "Oral Lineage" or "Whispered Transmission" school, is one of the main schools (''chos lugs'') of Tibetan Buddhism, Tibetan (or Himalayan) Buddhism. The Kagyu lineages trace themselves back to the 11th century Indian Mahasiddhas Naropa, Maitripa and the yogini Niguma, via their student Marpa Lotsawa (1012–1097), who brought their teachings to Tibet. Marpa's student Milarepa was also an influential poet and teacher. The Tibetan Kagyu tradition gave rise to a large number of independent sub-schools and lineages. The principal Kagyu lineages existing today as independent schools are those which stem from Milarepa's disciple, Gampopa (1079–1153), a monk who merged the Kagyu lineage with the Kadam (Tibetan Buddhism), Kadam tradition. The Kagyu schools which survive as independent institutions are mainly the Karma Kagyu, Drikung Kagyu, Drukpa Lineage and the Taklung Kagyu. The Karma Kag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1251 Deaths
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1180s Births
118 may refer to: *118 (number) *AD 118 *118 BC *118 (TV series) *118 (film) *118 (Tees) Corps Engineer Regiment *118 (Tees) Field Squadron, Royal Engineers See also *11/8 (other) *Oganesson, synthetic chemical element with atomic number 118 {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kagyud
The ''Kagyu'' school, also transliterated as ''Kagyü'', or ''Kagyud'' (), which translates to "Oral Lineage" or "Whispered Transmission" school, is one of the main schools (''chos lugs'') of Tibetan (or Himalayan) Buddhism. The Kagyu lineages trace themselves back to the 11th century Indian Mahasiddhas Naropa, Maitripa and the yogini Niguma, via their student Marpa Lotsawa (1012–1097), who brought their teachings to Tibet. Marpa's student Milarepa was also an influential poet and teacher. The Tibetan Kagyu tradition gave rise to a large number of independent sub-schools and lineages. The principal Kagyu lineages existing today as independent schools are those which stem from Milarepa's disciple, Gampopa (1079–1153), a monk who merged the Kagyu lineage with the Kadam tradition. The Kagyu schools which survive as independent institutions are mainly the Karma Kagyu, Drikung Kagyu, Drukpa Lineage and the Taklung Kagyu. The Karma Kagyu school is the largest of the sub-school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
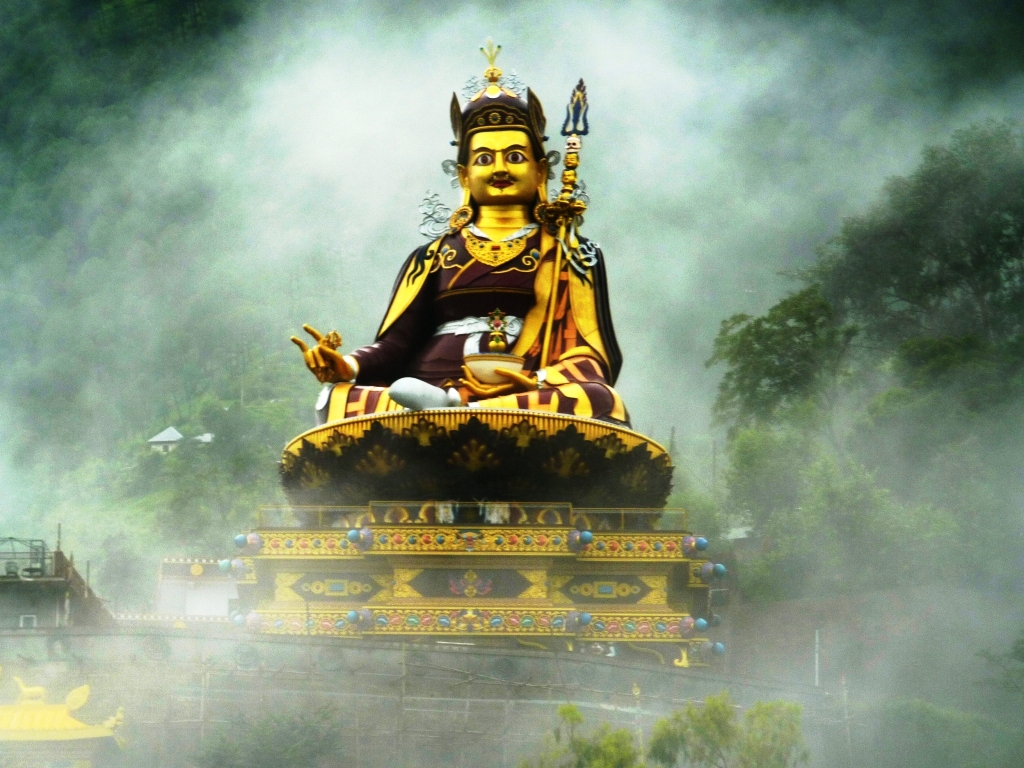
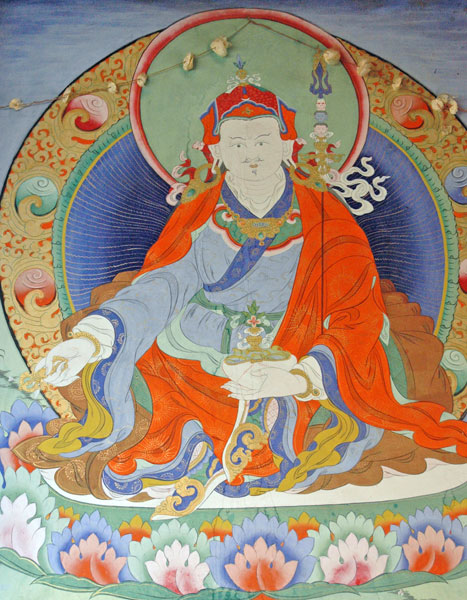
Padmasambhava
Padmasambhava ("Born from a Lotus"), also known as Guru Rinpoche (Precious Guru) and the Lotus from Oḍḍiyāna, was a tantric Buddhist Vajra master from India who may have taught Vajrayana in Tibet (circa 8th – 9th centuries)... According to some early Tibetan sources like the ''Testament of Ba'', he came to Tibet in the 8th century and helped construct Samye Monastery, the first Buddhist monastery in Tibet. However, little is known about the actual historical figure other than his ties to Vajrayana and Indian Buddhism. Padmasambhava later came to be viewed as a central figure in the transmission of Buddhism to Tibet. Starting from around the 12th century, hagiographies concerning Padmasambhava were written. These works expanded the profile and activities of Padmasambhava, now seen as taming all the Tibetan spirits and gods, and concealing various secret texts ('' terma'') for future tertöns. Nyangral Nyima Özer (1124–1192) was the author of the ''Zangling-ma'' (Jew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paro Taktsang
Paro Taktsang ( dz, སྤ་གྲོ་སྟག་ཚང་, also known as the Taktsang Palphug Monastery and the Tiger's Nest), is a sacred Vajrayana Himalayan Buddhist site located in the cliffside of the upper Paro valley in Bhutan. It is one of thirteen Tiger's Nest caves in historical Tibet in which Padmasambhava practiced and taught Vajrayana.Khenchen Palden Sherab Rinpoche, ''The Eight Manifestations of Guru Rinpoche'', (May 1992), https://turtlehill.org A later monastery complex was built in 1692, around the ''Taktsang Senge Samdup'' cave, where Guru Padmasambhava meditated and practiced with students including Yeshe Tsogyal before departing the kingdom of Tibet in the early 9th century. Padmasambhava is credited with introducing Vajrayana Buddhism to Bhutan, which was then part of Tibet, and is the tutelary deity of the country. Today, Paro Taktsang is the best known of the thirteen ''taktsang'' or "tiger lair" caves in which he and his students meditated. The shri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpeg/1200px-Tibetan_Buddhism_(214837929).jpeg)