|
Petroleum Play
In geology, a petroleum play, or simply a play, is a group of oil fields or prospects in the same region that are controlled by the same set of geological circumstances. The term is widely used in the realm of exploitation of hydrocarbon-based resources. The play cycle normally exhibits the following steps: # initial observations of a possible oil reserve # testing and adjustments to initial estimates of extraction # high success in locating and extracting oil from a reserve # lower success as the reserve is depleted # continued decrease in further exploration of the region A particular stratigraphic or structural geologic setting is also often known as a ''play.'' For example, in a relatively unexplored area (such as the Falkland Islands) one might speak of the "Paleozoic play" to refer to the potential oil reserves that might be found within Paleozoic strata. In a well-explored basin such as the Gulf of Mexico, explorers refer to the "Wilcox play" or the "Norphlet play" to colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Field
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations. Such reservoirs form when kerogen (ancient plant matter) is created in surrounding rock by the presence of high heat and pressure in the Earth's crust. Petroleum reservoirs are broadly classified as ''conventional'' and '' unconventional'' reservoirs. In conventional reservoirs, the naturally occurring hydrocarbons, such as crude oil or natural gas, are trapped by overlying rock formations with lower permeability, while in unconventional reservoirs, the rocks have high porosity and low permeability, which keeps the hydrocarbons trapped in place, therefore not requiring a cap rock. Reservoirs are found using hydrocarbon exploration methods. Oil field An oil field is an area of accumulation of liquid oil underground in multiple (potentially linked) reservoirs, trapped as it rises by impermeable rock formations. In industrial terms, an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock (geology), rock layers (Stratum, strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary rock, sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith (geologist), William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of Stratum, strata or rock layering and the importance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Geology
Structural geology is the study of the three-dimensional distribution of rock units with respect to their deformational histories. The primary goal of structural geology is to use measurements of present-day rock geometries to uncover information about the history of deformation (strain) in the rocks, and ultimately, to understand the stress field that resulted in the observed strain and geometries. This understanding of the dynamics of the stress field can be linked to important events in the geologic past; a common goal is to understand the structural evolution of a particular area with respect to regionally widespread patterns of rock deformation (e.g., mountain building, rifting) due to plate tectonics. Use and importance The study of geologic structures has been of prime importance in economic geology, both petroleum geology and mining geology. Folded and faulted rock strata commonly form traps that accumulate and concentrate fluids such as petroleum and natural gas. Simil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; es, Islas Malvinas, link=no ) is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about from Cape Dubouzet at the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, at a latitude of about 52°S. The archipelago, with an area of , comprises East Falkland, West Falkland, and 776 smaller islands. As a British overseas territory, the Falklands have internal self-governance, but the United Kingdom takes responsibility for their defence and foreign affairs. The capital and largest settlement is Stanley on East Falkland. Controversy exists over the Falklands' discovery and subsequent colonisation by Europeans. At various times, the islands have had French, British, Spanish, and Argentine settlements. Britain reasserted its rule in 1833, but Argentina maintains its claim to the islands. In April 1982, Argentine military forces invaded the islands. British a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838 by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (), "life", meaning "ancient life" ). It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from , and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): # Cambrian # Ordovician # Silurian # Devonian # Carboniferous # Permian The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic was a time of dramatic geological, climatic, and evolutionary change. The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared. Arthropods, molluscs, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and synapsids all evolved during the Paleozoic. Life began in the ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southwest and south by the Mexico, Mexican States of Mexico, states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatan, and Quintana Roo; and on the southeast by Cuba. The Southern United States, Southern U.S. states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, which border the Gulf on the north, are often referred to as the "Third Coast" of the United States (in addition to its Atlantic and Pacific Ocean, Pacific coasts). The Gulf of Mexico took shape approximately 300 million years ago as a result of plate tectonics.Huerta, A.D., and D.L. Harry (2012) ''Wilson cycles, tectonic inheritance, and rifting of the North American Gulf of Mexico continental margin.'' Geosphere. 8(1):GES00725.1, first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by Chicxulub impact, an asteroid impact and possibly volcanism, marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of living species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar, Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
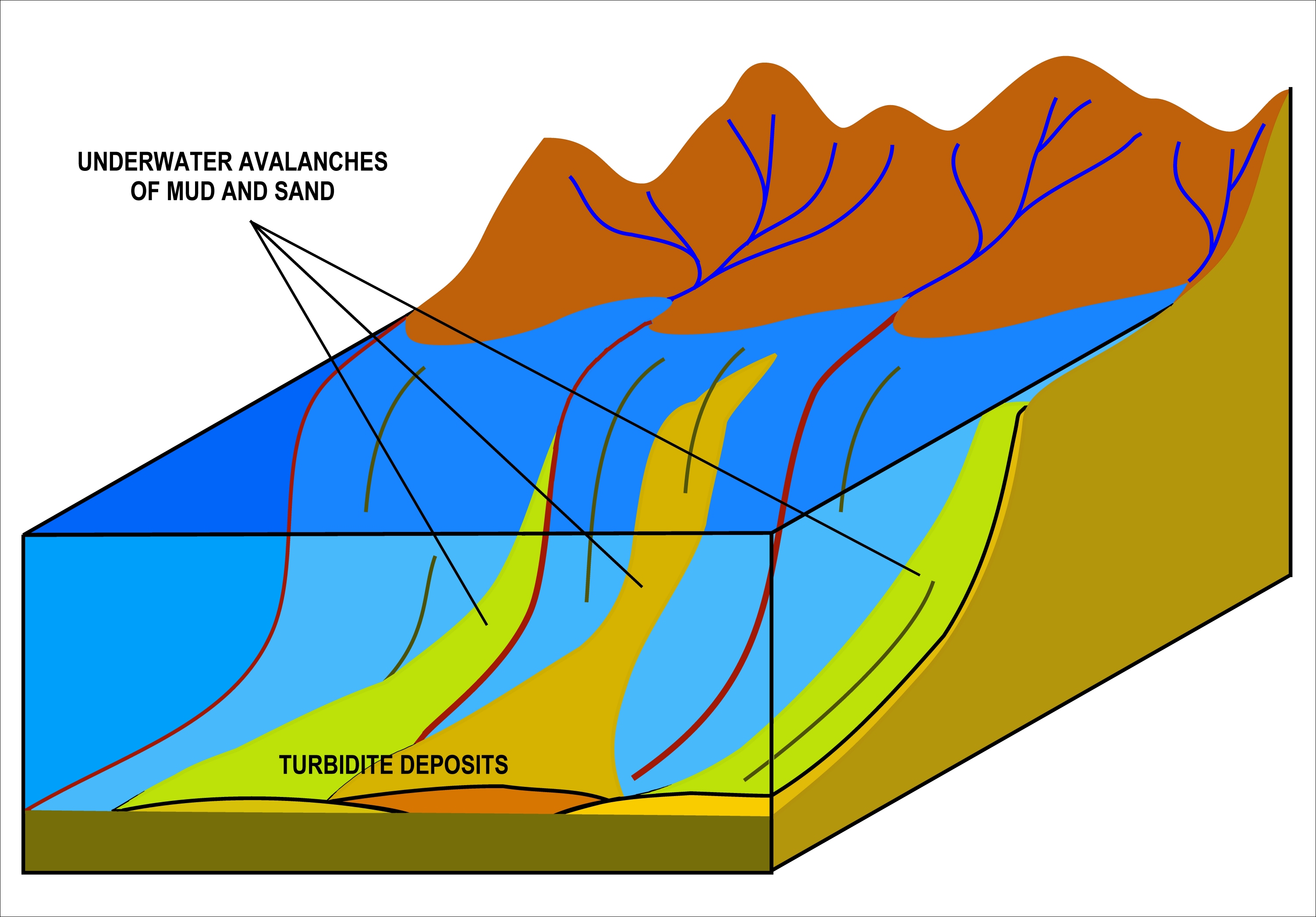
Turbidite
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean. Sequencing Turbidites were first properly described by Arnold H. Bouma (1962), who studied deepwater sediments and recognized particular "fining-up intervals" within deep water, fine-grained shales, which were anomalous because they started at pebble conglomerates and terminated in shales. This was anomalous because within the deep ocean it had historically been assumed that there was no mechanism by which tractional flow could carry and deposit coarse-grained sediments into the abyssal depths. Bouma cycles begin with an erosional contact of a coarse lower bed of pebble to granule conglomerate in a sandy matrix, and grade up through coarse then medium plane parallel sandstone; through cross-bedded sandstone; rippled cross-bedded sand/silty sand, and finally lami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"() , image_map = , map_caption = , capital = Luanda , religion = , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Portuguese , languages2_type = National languages , languages2 = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_ref = , ethnic_groups_year = 2000 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary dominant-party presidential republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = João Lourenço , leader_title2 = Vice President , leader_name2 = Esperança da CostaInvestidura do Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java Sea
The Java Sea ( id, Laut Jawa, jv, Segara Jawa) is an extensive shallow sea on the Sunda Shelf, between the Indonesian islands of Borneo to the north, Java to the south, Sumatra to the west, and Sulawesi to the east. Karimata Strait to its northwest links it to the South China Sea. It is a part of the western Pacific Ocean. Geography The Java Sea covers the southern section of the Sunda Shelf. A shallow sea, it has a mean depth of . It measures about east-west by north-southGoogleEarth and occupies a total surface area of . It formed as sea levels rose at the end of the last ice age. Its almost uniformly flat bottom, and the presence of drainage channels (traceable to the mouths of island rivers), indicate that the Sunda Shelf was once a stable, dry, low-relief land area (peneplain) above which were left standing a few monadnocks (granite hills that, due to their resistance to erosion, form the present islands). Extent The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |