|
Peter Breuer
Peter Christian Breuer (19 May 1856, Cologne – 1 May 1930, Berlin) was a German sculptor. He was a professor at the Prussian Academy of Arts (later, the Academy of Arts, Berlin) and was considered to be one of the pioneers of modern sculpture in Germany. Among his students were Hans Dammann, Fritz Röll, Leopold Fleischhacker, Felix Pfeifer and Rudolf Belling. Selected works * 1894: Berlin, Marble group "Adam and Eve". Seriously damaged in World War II; restored by and in 1954. * 1901: Berlin, Figure Group 23 in the Siegesallee (Victory Avenue) project. The central figure was John Sigismund, Elector of Brandenburg. He was flanked by Fabian Graf von Dohna (1550-1621, diplomat/statesman) and Thomas von dem Knesebeck (1559-1625, Geheimrat and Landeshauptmann). These figures were damaged during World War II and are now on display at the Spandau Citadel. * 1902: Bunzlau, Religious group "Let the Little Children Come to Me", commissioned by Kaiser Wilhelm II for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Breuer2
Peter may refer to: People * List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Peter (given name) ** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church * Peter (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) Culture * Peter (actor) (born 1952), stage name Shinnosuke Ikehata, Japanese dancer and actor * ''Peter'' (album), a 1993 EP by Canadian band Eric's Trip * ''Peter'' (1934 film), a 1934 film directed by Henry Koster * ''Peter'' (2021 film), Marathi language film * "Peter" (''Fringe'' episode), an episode of the television series ''Fringe'' * ''Peter'' (novel), a 1908 book by Francis Hopkinson Smith * "Peter" (short story), an 1892 short story by Willa Cather Animals * Peter, the Lord's cat, cat at Lord's Cricket Ground in London * Peter (chief mouser), Chief Mouser between 1929 and 1946 * Peter II (cat), Chief Mouser between 1946 and 1947 * Peter III (cat), Chief Mouser betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolesławiec
Bolesławiec (pronounced , szl, Bolesławiec, german: Bunzlau) is a historic city situated on the Bóbr River in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in western Poland. It is the administrative seat of Bolesławiec County, and of Gmina Bolesławiec (being an urban gmina in its own right). As of June 2021, it has a population of 38,280. Founded in the 13th century, the city is known for its long-standing pottery-making tradition and heritage Old Town. History The name Bolesławiec is derived from the Silesian duke Bolesław I the Tall. The castellany of ''Bolezlauez'' in Lower Silesia was first mentioned in a 1201 deed. According to tradition, its citizens took part in the Battle of Legnica during the first Mongol invasion of Poland in 1241. Bolesławiec celebrated its 750th anniversary in 2001. Middle Ages In the Early Middle Ages the region was inhabited by the Bobrzanie tribe, one of the Polish tribes, and it became part of the emerging Polish state under its first hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1856 Births
Events January–March * January 8 – Borax deposits are discovered in large quantities by John Veatch in California. * January 23 – American paddle steamer SS Pacific (1849), SS ''Pacific'' leaves Liverpool (England) for a transatlantic voyage on which she will be lost with all 186 on board. * January 24 – U.S. President Franklin Pierce declares the new Free-Stater (Kansas), Free-State Topeka Constitution, Topeka government in "Bleeding Kansas" to be in rebellion. * January 26 – First Battle of Seattle (1856), Battle of Seattle: Marines from the suppress an indigenous uprising, in response to Governor Stevens' declaration of a "war of extermination" on Native communities. * January 29 ** The 223-mile North Carolina Railroad is completed from Goldsboro, North Carolina, Goldsboro through Raleigh, North Carolina, Raleigh and Salisbury, North Carolina, Salisbury to Charlotte, North Carolina, Charlotte. ** Queen Victoria institutes the Victoria Cross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thieme-Becker
Thieme-Becker is a German biographical dictionary of artists. Thieme-Becker The dictionary was begun under the editorship of Ulrich Thieme (1865–1922) (volumes one to fifteen) and Felix Becker (1864–1928) (volumes one to four). It was completed under the editorship of Frederick Charles Willis (b. 1883) (volumes fourteen and fifteen) and Hans Vollmer (1878–1969) (volumes sixteen to thirty-seven)."The Project: From Thieme-Becker to the Artists’ Database," GmbH.Heinz Ladendorf, "Das Allgemeine Lexikon der bildenden Künstler Thieme-Becker-Vollmer," in Magdalena George (ed.), ''Festschrift Hans Vollm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icarus
In Greek mythology, Icarus (; grc, Ἴκαρος, Íkaros, ) was the son of the master craftsman Daedalus, the architect of the labyrinth of Crete. After Theseus, king of Athens and enemy of Minos, escaped from the labyrinth, King Minos suspected that Icarus and Daedalus had revealed the labyrinth's secrets and imprisoned them--either in a large tower overlooking the ocean or the labyrinth itself, depending upon the account. Icarus and Daedalus escaped using wings Daedalus constructed from feathers, threads from blankets, clothes, and beeswax. Daedalus warned Icarus first of complacency and then of hubris, instructing him to fly neither too low nor too high, lest the sea's dampness clog his wings or the sun's heat melt them. Icarus ignored Daedalus’ instructions not to fly too close to the sun, causing the beeswax in his wings to melt. Icarus fell from the sky, plunged into the sea, and drowned. The myth gave rise to the idiom, " fly too close to the sun". In some versions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
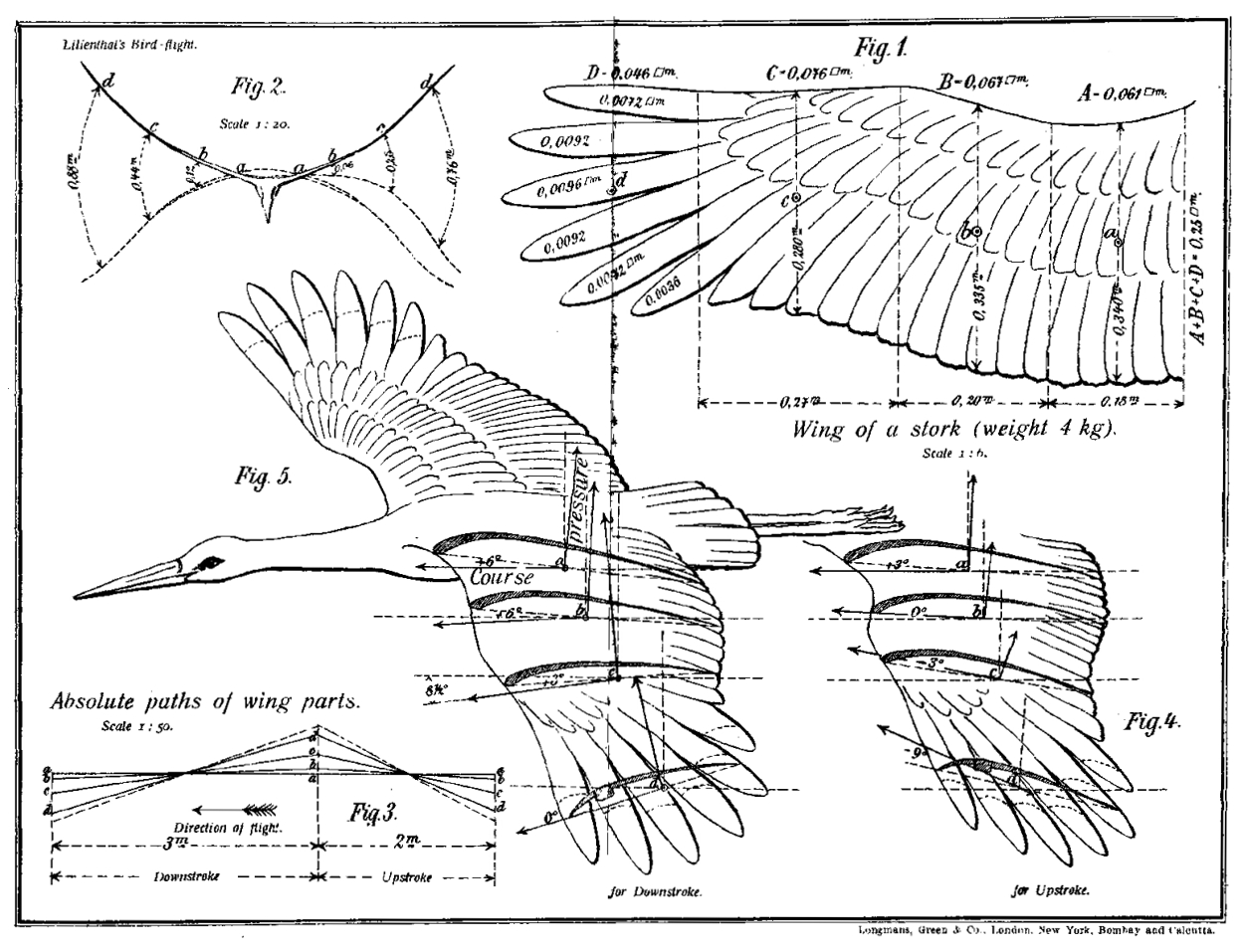
Otto Lilienthal
Karl Wilhelm Otto Lilienthal (23 May 1848 – 10 August 1896) was a German pioneer of aviation who became known as the "flying man". He was the first person to make well-documented, repeated, successful flights with gliders, therefore making the idea of " heavier than air" a reality. Newspapers and magazines published photographs of Lilienthal gliding, favourably influencing public and scientific opinion about the possibility of flying machines becoming practical. Lilienthal's work led to him developing the concept of the modern wing. His flight attempts in 1891 are seen as the beginning of human flight and the "Lilienthal Normalsegelapparat" is considered to be the first airplane in series production, making the ''Maschinenfabrik Otto Lilienthal'' the first air plane production company in the world. Otto Lilienthal is often referred to as either the "father of aviation" or "father of flight". On 9 August 1896, his glider stalled and he was unable to regain control. Falling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin-Steglitz
Steglitz () is a locality of the Steglitz-Zehlendorf borough in Southwestern Berlin, the capital of Germany. is a Slavic name for the European goldfinch, similar to the German . Steglitz was also a borough from 1920 to 2000. It contained the localities Steglitz, Südende, Lichterfelde and Lankwitz. In 1960, Südende became a neighborhood within Steglitz. History While one Knight Henricus of Steglitz was already mentioned in an 1197 deed, the village of Steglitz was first mentioned in the 1375 of Emperor Charles IV, at this time also ruler of the Electorate of Brandenburg. Steglitz witnessed the construction of the first paved Prussian country road, in 1792. The former village profited largely from its location on the Imperial Highway , today , which follows a trading route that dates back to the Middle Ages. The old stretched from the far west of Germany through Aachen and Cologne to Berlin, then continued on eastward to end some two hundred miles northeast of Königsber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Wilhelm, Elector Of Brandenburg
Frederick William (german: Friedrich Wilhelm; 16 February 1620 – 29 April 1688) was Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, thus ruler of Brandenburg-Prussia, from 1640 until his death in 1688. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, he is popularly known as "the Great Elector" (') because of his military and political achievements. Frederick William was a staunch pillar of the Calvinist faith, associated with the rising commercial class. He saw the importance of trade and promoted it vigorously. His shrewd domestic reforms gave Prussia a strong position in the post-Westphalian political order of north-central Europe, setting Prussia up for elevation from duchy to kingdom, achieved under his son and successor. Biography Elector Frederick William was born in Berlin to George William, Elector of Brandenburg, and Elisabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate. His inheritance consisted of the Margraviate of Brandenburg, the Duchy of Cleves, the County of Mark, and the Duchy of Prussi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleve
Kleve (; traditional en, Cleves ; nl, Kleef; french: Clèves; es, Cléveris; la, Clivia; Low Rhenish: ''Kleff'') is a town in the Lower Rhine region of northwestern Germany near the Dutch border and the River Rhine. From the 11th century onwards, Cleves was capital of a county and later a duchy. Today, Cleves is the capital of the district of Cleves in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The city is home to one of the campuses of the Rhine-Waal University of Applied Sciences. Territory of the municipality In addition to the inner city, the territory of Kleve comprises fourteen villages and populated places: Bimmen, Brienen, Donsbrüggen, Düffelward, Griethausen, Keeken, Kellen, Materborn, Reichswalde, Rindern, Salmorth, Schenkenschanz, Warbeyen and Wardhausen. History The name ''Kleff'' probably derives from Middle Dutch ''clef'', ''clif'' 'cliff, bluff', referring to the promontory on which the Schwanenburg castle was constructed. Since the city's coat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaipėda Revolt
The Klaipėda Revolt took place in January 1923 in the Klaipėda Region (also known as the Memel Territory or ). The region, located north of the Neman River, was detached from East Prussia, German Empire by the Treaty of Versailles and became a mandate of the League of Nations. It was placed under provisional French administration until a more permanent solution could be worked out. Lithuania wanted to unite with the region (part of Lithuania Minor) due to its large Lithuanian-speaking minority of Prussian Lithuanians and major port of Klaipėda (Memel) – the only viable access to the Baltic Sea for Lithuania. As the Conference of Ambassadors favored leaving the region as a free city, similar to the Free City of Danzig, the Lithuanians organized and staged a revolt. Presented as an uprising of the local population, the revolt met little resistance from either the German police or the French troops. The rebels established a pro-Lithuanian administration, which petitioned to u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace Of Tilsit
The Treaties of Tilsit were two agreements signed by French Emperor Napoleon in the town of Tilsit in July 1807 in the aftermath of his victory at Friedland. The first was signed on 7 July, between Napoleon and Russian Emperor Alexander, when they met on a raft in the middle of the Neman River. The second was signed with Prussia on 9 July. The treaties were made at the expense of the Prussian king, who had already agreed to a truce on 25 June after the Grande Armée had captured Berlin and pursued him to the easternmost frontier of his realm. In Tilsit, he ceded about half of his pre-war territories. From those territories, Napoleon had created French sister republics, which were formalized and recognized at Tilsit: the Kingdom of Westphalia, the Duchy of Warsaw and the Free City of Danzig; the other ceded territories were awarded to existing French client states and to Russia. Napoleon not only cemented his control of Central Europe but also had Russia and the truncate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Königsberg
Königsberg (, ) was the historic Prussian city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia. Königsberg was founded in 1255 on the site of the ancient Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, and was named in honour of King Ottokar II of Bohemia. A Baltic port city, it successively became the capital of the Królewiec Voivodeship, the State of the Teutonic Order, the Duchy of Prussia and the provinces of East Prussia and Prussia. Königsberg remained the coronation city of the Prussian monarchy, though the capital was moved to Berlin in 1701. Between the thirteenth and the twentieth centuries, the inhabitants spoke predominantly German, but the multicultural city also had a profound influence upon the Lithuanian and Polish cultures. The city was a publishing center of Lutheran literature, including the first Polish translation of the New Testament, printed in the city in 1551, the first book in Lithuanian and the first Lutheran ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
.jpg)