|
Permian Basin (Europe)
The European Permian Basin is a thick sequence of sedimentary rocks deposited in a large sedimentary basin during the Permian period (from 298.9 to 251.902 million years ago) in Northern Europe. The basin underlies northern Poland, northern Germany, Denmark, the Netherlands, a significant portion of the North Sea to the east coast of England and up to Scotland. A major natural gas discovery was made in the Rotliegend Formation at Slochteren, Netherlands in 1959. The Rotliegend is the lower portion of the Permian sequence and consists of over of sandstones and evaporites. It is overlain by thick sequence of evaporites known as the Zechstein Formation.H. Zimmerle, Petroleum Sedimentology, Springer, 2008, pp. 235 - 236, See also *Permian Basin (North America) The Permian Basin is a large sedimentary basin in the southwestern part of the United States. The basin contains the Mid-continent oil field province. This sedimentary basin is located in western Texas and southeastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, and helium are also usually present. Natural gas is colorless and odorless, so odorizers such as mercaptan (which smells like sulfur or rotten eggs) are commonly added to natural gas supplies for safety so that leaks can be readily detected. Natural gas is a fossil fuel and non-renewable resource that is formed when layers of organic matter (primarily marine microorganisms) decompose under anaerobic conditions and are subjected to intense heat and pressure underground over millions of years. The energy that the decayed organisms originally obtained from the sun via photosynthesis is stored as chemical energy within the molecules of methane and other hydrocarbons. Natural gas can be burned fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum Geology
Petroleum geology is the study of origin, occurrence, movement, accumulation, and exploration of hydrocarbon fuels. It refers to the specific set of geological disciplines that are applied to the search for hydrocarbons (oil exploration). Sedimentary basin analysis Petroleum geology is principally concerned with the evaluation of seven key elements in sedimentary basins: * Source * Reservoir * Seal * Trap * Timing * Maturation * Migration In general, all these elements must be assessed via a limited 'window' into the subsurface world, provided by one (or possibly more) exploration wells. These wells present only a 1-dimensional segment through the Earth, and the skill of inferring 3-dimensional characteristics from them is one of the most fundamental in petroleum geology. Recently, the availability of inexpensive, high quality 3D seismic data (from reflection seismology) and data from various electromagnetic geophysical techniques (such as magnetotellurics) has greatly aide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian Europe
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids (reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their amphibian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian Basin (North America)
The Permian Basin is a large sedimentary basin in the southwestern part of the United States. The basin contains the Mid-Continent oil province, Mid-continent oil field province. This sedimentary basin is located in western Texas and southeastern New Mexico. It reaches from just south of Lubbock, Texas, Lubbock, past Midland, Texas, Midland and Odessa, Texas, Odessa, south nearly to the Rio Grande River in southern West Central Texas, and extending westward into the southeastern part of New Mexico. It is so named because it has one of the world's thickest deposits of Rock (geology), rocks from the Permian geologic period. The greater Permian Basin comprises several component basins; of these, the Midland Basin is the largest, Delaware Basin is the second largest, and Marfa, Texas, Marfa Basin is the smallest. The Permian Basin covers more than , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zechstein
The Zechstein (German either from ''mine stone'' or ''tough stone'') is a unit of sedimentary rock layers of Middle to Late Permian (Guadalupian to Lopingian) age located in the European Permian Basin which stretches from the east coast of England to northern Poland. The name Zechstein was formerly also used as a unit of time in the geologic timescale, but nowadays it is only used for the corresponding sedimentary deposits in Europe. The Zechstein lies on top of the Rotliegend; on top of the Zechstein is the Buntsandstein or Bunter. Formation The evaporite rocks of the Zechstein formation were laid down by the Zechstein Sea, an epicontinental or epeiric sea that existed in the Guadalupian and Lopingian epochs of the Permian period. The Zechstein Sea occupied the region of what is now the North Sea, plus lowland areas of Britain and the north European plain through Germany and Poland. The Zechstein sea lay in the rain shadow of the Central Pangean Mountains to the south. At times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaporite
An evaporite () is a water-soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as ocean deposits, and non-marine, which are found in standing bodies of water such as lakes. Evaporites are considered sedimentary rocks and are formed by chemical sediments. Formation of evaporite rocks Although all water bodies on the surface and in aquifers contain dissolved salts, the water must evaporate into the atmosphere for the minerals to precipitate. For this to happen, the water body must enter a restricted environment where water input into this environment remains below the net rate of evaporation. This is usually an arid environment with a small basin fed by a limited input of water. When evaporation occurs, the remaining water is enriched in salts, and they precipitate when the water becomes supersaturated. Evaporite depositi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
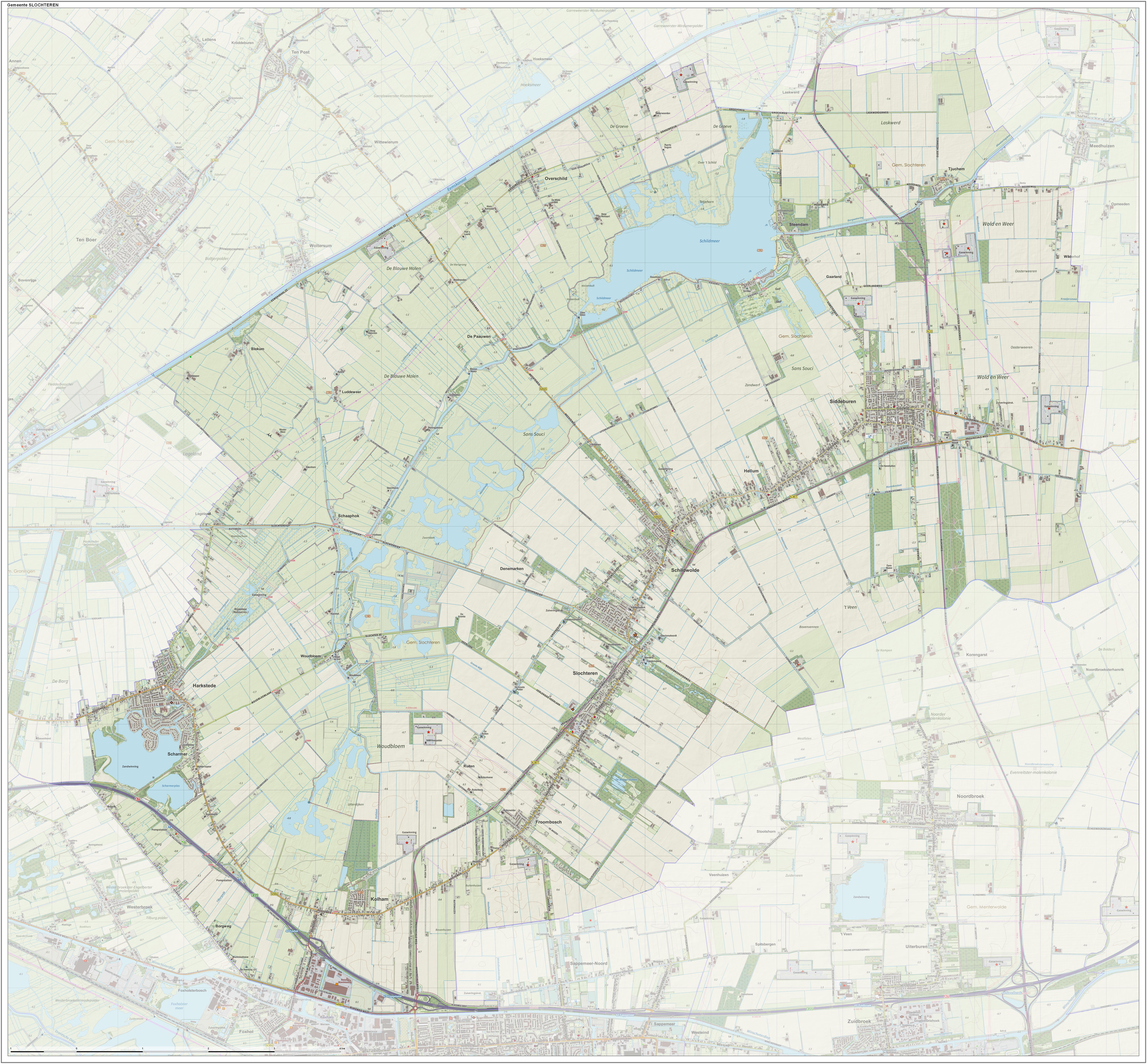
Slochteren
Slochteren () is a village and former municipality with a population of 15,546 in the province of Groningen in the northeast of the Netherlands. On 1 January 2018, Slochteren merged with Hoogezand-Sappemeer and Menterwolde, forming the municipality Midden-Groningen. The former municipality can be characterized as a chain of small villages dividing a mostly agricultural landscape. Having an agricultural background for at least a thousand years, the community houses for the most part commuters to nearby towns like Hoogezand, Groningen and Delfzijl. The mansion Fraeylemaborg (a small 'castle', the oldest parts of which are dated in the Middle Ages) is located in Slochteren. Geography The population centres in the former municipality are: * Denemarken * Froombosch * Harkstede * Hellum * Kolham * Lageland * Luddeweer * Overschild * Schaaphok * Scharmer * Schildwolde * Siddeburen * Slochteren * Steendam * Tjuchem * Woudbloem ''Topographic map of the municipality of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotliegend
The Rotliegend, Rotliegend Group or Rotliegendes (german: the underlying red) is a lithostratigraphy, lithostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) of latest Carboniferous to Guadalupian (middle Permian) age that is found in the subsurface of large areas in western and central Europe. The Rotliegend mainly consists of sandstone layers. It is usually covered by the Zechstein and lies on top of regionally different formation (stratigraphy), formations of late Carboniferous age. The name Rotliegend has in the past not only been used to address the rock strata themselves, but also the time span in which they were formed (in which case the Rotliegend was considered a series (stratigraphy), series or subsystem of the Permian). This time span corresponds roughly with the length of the Cisuralian Epoch (reference date), epoch. Facies and formation In large parts of Pangaea, the last tectonic phase, phases of the Hercynian orogeny were still ongoing during the start of the Permian. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus (organic matter). The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)