|
Perm Salt
Ammonium thioglycolate, also known as perm salt, is the salt of thioglycolic acid and ammonia. It has the formula HSCH2CO2NH4 and has use in perming hair. Chemistry Being the salt of a weak acid and weak base, ammonium thioglycolate exists in solution as an equilibrium mixture of the salt itself as well as thioglycolic acid and ammonia: :HSCH2COO− + NH4+ ⇌ HSCH2COOH + NH3 Thioglycolate, in turn, is able to cleave disulfide bonds, capping one side with a hydrogen and forming a new disulfide with the other side: :RSH + R'SSR' ⇌ R'SH + RSSR' Use in Perms A solution containing ammonium thioglycolate contains a lot of free ammonia, which swells hair, rendering it permeable. The thioglycolic acid in the perm solution reduces the disulfide cystine bonds in the cortex of the hair. In a sense, the thioglycolate removes crosslinks. After washing, the hair is treated with a mild solution of hydrogen peroxide, which oxidizes the cysteines back to cystine. These ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions. The component ions in a salt compound can be either inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic, such as fluoride (F−), or polyatomic, such as sulfate (). Types of salt Salts can be classified in a variety of ways. Salts that produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are called ''alkali salts'' and salts that produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water are called ''acid salts''. ''Neutral salts'' are those salts that are neither acidic nor basic. Zwitterions contain an anionic and a cationic centre in the same molecule, but are not considered salts. Examples of zwitterions are amino acids, many metabolites, peptid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Compounds
The ammonium cation is a positively-charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations (), where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups (indicated by R). Acid–base properties The ammonium ion is generated when ammonia, a weak base, reacts with Brønsted acids (proton donors): :H+ + NH3 -> H4 The ammonium ion is mildly acidic, reacting with Brønsted bases to return to the uncharged ammonia molecule: : H4 + B- -> HB + NH3 Thus, treatment of concentrated solutions of ammonium salts with strong base gives ammonia. When ammonia is dissolved in water, a tiny amount of it converts to ammonium ions: :H2O + NH3 OH- + H4 The degree to which ammonia forms the ammonium ion depends on the pH of the solution. If the pH is low, the equilibrium shifts to the right: more ammonia molecules are conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legally Blonde
''Legally Blonde'' is a 2001 American comedy film directed by Robert Luketic in his List of directorial debuts, feature-length directorial debut, and scripted by Karen McCullah, Karen McCullah Lutz and Kirsten Smith (writer), Kirsten Smith from Amanda Brown (novelist), Amanda Brown's 2001 Legally Blonde (novel), novel of the same name. It stars Reese Witherspoon, Luke Wilson, Selma Blair, Matthew Davis, Victor Garber, and Jennifer Coolidge. The story follows Elle Woods (Witherspoon), a Fraternities and sororities#Sororities, sorority girl who attempts to win back her ex-boyfriend Warner Huntington III (Davis) by getting a Juris Doctor degree at Harvard Law School, and in the process, overcomes Blonde stereotype, stereotypes against blondes and triumphs as a successful lawyer. The outline of ''Legally Blonde'' originated from Brown's experiences as a blonde going to Stanford Law School while being obsessed with fashion and beauty, reading ''Elle (magazine), Elle'' magazine, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanethiol
Methanethiol (also known as methyl mercaptan) is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula . It is a colorless gas with a distinctive putrid smell. It is a natural substance found in the blood, brain and feces of animals (including humans), as well as in plant tissues. It also occurs naturally in certain foods, such as some nuts and cheese. It is one of the chemical compounds responsible for bad breath and the smell of flatus. Methanethiol is the simplest thiol and is sometimes abbreviated as MeSH. It is very flammable. Structure and reactions The molecule is tetrahedral at the carbon atom, like methanol. It is a weak acid, with a p''K''a of ~10.4, but is about a hundred thousand times more acidic than methanol. The colorless salt can be obtained in this way: :CH3SH + CH3ONa → CH3SNa + CH3OH The resulting thiolate anion is a strong nucleophile. It can be oxidized to dimethyl disulfide: :2CH3SH + → CH3SSCH3 + H2O Further oxidation takes the disulfide to two mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulcanization
Vulcanization (British: Vulcanisation) is a range of processes for hardening rubbers. The term originally referred exclusively to the treatment of natural rubber with sulfur, which remains the most common practice. It has also grown to include the hardening of other (synthetic) rubbers via various means. Examples include silicone rubber via room temperature vulcanizing and chloroprene rubber (neoprene) using metal oxides. Vulcanization can be defined as the curing of elastomers, with the terms 'vulcanization' and 'curing' sometimes used interchangeably in this context. It works by forming cross-links between sections of polymer chain which results in increased rigidity and durability, as well as other changes in the mechanical and electrical properties of the material. Vulcanization, in common with the curing of other thermosetting polymers, is generally irreversible. The word vulcanization is derived from Vulcan, the Roman god of fire and forge. History Rubber—latex� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometimes the symbol Cyz is used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. Cysteine is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC. The sulfur-containing amino acids cysteine and methionine are more easily oxidized than the other amino acids. Structure Like other amino acids (not as a residue of a protein), cysteine exists as a zwitterion. Cysteine has chirality in the older / notation based on homology to - and -glyceraldehyde. In the newer ''R''/''S'' system of designating chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use, and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or " high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as a propellant in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in a dark bottle to block light. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that use or decompose hydrogen peroxide are classified as peroxidases. Properties The boiling poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
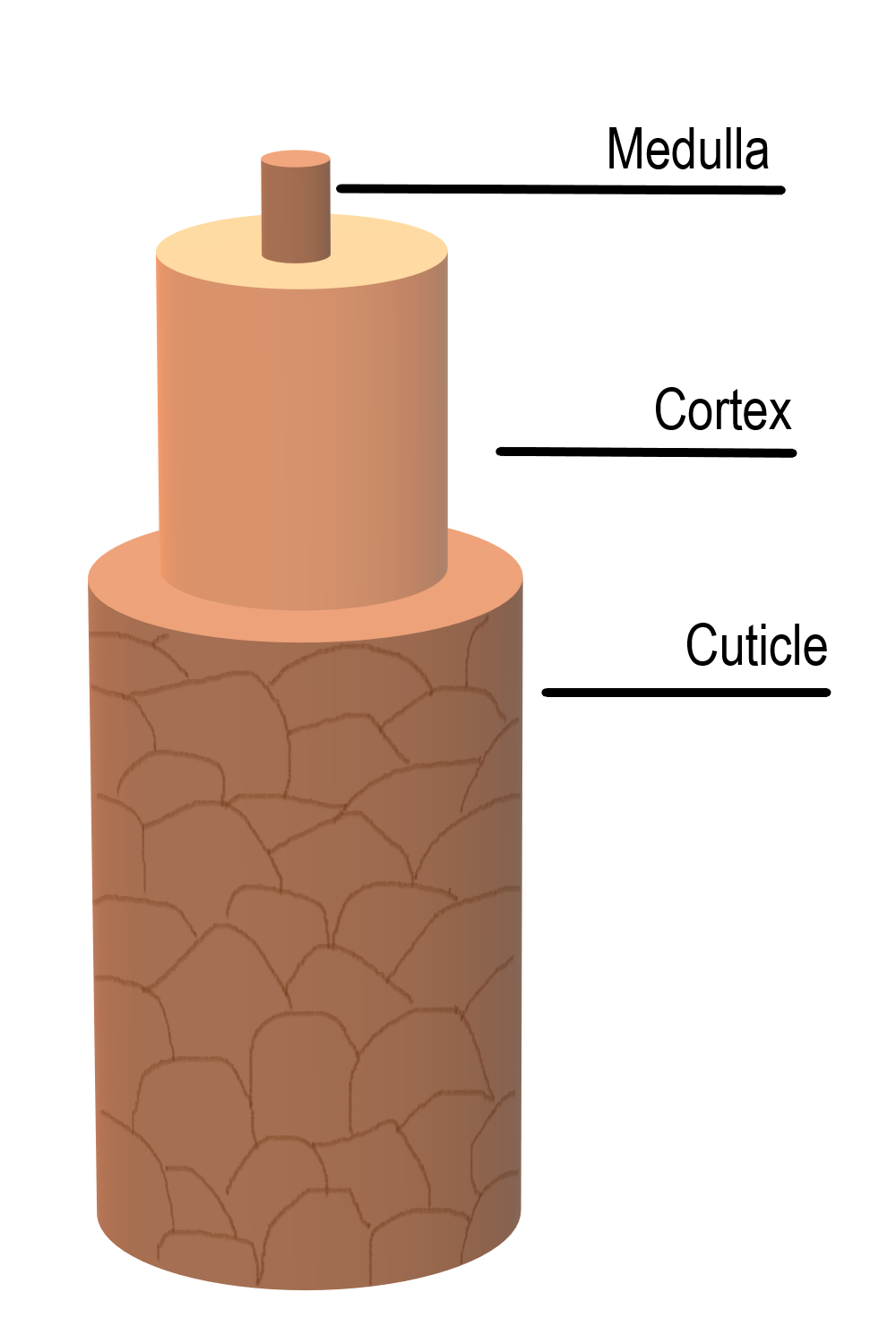
Cortex (hair)
The cortex of the hair shaft is located between the hair cuticle and medulla and is the thickest hair layer. It contains most of the hair's pigment, giving the hair its color. The major pigment in the cortex is melanin, which is also found in skin. The distribution of this pigment varies from animal to animal and person to person. In humans, the melanin is primarily denser nearer the cuticle whereas in animals, melanin is primarily denser nearer the medulla Medulla or Medullary may refer to: Science * Medulla oblongata, a part of the brain stem * Renal medulla, a part of the kidney * Adrenal medulla, a part of the adrenal gland * Medulla of ovary, a stroma in the center of the ovary * Medulla of t ....James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005) ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology'' (10th ed.). Saunders. Page 8. . References Hair anatomy {{Dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystine
Cystine is the oxidized derivative of the amino acid cysteine and has the formula (SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H)2. It is a white solid that is poorly soluble in water. As a residue in proteins, cystine serves two functions: a site of redox reactions and a mechanical linkage that allows proteins to retain their three-dimensional structure. Formation and reactions Structure Cystine is the disulfide derived from the amino acid cysteine. The conversion can be viewed as an oxidation: : Cystine contains a disulfide bond, two amine groups, and two carboxylic acid groups. As for other amino acids, the amine and carboxylic acid groups exist is rapid equilibrium with the ammonium-carboxylate tautomer. The great majority of the literature concerns the ''l,l-''cystine, derived from ''l''-cysteine. Other isomers include ''d,d''-cystine and the meso isomer d,l-cystine, neither of which is biologically significant. Occurrence Cystine is common in many foods such as eggs, meat, dairy products, and whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
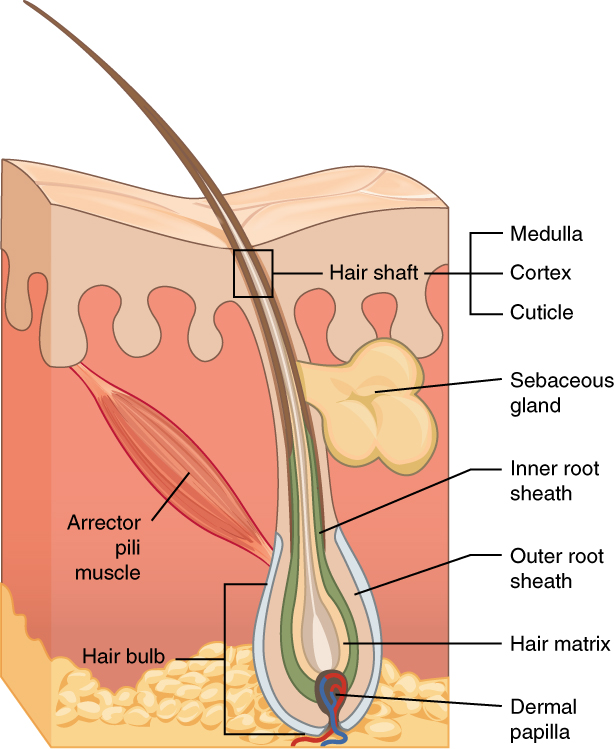
Hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types, and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably alpha-keratin. Attitudes towards different forms of hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, sex, or religion. Overview The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures: #the part beneath the skin, called the hair follicle, or, when pulled from the skin, the bulb or root. This organ is located in the dermis and maintains stem cells, which not only re-grow the hair after it falls out, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioglycolic Acid
Thioglycolic acid (TGA) is the organic compound HSCH2CO2H. TGA is often called mercaptoacetic acid (MAA). It contains both a thiol ( mercaptan) and carboxylic acid functional groups. It is a colorless liquid with a strongly unpleasant odor. TGA is miscible with polar organic solvents.''The Merck index'', 14th ed.; O’Neil, Maryadele J., Ed.; Merck & Co., Inc.: Whitehouse Station, NJ, 2006; p. 9342.Robert Rippel "Mercaptoacetic Acid and Derivatives" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2012, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . Uses TGA is used as a chemical depilatory and is still used as such, especially in salt forms, including calcium thioglycolate and sodium thioglycolate. TGA is the precursor to ammonium thioglycolate, which is used for permanents. TGA and its derivatives break the disulfide bonds in the cortex of hair. One reforms these broken bonds in giving hair a "perm". Alternatively and more commonly, the process leads to depilation, as is done commonly in l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |