|
Periodontal Scaler
Periodontal scalers are dental instruments used in the prophylactic and periodontal care of teeth (most often human teeth), including scaling and root planing. The working ends come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but they are always narrow at the tip, so as to allow for access to narrow embrasure spaces between teeth. They differ from periodontal curettes, which possess a blunt tip. Use Together with periodontal curettes, periodontal scalers are used to remove calculus from teeth. While curettes are often universal in that they can be used on both supra- and sub-gingival calculus removals, scalers are restricted to supra-gingival use. Use of a scaler below the gum line is likely to damage the gingiva (gums). Scalers have scraping edges on both sides of their blades and thus are fit for both mesial and distal surfaces of any tooth in the area in which they are being used. Scalers are best used when their terminal shank, namely, the last portion of the functional shank clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
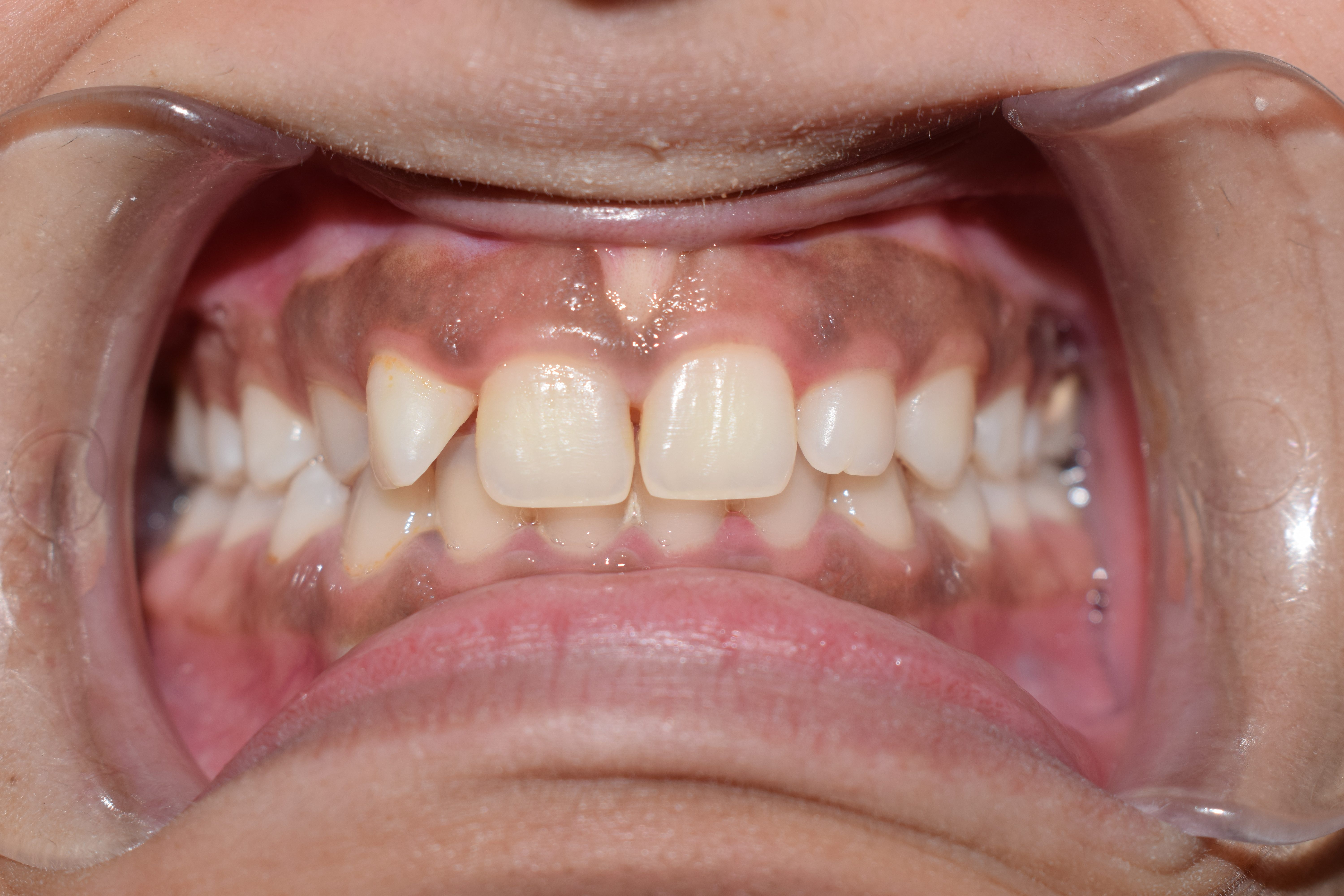
Gingiva
The gums or gingiva (: gingivae) consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. Structure The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation. Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an inflammation that is possibly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology, both in hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontium
The periodontium () is the specialized tissues that both surround and support the teeth, maintaining them in the maxillary and mandibular bones. Periodontics is the dental specialty that relates specifically to the care and maintenance of these tissues. It provides the support necessary to maintain teeth in function. It consists of four principal components, namely: * Gingiva (the gums) * Periodontal ligament (PDL) * Cementum * Alveolar bone proper Each of these components is distinct in location, architecture, and biochemical properties, which adapt during the life of the structure. For example, as teeth respond to forces or migrate medially, bone resorbs on the pressure side and is added on the tension side. Cementum similarly adapts to wear on the occlusal surfaces of the teeth by apical deposition. The periodontal ligament in itself is an area of high turnover that allows the tooth not only to be suspended in the alveolar bone but also to respond to the forces. Thus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cause of tooth loss for adults worldwide. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or fall out. Halitosis (bad breath) may also occur. Periodontal disease typically arises from the development of plaque biofilm, which harbors harmful bacteria such as ''Porphyromonas gingivalis'' and ''Treponema denticola''. These bacteria infect the gum tissue surrounding the teeth, leading to inflammation and, if left untreated, progressive damage to the teeth and gum tissue. Recent meta-analysis have shown that the composition of the oral microbiota and its response to periodontal disease differ between men and women. These differences are particularly notable in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musculoskeletal Disorder
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are injuries or pain in the human musculoskeletal system, including the joints, ligaments, muscles, nerves, tendons, and structures that support limbs, neck and back. MSDs can arise from a sudden exertion (e.g., lifting a heavy object), or they can arise from making the same motions repeatedly (repetitive strain), or from repeated exposure to force, vibration, or awkward posture. Injuries and pain in the musculoskeletal system caused by acute traumatic events like a car accident or fall are not considered musculoskeletal disorders. MSDs can affect many different parts of the body including upper and lower back, neck, shoulders and extremities (arms, legs, feet, and hands). Examples of MSDs include carpal tunnel syndrome, epicondylitis, tendinitis, back pain, tension neck syndrome, and hand-arm vibration syndrome. Causes MSDs can arise from the interaction of physical factors with ergonomic, psychological, social, and occupational factors. Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinician
A clinician is a health care professional typically employed at a skilled nursing facility or clinic. Clinicians work directly with patients rather than in a laboratory, community health setting or in research. A clinician may diagnose, treat and care for patients as a psychologist, clinical pharmacist, clinical scientist, nurse, occupational therapist, speech-language pathologist, physiotherapist, dentist, optometrist, physician assistant, clinical officer, physician, paramedic, or chaplain. Clinicians undergo and take comprehensive training and exams to be licensed and some complete graduate degrees (master's or doctorates) in their field of expertise. The main function of a clinician is to manage a sick person in order to cure their illness, reduce pain and suffering, and extend life considering the impact of illness upon the patient and their family as well as other social factors. See also * List of healthcare occupations A listing of health care professions by m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonly Used Terms Of Relationship And Comparison In Dentistry
This is a list of definitions of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. This set of terms provides orientation within the oral cavity, much as anatomical terms of location provide orientation throughout the body. Terms Combining of terms Most of the principal terms can be combined using their corresponding combining forms (such as ''mesio-'' for ''mesial'' and ''disto-'' for ''distal''). They provide names for directions (vectors) and axes; for example, the coronoapical axis is the long axis of a tooth. Such combining yields terms such as those in the following list. The abbreviations should be used only in restricted contexts, where they are explicitly defined and help avoid extensive repetition (for example, a journal article that uses the term "mesiodistal" dozens of times might use the abbreviation "MD"). The abbreviations are ambiguous: (1) they are not spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculus (dental)
In dentistry, calculus or tartar is a form of hardened dental plaque. It is caused by precipitation of minerals from saliva and Gingival sulcus, gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) in plaque on the teeth. This process of precipitation kills the bacterial cells within dental plaque, but the rough and hardened surface that is formed provides an ideal surface for further plaque formation. This leads to calculus buildup, which compromises the health of the gingiva (gums). Calculus can form both along the gumline, where it is referred to as supragingival (), and within the narrow Sulcus (morphology), sulcus that exists between the teeth and the gingiva, where it is referred to as subgingival (). Calculus formation is associated with a number of clinical manifestations, including halitosis, bad breath, receding gums and Chronic (medicine), chronically inflamed gingiva. Brushing and flossing can remove plaque from which calculus forms; however, once formed, calculus is too hard (firmly att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaler - Top
Scaler may refer to: * Periodontal scaler, an anti-plaque tool * Video scaler A video scaler is a system that converts video signals from one display resolution to another; typically, scalers are used to convert a signal from a lower resolution (such as 480p standard definition) to a higher resolution (such as 1080i hig ..., a system which converts video signals from one resolution to another * ''Scaler'' (video game), a 2004 video game * Fish scaler, a food preparation utensil See also * Scalar (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontal Curette
The periodontal curette is a type of hand-activated instrument used in dentistry and dental hygiene for the purpose of scaling and root planing.Darby ML, Walsh MM, editors. ''Dental Hygiene: Theory and Practice.'' 4th ed. St. Louis: Saunders/Elsevier; 2015. The periodontal curette is considered a treatment instrument and is classified into two main categories: universal curettes and Gracey curettes. Periodontal curettes have one face, one or two cutting edges and a rounded back and rounded toe. They are typically the instrument of choice for subgingival Calculus (dental), calculus removal. Universal and Gracey curettes are typically used during nonsurgical periodontal therapy of a patient's dental hygiene care.Gehrig JS, Willmann DE. ''Foundations of Periodontics for the Dental Hygienist.'' 4th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2016. The goal of nonsurgical periodontal therapy is to eliminate inflammation and return the patient's periodontium back to health.Newman MG, Takei HH, Klok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaling And Root Planing
Scaling and root planing, also known as conventional periodontal therapy, non-surgical periodontal therapy or deep cleaning, is a procedure involving removal of dental plaque and calculus (scaling or debridement) and then smoothing, or planing, of the (exposed) surfaces of the roots, removing cementum or dentine that is impregnated with calculus, toxins, or microorganisms, the agents that cause inflammation. It is a part of non-surgical periodontal therapy. This helps to establish a periodontium that is in remission of periodontal disease. Periodontal scalers and periodontal curettes are some of the tools involved. A regular, non-deep teeth cleaning includes tooth scaling, tooth polishing, and debridement if too much tartar has accumulated, but does not include root planing. Plaque Plaque is a soft yellow-grayish substance that adheres to the tooth surfaces including removable and fixed restorations. It is an organised biofilm that is primarily composed of bacteria in a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |