|
Percy Shaw Jeffrey
Percy Shaw Jeffrey FRGS (14 March 1862 Cheltenham, England – 22 February 1952) was a respected English schoolmaster and author of several books on a range of topics, including significant contributions towards the teaching of phonetics in schools. Shaw Jeffrey taught at a variety of schools before spending sixteen years as headmaster at Colchester Royal Grammar School. With his wife, Alice, he retired first to South Africa, then to the town of Whitby, North Yorkshire, in 1916, where he spent his time between numerous trips to countries around the world. Early life Percy Shaw Jeffrey grew up with his parents, Thomas Ashby Jeffrey, a chemist, and Mary Helen Jeffrey (née Sparrow), in Cheltenham, Gloucestershire, and with his younger siblings Ada Constance, Russell Henry, Ethel Maude and Amy Louise. For three years from 1875, he attended Trent College, Long Eaton, where he rose to become "Head of the School, proxime accessit unner upfor the Duke of Devonshire's Gold Medal, with fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
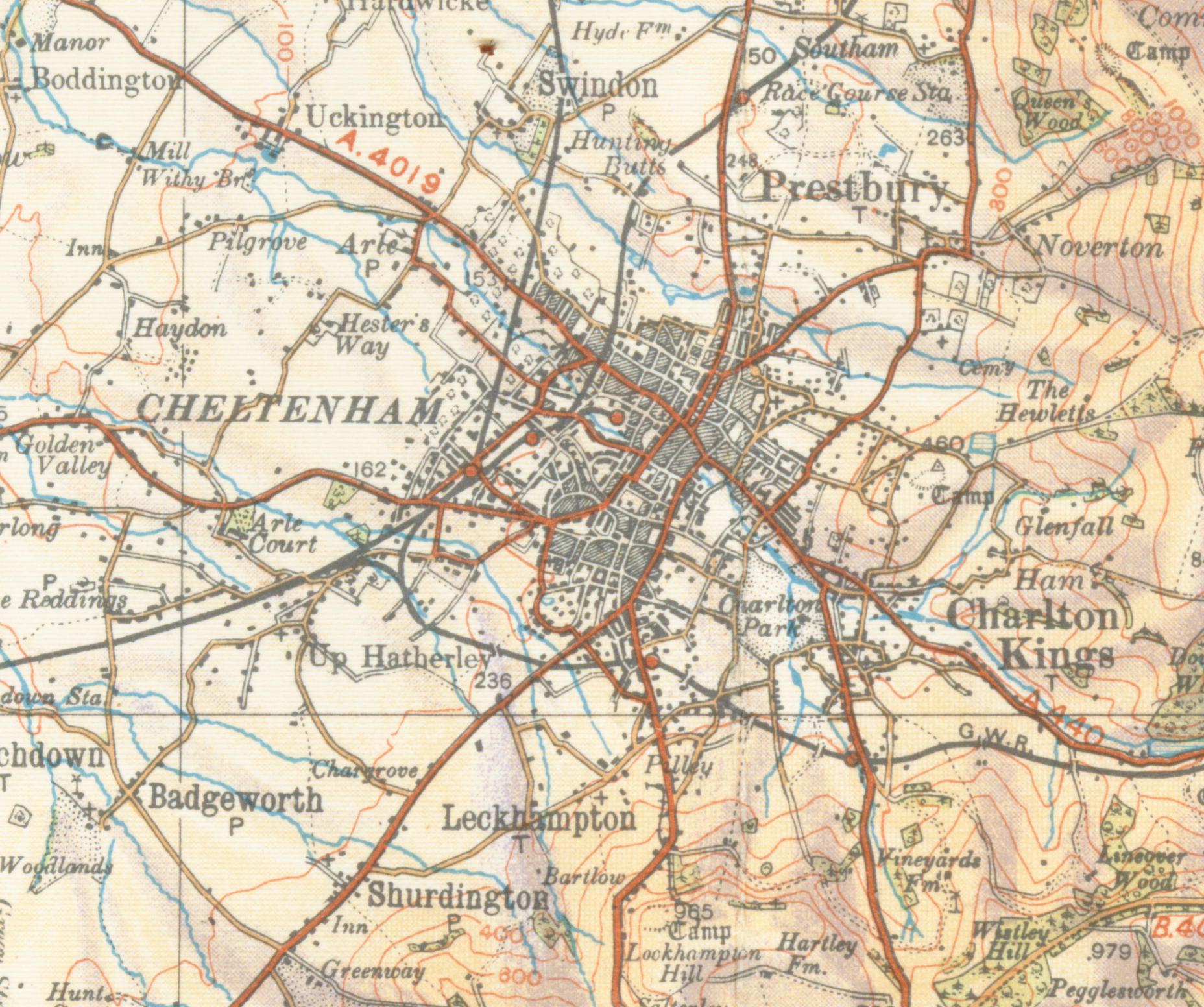
Cheltenham
Cheltenham (), also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a spa town and borough on the edge of the Cotswolds in the county of Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort, following the discovery of mineral springs in 1716, and claims to be the most complete Regency town in Britain. The town hosts several festivals of culture, often featuring nationally and internationally famous contributors and attendees; they include the Cheltenham Literature Festival, the Cheltenham Jazz Festival, the Cheltenham Science Festival, the Cheltenham Music Festival, the Cheltenham Cricket Festival and the Cheltenham Food & Drink Festival. In steeplechase horse racing, the Gold Cup is the main event of the Cheltenham Festival, held every March. History Cheltenham stands on the small River Chelt, which rises nearby at Dowdeswell and runs through the town on its way to the Severn. It was first recorded in 803, as ''Celtan hom''; the meaning has not been resol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Skinners' School
The Skinners' School (formally The Skinners' Company's Middle School for Boys and commonly known as Skinners'), is a British Grammar School with academy status for boys located in the town of Royal Tunbridge Wells, Kent, England. Established in 1887, the school was founded by the Worshipful Company of Skinners (one of the 108 livery companies of the City of London) in response to a demand for education in the region. Today Skinners' remains an all-boys grammar school, recently awarded specialist status in science and mathematics in recognition of these disciplines' excellent teaching. The current enrolment is 1119 pupils, of whom around 325 are in the sixth form. The first headmaster was Reverend Frederick Knott, after whom Knott House is named. The current Headmaster is Edward Wesson. Skinners' boys generally take eleven General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) tests in Year Eleven (aged 15–16), and they have a choice of three or four A-levels in the sixth form. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Ernest Sadler
Sir Michael Ernest Sadler (3 July 1861 – 14 October 1943) was an English historian, educationalist and university administrator. He worked at Victoria University of Manchester and was the vice-chancellor of the University of Leeds. He was also a champion of the English public school system. Early life and education Michael Ernest Sadler, born into a radical home in 1861 at Barnsley in the industrial north of England, died in Oxford in 1943.A detailed biography from UNESCO accessed July 2007. His early youth was coloured by the fact that one of his forebears, , was among the pioneers of the |
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, and a part of Antarctica. The earliest recorded human prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRGS Pre1908 , a grammar school in Essex, England
{{disambiguation ...
CRGS may stand for: * Central Region Gliding School, a flight training program for young adults in Canada * Cleveland Regional Geodetic Survey, a map projection used in Northeast Ohio * Clitheroe Royal Grammar School, a grammar school in Lancashire, England * Colchester Royal Grammar School Colchester Royal Grammar School (CRGS) is a state-funded grammar school in Colchester, Essex. It was founded in 1128 and was later granted two royal charters - by Henry VIII in 1539 and by Elizabeth I in 1584.Trevor J. Hearn, ''Vitae Corona Fide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in South West England. The wider Bristol Built-up Area is the eleventh most populous urban area in the United Kingdom. Iron Age hillforts and Roman villas were built near the confluence of the rivers Frome and Avon. Around the beginning of the 11th century, the settlement was known as (Old English: 'the place at the bridge'). Bristol received a royal charter in 1155 and was historically divided between Gloucestershire and Somerset until 1373 when it became a county corporate. From the 13th to the 18th century, Bristol was among the top three English cities, after London, in tax receipts. A major port, Bristol was a starting place for early voyages of exploration to the New World. On a ship out of Bristol in 1497, John Cabot, a Venetia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clifton College
''The spirit nourishes within'' , established = 160 years ago , closed = , type = Public schoolIndependent boarding and day school , religion = Christian , president = , head_label = Head of College , head = Dr Tim Greene , r_head_label = , r_head = , chair_label = , chair = , founder = John Percival , address = College Road , city = Bristol , county = , country = England , postcode = BS8 3JH , local_authority = , dfeno = , urn = 109334 , ofsted = , capacity = 1,200 , enrolment = 1,171 , gender = Mixed , lower_age = 2 , upper_age = 18 , houses = 12 (in the Upper School) , colours = Blue, Green, Navy , publication = , free_label_1 = Former pupils , free_1 = Old Cliftonians , free_label_2 = , free_2 = , free_label_3 = , free_3 = , websit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dean (education)
Dean is a title employed in academic administrations such as colleges or universities for a person with significant authority over a specific academic unit, over a specific area of concern, or both. In the United States and Canada, deans are usually the head of each constituent college and school that make up a university. Deans are common in private preparatory schools, and occasionally found in middle schools and high schools as well. Origin A "dean" (Latin: ''decanus'') was originally the head of a group of ten soldiers or monks. Eventually an ecclesiastical dean became the head of a group of canons or other religious groups. When the universities grew out of the cathedral schools and monastic schools, the title of dean was used for officials with various administrative duties. Use Bulgaria and Romania In Bulgarian and Romanian universities, a dean is the head of a faculty, which may include several academic departments. Every faculty unit of university or academy. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merton College, Oxford
Merton College (in full: The House or College of Scholars of Merton in the University of Oxford) is one of the Colleges of Oxford University, constituent colleges of the University of Oxford in England. Its foundation can be traced back to the 1260s when Walter de Merton, chancellor to Henry III of England, Henry III and later to Edward I of England, Edward I, first drew up statutes for an independent academic community and established endowments to support it. An important feature of de Merton's foundation was that this "college" was to be self-governing and the endowments were directly vested in the Warden and Fellows. By 1274, when Walter retired from royal service and made his final revisions to the college statutes, the community was consolidated at its present site in the south east corner of the city of Oxford, and a rapid programme of building commenced. The hall and the Merton College Chapel, chapel and the rest of the front quad were complete before the end of the 13th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
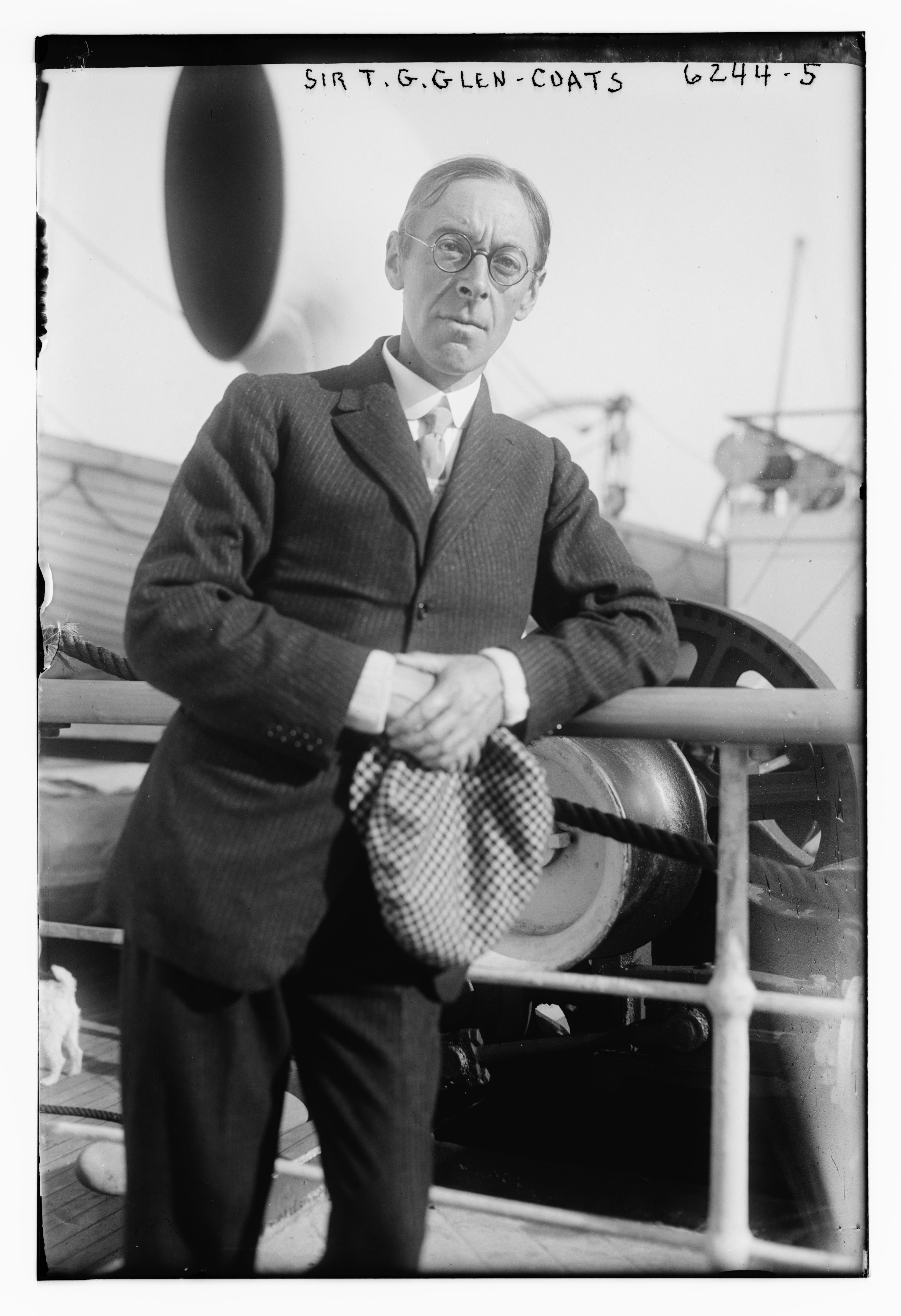
Sir Thomas Glen-Coats, 2nd Baronet
Sir Thomas Coats Glen Glen-Coats, 2nd Baronet (5 May 1878, in Paisley – 7 March 1954, in Glasgow) was a Scottish sailor who competed for the Royal Clyde Yacht Club in the 12-metre class at the 1908 Summer Olympics. He was the son of Sir Thomas Glen-Coats, 1st Baronet, Member of Parliament for West Renfrewshire. The 12-Metre ''Heatherbell'' was designed by Thomas C Glenn-Coates (skipper) for Major Andrew Coates and built by Alexander Robertson & Sons in 1907. She was the first yacht in the new metre-class to be built in the UK. The 'Coates' name (textile/thread dynasty of Paisley) became well known for racing 8-Metres on the Clyde, between 1911 and 1938. ''Heatherbell'' later represented Finland in the 1912 Helsinki Summer Olympics. He was also the designer and helm of the British boat ''Hera'', which won the 1908 gold medal in the 12-metre class. He was apprentice to Alfred Mylne, who crewed on the yacht for his young protégé. On his father's death in 1922 he became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal West Kent Regiment
The Queen's Own Royal West Kent Regiment was a line infantry regiment of the British Army based in the county of Kent in existence from 1881 to 1961. The regiment was created on 1 July 1881 as part of the Childers Reforms, originally as the Queen's Own (Royal West Kent Regiment), by the amalgamation of the 50th (Queen's Own) Regiment of Foot and the 97th (The Earl of Ulster's) Regiment of Foot. In January 1921, the regiment was renamed the Royal West Kent Regiment (Queen's Own) and, in April of the same year, was again renamed, this time as the Queen's Own Royal West Kent Regiment. After distinguished service in the Second Boer War, along with both the First and the Second World Wars, on 1 March 1961, the regiment was amalgamated with the Buffs (Royal East Kent Regiment) to form the Queen's Own Buffs, The Royal Kent Regiment, which was destined to be short-lived. On 31 December 1966, the Queen's Own Buffs was merged with the other regiments of the Home Counties Brigade—the Quee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Officer (armed Forces)
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service. Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer, or a warrant officer. However, absent contextual qualification, the term typically refers only to a force's ''commissioned officers'', the more senior members who derive their authority from a commission from the head of state. Numbers The proportion of officers varies greatly. Commissioned officers typically make up between an eighth and a fifth of modern armed forces personnel. In 2013, officers were the senior 17% of the British armed forces, and the senior 13.7% of the French armed forces. In 2012, officers made up about 18% of the German armed forces, and about 17.2% of the United States armed forces. Historically, however, armed forces have generally had much lower proportions of officers. During the First World War, fewer than 5% of British soldiers were officers (partly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_008.jpg)



