|
Peptoid Nanosheet
In nanobiotechnology, a peptoid nanosheet is a synthetic protein structure made from peptoids. Peptoid nanosheets have a thickness of about three nanometers and a length of up to 100 micrometers, meaning that they have a two-dimensional, flat shape that resembles paper on the nanoscale. This makes them one of the thinnest known two-dimensional organic crystalline materials with an area to thickness ratio of greater than 109 nm. Peptoid nanosheets were discovered in the laboratory of Dr. Ron Zuckermann at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in 2010. Due to the ability to customize peptoids and therefore the properties of the peptoid nanosheet, it has possible applications in the areas of drug and small molecule delivery and biosensing. Synthesis For assembly, a purified amphiphilic polypeptoid of specific sequence is dissolved in aqueous solution. These form a monolayer ( Langmuir–Blodgett film) on the air-water interface with their hydrophobic side chains oriented in air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
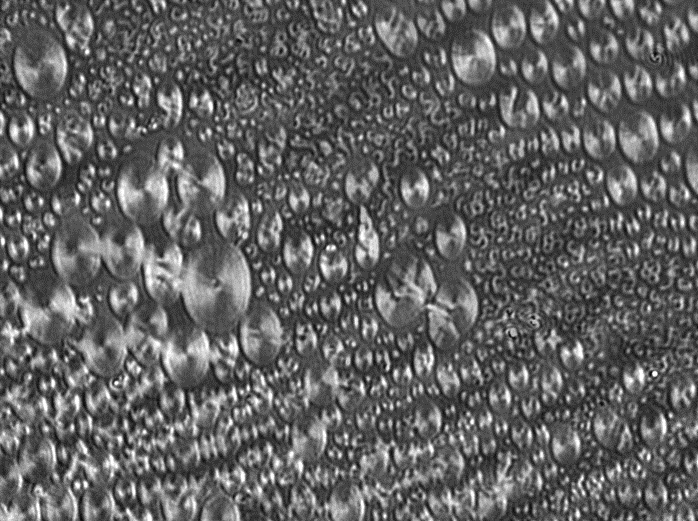
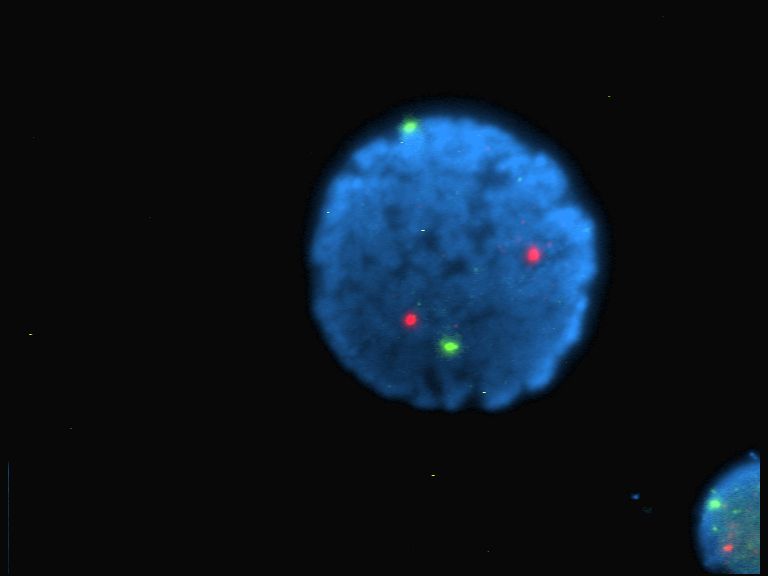
Peptoid Nanosheets, Fluorescent Microscopy, June 2013
Peptoids (root from the Greek πεπτός, ''peptós'' "digested"; derived from πέσσειν, ''péssein'' "to digest" and the Greek-derived suffix -oid meaning "like, like that of, thing like a ______," ), or poly-''N''-substituted glycines, are a class of biochemicals known as biomimetics that replicate the behavior of biological molecules. Peptidomimetics are recognizable by side chains that are appended to the nitrogen atom of the peptide backbone, rather than to the α-carbons (as they are in amino acids). Chemical structure and synthesis In peptoids, the side chain is connected to the nitrogen of the peptide backbone, instead of the α-carbon as in peptides. Notably, peptoids lack the amide hydrogen which is responsible for many of the secondary structure elements in peptides and proteins. Peptoids were first invented by Reyna J. Simon, Ronald N. Zuckermann, Paul Bartlett and Daniel V. Santi to mimic protein/peptide products to aid in the discovery of protease-stable sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanobiotechnology
Nanobiotechnology, bionanotechnology, and nanobiology are terms that refer to the intersection of nanotechnology and biology. Given that the subject is one that has only emerged very recently, bionanotechnology and nanobiotechnology serve as blanket terms for various related technologies. This discipline helps to indicate the merger of biological research with various fields of nanotechnology. Concepts that are enhanced through nanobiology include: nanodevices (such as biological machines), nanoparticles, and nanoscale phenomena that occurs within the discipline of nanotechnology. This technical approach to biology allows scientists to imagine and create systems that can be used for biological research. Biologically inspired nanotechnology uses biological systems as the inspirations for technologies not yet created. However, as with nanotechnology and biotechnology, bionanotechnology does have many potential ethical issues associated with it. The most important objectives that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanosheet
A nanosheet is a two-dimensional nanostructure with thickness in a scale ranging from 1 to 100 nm. A typical example of a nanosheet is graphene, the thinnest two-dimensional material (0.34 nm) in the world. It consists of a single layer of carbon atoms with hexagonal lattices. Examples and applications , Silicon nanosheets are being used to prototype future generations of small (5 nm) transistors. Carbon nanosheets (from hemp) may be an alternative to graphene as electrodes in supercapacitors. Synthesis The most commonly used nanosheet synthesis methods use a bottom-up approach, e.g., pre-organization and polymerization at interfaces like Langmuir–Blodgett films, solution phase synthesis and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). For example, CdTe ( cadmium telluride) nanosheets could be synthesized by precipitating and aging CdTe nanoparticles in deionized water. The formation of free-floating CdTe nanosheets was due to directional hydrophobic attraction and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptoid
Peptoids (root from the Greek language, Greek πεπτός, ''peptós'' "digested"; derived from πέσσειν, ''péssein'' "to digest" and the Greek-derived suffix -oid meaning "like, like that of, thing like a ______," ), or poly-''N''-substituted glycines, are a class of biochemicals known as biomimetics that replicate the behavior of biological molecules. Peptidomimetics are recognizable by side chains that are appended to the nitrogen atom of the peptide backbone, rather than to the α-carbons (as they are in amino acids). Chemical structure and synthesis In peptoids, the side chain is connected to the nitrogen of the peptide backbone, instead of the α-carbon as in peptides. Notably, peptoids lack the amide hydrogen which is responsible for many of the secondary structure elements in peptides and proteins. Peptoids were first invented by Reyna J. Simon, Ronald N. Zuckermann, Paul Bartlett and Daniel V. Santi to mimic protein/peptide products to aid in the discovery of pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), commonly referred to as the Berkeley Lab, is a United States Department of Energy National Labs, United States national laboratory that is owned by, and conducts scientific research on behalf of, the United States Department of Energy. Located in the Berkeley Hills, hills of Berkeley, California, the lab overlooks the campus of the University of California, Berkeley, and is managed by the University of California system. History 1931–1941 The laboratory was founded on August 26, 1931, by Ernest Lawrence, as the Radiation Laboratory of the University of California, Berkeley, associated with the Physics Department. It centered physics research around his new instrument, the cyclotron, a type of particle accelerator for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1939. Throughout the 1930s, Lawrence pushed to create larger and larger machines for physics research, courting private philanthropy, philanthropists for funding. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosensing
A biosensor is an analytical device, used for the detection of a chemical substance, that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector. The ''sensitive biological element'', e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell receptors, enzymes, antibodies, nucleic acids, etc., is a biologically derived material or biomimetic component that interacts with, binds with, or recognizes the analyte under study. The biologically sensitive elements can also be created by biological engineering. The ''transducer'' or the ''detector element'', which transforms one signal into another one, works in a physicochemical way: optical, piezoelectric, electrochemical, electrochemiluminescence etc., resulting from the interaction of the analyte with the biological element, to easily measure and quantify. The biosensor reader device connects with the associated electronics or signal processors that are primarily responsible for the display of the results in a user-friendly way. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langmuir–Blodgett Film
A Langmuir–Blodgett (LB) film is a nanostructured system formed when Langmuir films—or Langmuir monolayers (LM)—are transferred from the liquid-gas interface to solid supports during the vertical passage of the support through the monolayers. LB films can contain one or more monolayers of an organic material, deposited from the surface of a liquid onto a solid by immersing (or emersing) the solid substrate into (or from) the liquid. A monolayer is adsorbed homogeneously with each immersion or emersion step, thus films with very accurate thickness can be formed. This thickness is accurate because the thickness of each monolayer is known and can therefore be added to find the total thickness of a Langmuir–Blodgett film. The monolayers are assembled vertically and are usually composed either of amphiphilic molecules (see chemical polarity) with a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail (example: fatty acids) or nowadays commonly of nanoparticles. Langmuir–Blodgett films ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile Red
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists Say Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About long, its covers eleven countries: the |
Fluorophores
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with several π bonds. Fluorophores are sometimes used alone, as a tracer in fluids, as a dye for staining of certain structures, as a substrate of enzymes, or as a probe or indicator (when its fluorescence is affected by environmental aspects such as polarity or ions). More generally they are covalently bonded to a macromolecule, serving as a marker (or dye, or tag, or reporter) for affine or bioactive reagents (antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids). Fluorophores are notably used to stain tissues, cells, or materials in a variety of analytical methods, i.e., fluorescent imaging and spectroscopy. Fluorescein, via its amine-reactive isothiocyanate derivative fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), has been one of the most popular fluorophores. From an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to saturated compounds having single bonds, and other geometric or connective non-cyclic arrangements with the same set of atoms. Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. Organic compounds that are not aromatic are classified as aliphatic compounds—they might be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have enhanced stability. The term ''aromaticity'' with this meaning is historically related to the concept of having an aroma, but is a distinct property from that meaning. Since the most common aromatic compounds are derivatives of benzene (an aromatic hydrocarbon common in petroleum and its distillates), the word ''aromatic'' occasionally refers informally to benzene derivatives, and so it was first defined. Nevertheless, many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoparticles
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At the lowest range, metal particles smaller than 1 nm are usually called atom clusters instead. Nanoparticles are usually distinguished from microparticles (1-1000 µm), "fine particles" (sized between 100 and 2500 nm), and "coarse particles" (ranging from 2500 to 10,000 nm), because their smaller size drives very different physical or chemical properties, like colloidal properties and ultrafast optical effects or electric properties. Being more subject to the brownian motion, they usually do not sediment, like colloidal particles that conversely are usually understood to range from 1 to 1000 nm. Being much smaller than the wavelengths of visible light (400-700 nm), nano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.png)
